|
Great Famine (Ireland) Museums
Great Famine may refer to: China * Great Chinese Famine (1958–1961) Greece * Great Famine (Greece) (1941–1944) India * Great Bengal famine of 1770 * Great Rajputana Famine (1869) * Great Famine of 1876–1878 Ireland * Great Famine (Ireland) (1845–1852), occasion for the great exodus of Irish and the Irish diaspora Japan * Kan'ei Great Famine (1640–1643) * Great Tenmei famine (1782–1788) * Tenpō famine or Great Tenpō famine (1833–1837) Lebanon * Great Famine of Mount Lebanon (1915–1918) North Korea * North Korean famine (1994–1998) Northern Europe * Great Famine of 1315–1317 * Great Famine of 1695–1697 Ukraine * Holodomor or the Great Famine of 1932–1933 Other uses * ''The Great Famine'', a 2011 documentary about the Russian famine of 1921 See also * Droughts and famines in Russia and the Soviet Union * List of famines This is a list of famines. List See also Main article lists * Bengal famine * Droughts and famines in Russia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Chinese Famine
The Great Chinese Famine () was a period between 1959 and 1961 in the history of the People's Republic of China (PRC) characterized by widespread famine. Some scholars have also included the years 1958 or 1962. It is widely regarded as the deadliest famine and one of the greatest man-made disasters in human history, with an estimated death toll due to starvation that ranges in the tens of millions (15 to 55 million). The most stricken provinces were Anhui (18% dead), Chongqing (15%), Sichuan (13%), Guizhou (11%) and Hunan (8%). The major contributing factors in the famine were the policies of the Great Leap Forward (1958 to 1962) and people's communes, launched by Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party Mao Zedong, such as inefficient distribution of food within the nation's planned economy; requiring the use of poor agricultural techniques; the Four Pests campaign that reduced sparrow populations (which disrupted the ecosystem); over-reporting of grain production; and order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Famine (Greece)
The Great Famine ( el, Μεγάλος Λιμός, and sometimes known as the Grand Famine) was a period of mass starvation during the Axis occupation of Greece, during World War II (1941–1944). The local population suffered greatly during this period, while the Axis Powers initiated a policy of large scale plunder. Moreover, requisitions, together with the Allied blockade of Greece, the ruined state of the country's infrastructure, and the emergence of a powerful and well-connected black market, resulted in the Great Famine, with the mortality rate reaching a peak during the winter of 1941–42.Mazower, 1995: 44–48 The great suffering and the pressure of the Greek diaspora eventually forced the British to lift the blockade partially. Thus through the ends of 1941, Kızılay (the Turkish Red Crescent), and from the summer of 1942 the International Red Cross, were able to distribute supplies in sufficient quantities with the help of several foreign, and Hellenic-based humanit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Bengal Famine Of 1770
The Bengal Famine of 1770 was a famine that struck Bengal and Bihar between 1769 and 1770 and affected some 30 million people. It occurred during a period of dual governance in Bengal. This existed after the East India Company had been granted the ''diwani'', or the right to collect revenue in Bengal by the Mughal emperor in Delhi, but before it had wrested the ''nizamat'', or control of civil administration, which continued to lie with the Mughal governor, the Nawab of Bengal Nazm ud Daula (1765-72). Crop failure in autumn 1768 and summer 1769 and an accompanying smallpox epidemic were thought to be the manifest reasons for the famine. The East India Company had farmed out tax collection on account of a shortage of trained administrators, and the prevailing uncertainty may have worsened the famine's impact. Other factors adding to the pressure were: grain merchants ceased offering grain advances to peasants, but the market mechanism for exporting the merchants' grain to othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
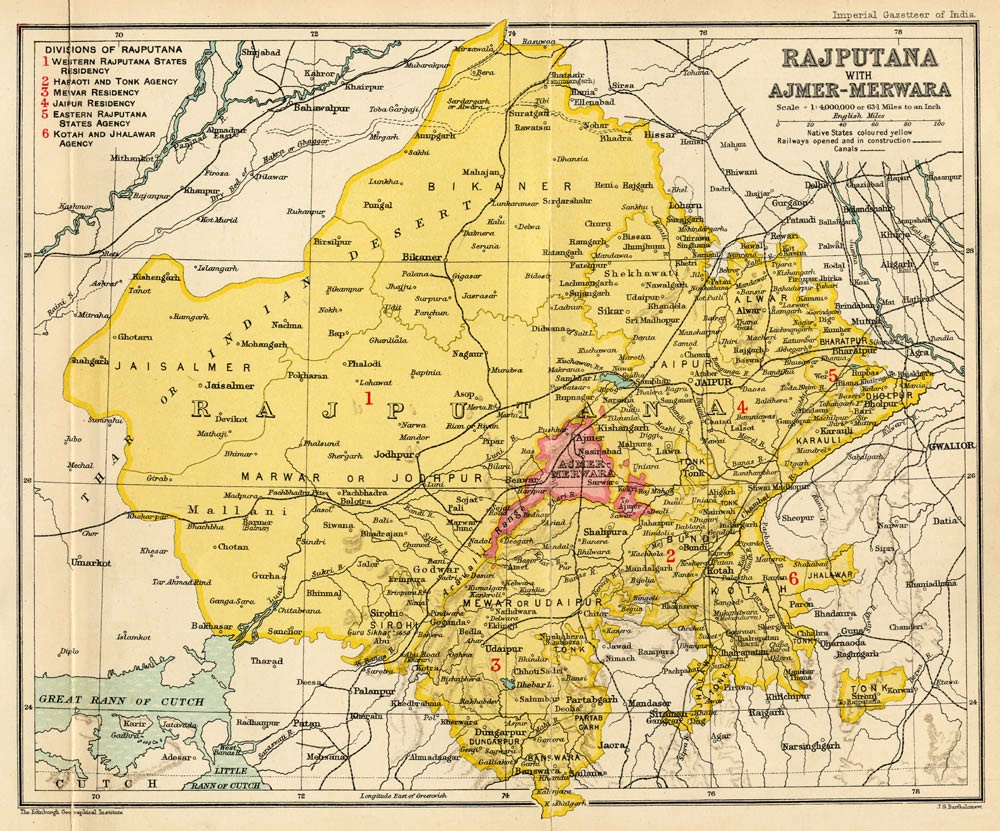
Great Rajputana Famine
The Rajputana famine of 1869 (also the Great Rajputana Famine, Bundelkhand and Upper Hindustan famine, Rajputana famine of 1868-70) affected an area of and a population of 44,500,000, primarily in the princely states of Rajputana, India, and the British territory of Ajmer. Other areas affected included Gujarat, the North Deccan districts, the Jubbalpore division of the Central Provinces and Berar, the Agra and Bundelkhand division of the United Provinces, and the Hissar division of the Punjab. Course of famine The monsoon of 1868 was late in coming. When it came, was light and brief, lasting until only August 1868. There was a shortage of fodder in most areas of Rajputana, and some areas had water shortages as well. Since the much-needed grain could be brought in only on slow camel trains, the stricken areas were more or less inaccessible. Many inhabitants of the famine-stricken regions of Rajputana (for example, two-thirds of the population of Marwar) emigrated with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
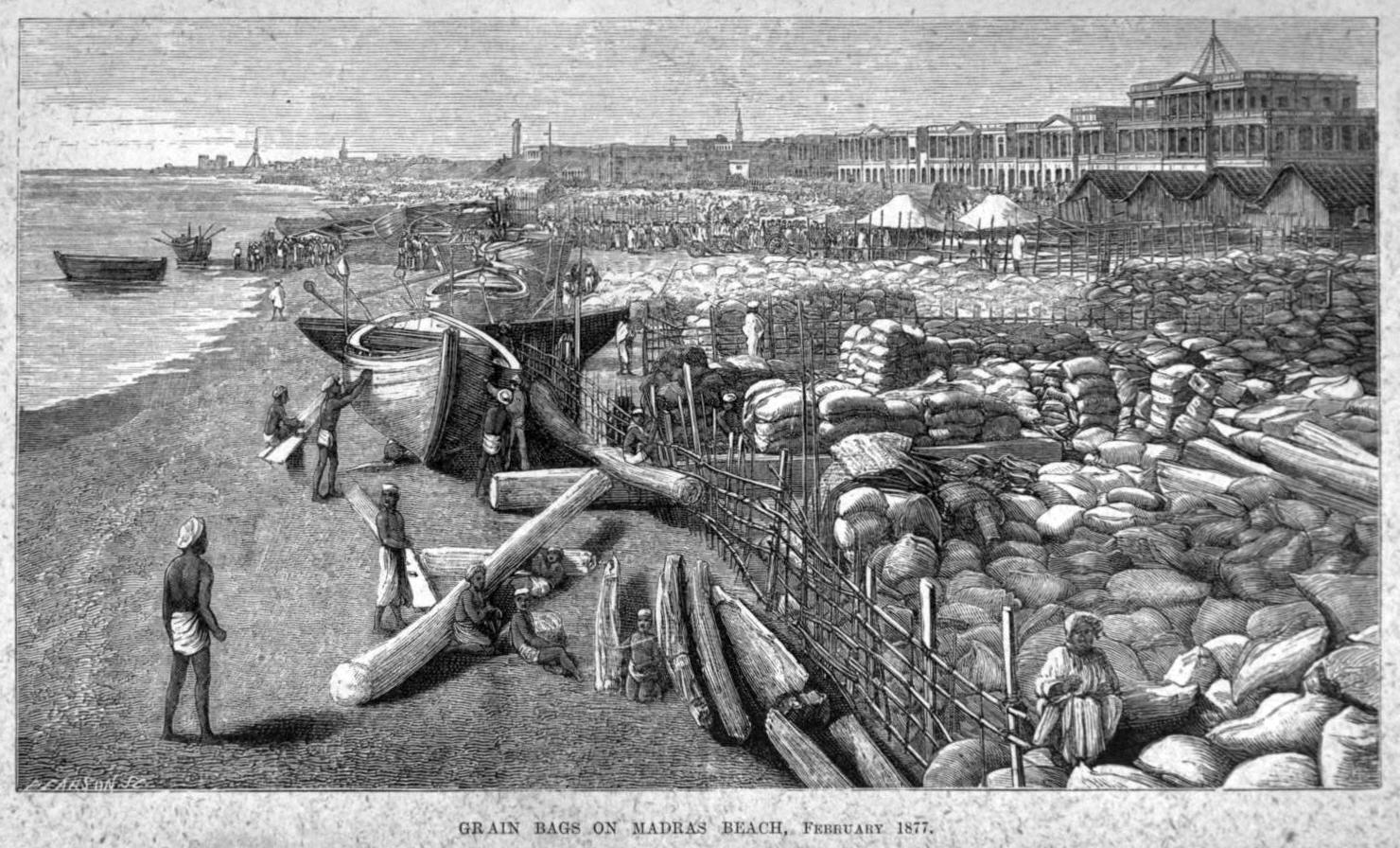
Great Famine Of 1876–1878
The Great Famine of 1876–1878 was a famine in British Raj, India under Crown rule. It began in 1876 after an intense drought resulted in crop failure in the Deccan Plateau. It affected South India, south and West India, Southwestern India—the British-administered presidencies of Madras Presidency, Madras and Bombay Presidency, Bombay, and the princely states of Kingdom of Mysore, Mysore and Hyderabad State, Hyderabad—for a period of two years. In 1877, famine came to affect regions northward, including parts of the Central Provinces and the North-Western Provinces, and a small area in the Punjab region, Punjab. The famine ultimately affected an area of and caused distress to a population totalling 58,500,000. The excess mortality in the famine has been estimated in a range whose low end is 5.6 million human fatalities, high end 9.6 million fatalities, and a careful modern demographic estimate 8.2 million fatalities. The famine is also known as the Southern India famine of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Famine (Ireland)
The Great Famine ( ga, an Gorta Mór ), also known within Ireland as the Great Hunger or simply the Famine and outside Ireland as the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of starvation and disease in Ireland from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis which subsequently had a major impact on Irish society and history as a whole. With the most severely affected areas in the west and south of Ireland, where the Irish language was dominant, the period was contemporaneously known in Irish as , literally translated as "the bad life" (and loosely translated as "the hard times"). The worst year of the period was 1847, which became known as "Black '47".Éamon Ó Cuív – the impact and legacy of the Great Irish Famine During the Great Hunger, roughly 1 million people died and more than 1 million Irish diaspora, fled the country, causing the country's population to fall by 20–25% (in some towns falling as much as 67%) between 1841 and 1871.Carolan, MichaelÉireann's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kan'ei Great Famine
The Kan'ei Great Famine ( ') was a famine which affected Japan during the reign of Empress Meishō in the Edo period. The estimated number of deaths due to starvation is between 50,000 and 100,000. The famine is generally considered to have begun in 1640 and lasted into 1643. It was named after the Kan'ei era (1624–1644). The ruling ''shōgun'' during the famine was Tokugawa Iemitsu. Events leading to the famine Due to large numbers of internally displaced persons in the aftermath of the Shimabara Rebellion, and the rinderpest epizooty, which broke out in Kyushu in 1638 and was impossible to contain, led to mass deaths of cattle in Western Japan, which reduced agricultural productivity in 1640 due to the scarcity of working animals. Also, motivation among farmers was weakening due to the extreme impoverishment of low-ranking samurai class members. The increased spending after the 1635 reformation of Sankin-kōtai (increasing frequency of ''daimyō'' annual trips to Edo) did not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Tenmei Famine
The Great Tenmei famine (天明の大飢饉, ''Tenmei no daikikin'') was a famine which affected Japan during the Edo period. It is considered to have begun in 1782, and lasted until 1788. It was named after the Tenmei era (1781–1789), during the reign of Emperor Kōkaku. The ruling ''shoguns'' during the famine were Tokugawa Ieharu and Tokugawa Ienari. The famine was the deadliest one during the early modern period in Japan. Causes The 1783 eruption of Mount Asama is said to have caused the Great Tenmei famine. Starting in the 1770s, there was a sharp decline in crop yield in Tōhoku, which is the north-eastern region of Honshū, due to poor and cold weather, so food stocks in rural areas were exhausted. The situation was exacerbated by natural disasters: Mount Iwaki erupted on April 13, 1783 (3rd month, 12th day, in the year Tenmei-3, according to the Japanese calendar), as did Mount Asama on July 6, so volcanic ash was sent down into the atmosphere of Japan. Aside from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenpō Famine
The Tenpō famine (天保の飢饉, ''Tenpō no kikin''), also known as the Great Tenpō famine (天保の大飢饉, ''Tenpō no daikikin'') was a famine that affected Japan during the Edo period. Considered to have lasted from 1833 to 1837, it was named after the Tenpō era (1830–1844), during the reign of Emperor Ninkō. The ruling shōgun during the famine was Tokugawa Ienari. The famine was most severe in northern Honshū and was caused by flooding and cold weather. The famine was one of a series of calamities that shook the faith of the people in the ruling ''bakufu''. During the same period as the famine, there were also the Kōgo Fires of Edo (1834) and a 7.6 magnitude earthquake in the Sanriku region (1835). In the last year of the famine, Ōshio Heihachirō led a revolt in Osaka against corrupt officials, who refused to help feed the impoverished residents of the city. Another revolt sprung up in Chōshū Domain. Also in 1837, the American merchant vessel ''Morrison' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Famine Of Mount Lebanon
The Great Famine of Mount Lebanon (1915–1918) ( syc, ܟܦܢܐ, lit=Starvation, translit=Kafno; ar, مجاعة لبنان, translit=Majā'at Lubnān; tr, Lübnan Dağı'nın Büyük Kıtlığı) was a period of mass starvation during World War I that resulted in 200,000 deaths of largely Christian and Druze inhabitants. Allied forces blockaded the Eastern Mediterranean, as they had done with the German Empire and Austro-Hungarian Empire in Europe, in order to strangle the economy and weaken the Ottoman war effort. The situation was exacerbated by Jamal Pasha, commander of the Fourth Army of the Ottoman Empire, who deliberately barred crops from neighbouring Syria from entering Mount Lebanon, in response to the Allied blockade. Additionally, a swarm of locusts devoured the remaining crops, creating a famine that led to the deaths of half of the population of the Mount Lebanon Mutasarrifate, a semi-autonomous subdivision of the Ottoman Empire and the precursor of modern-day Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Korean Famine
The North Korean Famine (), also known as the Arduous March or the March of Suffering (), was a period of mass starvation together with a general economic crisis from 1994 to 1998 in North Korea. During this time there was an increase in defection from North Korea which peaked towards the end of the famine period. The famine stemmed from a variety of factors. Economic mismanagement and the loss of Soviet support caused food production and imports to decline rapidly. A series of floods and droughts exacerbated the crisis. The North Korean government and its centrally planned system proved too inflexible to effectively curtail the disaster. North Korea attempted to obtain aid and commercial opportunities, but failed to receive initial attention. Estimates of the death toll vary widely. Out of a total population of approximately 22 million, somewhere between 240,000 and 3,500,000 North Koreans died from starvation or hunger-related illnesses, with the deaths peaking in 1997.No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Famine Of 1315–1317
The Great Famine of 1315–1317 (occasionally dated 1315–1322) was the first of a series of large-scale crises that struck Europe early in the 14th century. Most of Europe (extending east to Russia and south to Italy) was affected. The famine caused many deaths over an extended number of years and marked a clear end to the period of growth and prosperity from the 11th to the 13th centuries. The Great Famine started with bad weather in spring 1315. Crop failures lasted through 1316 until the summer harvest in 1317, and Europe did not fully recover until 1322. Crop failures were not the only problem; cattle disease caused sheep and cattle numbers to fall as much as 80%. The period was marked by extreme levels of crime, disease, mass death, and even cannibalism and infanticide. The crisis had consequences for the Church, state, European society, and for future calamities to follow in the 14th century. Background Famines were familiar occurrences in medieval Europe. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |