|
Gray-faced Buzzard
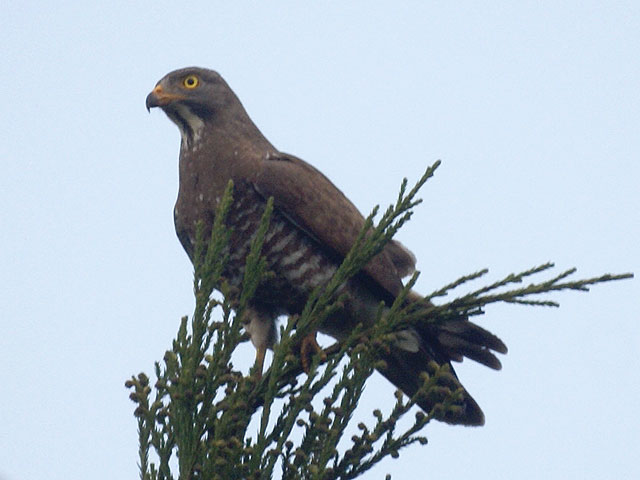
The grey-faced buzzard (''Butastur indicus'') is an Asian bird of prey. It is typically in length, making it a small-sized raptor. It breeds in Manchuria, Korea and Japan; it winters in South-east Asia. It is a bird of open land. It eats lizards, small mammals and large insects. The adult has a grey head, breast and neck, white throat, black moustaches and mesial stripes, brown back and upperwings, and brown bars on white underparts and underwings. The juvenile is brown and mottled above, pale below with brown streaks, and has a broad white supercilium and brown face. Taxonomy The gray-faced buzzard was formally described in 1788 by the German naturalist Johann Friedrich Gmelin in his revised and expanded edition of Carl Linnaeus's ''Systema Naturae''. He placed it with the eagles, hawks and relatives in the genus '' Falco'' and coined the binomial name ''Falco indicus''. Gmelin based his account on the "Javan hawk" that had been described in 1781 by John Latham from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Friedrich Gmelin
, fields = , workplaces = University of GöttingenUniversity of Tübingen , alma_mater = University of Tübingen , doctoral_advisor = Philipp Friedrich GmelinFerdinand Christoph Oetinger , academic_advisors = , doctoral_students = Georg Friedrich HildebrandtFriedrich StromeyerCarl Friedrich KielmeyerWilhelm August LampadiusVasily Severgin , notable_students = , known_for = Textbooks on chemistry, pharmaceutical science, mineralogy, and botany , author_abbrev_bot = J.F.Gmel. , author_abbrev_zoo = Gmelin , influences = Carl Linnaeus , influenced = , relatives = Leopold Gmelin (son) , awards = Johann Friedrich Gmelin (8 August 1748 – 1 November 1804) was a German naturalist, botanist, entomologist, herpetologist, and malacologist. Education Johann Friedrich Gmelin was born as the eldest son of Philipp Friedrich Gmelin in 1748 in Tübingen. He studied medicine under his father at University of Tübingen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Latham (ornithologist)
John Latham (27 June 1740 – 4 February 1837) was an English physician, naturalist and author. His main works were ''A General Synopsis of Birds'' (1781–1801) and ''General History of Birds'' (1821–1828). He was able to examine specimens of Australian birds which reached England in the last twenty years of the 18th century, and was responsible for providing English names for many of them. He named some of Australia's most famous birds, including the emu, sulphur-crested cockatoo, wedge-tailed eagle, superb lyrebird, Australian magpie, magpie-lark and pheasant coucal. He was also the first to describe the hyacinth macaw. Latham has been called the "grandfather" of Australian ornithology. Biography John Latham was born on 27 June 1740 at Eltham in northwest Kent. He was the eldest son of John Latham (died 1788), a surgeon, and his mother, who was a descendant of the Sothebys, in Yorkshire. He was educated at Merchant Taylors' School and then studied anatomy under William Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coniferous
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extant conifers are perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The great majority are trees, though a few are shrubs. Examples include cedars, Douglas-firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews.Campbell, Reece, "Phylum Coniferophyta". Biology. 7th. 2005. Print. P. 595 As of 1998, the division Pinophyta was estimated to contain eight families, 68 genera, and 629 living species. Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are ecologically important. They are the dominant plants over large areas of land, most notably the taiga of the Northern Hemisphere, but also in similar cool climates in mountains further south. Boreal conifers have many wintertime adaptations. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satoyama
is a Japanese term applied to the border zone or area between mountain foothills and arable flat land. Literally, ''sato'' () means village, and ''yama'' () means hill or mountain. Satoyama have been developed through centuries of small-scale agricultural and forestry use. The concept of satoyama has several definitions. The first definition is the management of forests through local agricultural communities, using coppicing. During the Edo era, young and fallen leaves were gathered from community forests to use as fertilizer in wet rice paddy fields. Villagers also used wood for construction, cooking and heating. More recently, satoyama has been defined not only as mixed community forests, but also as entire landscapes that are used for agriculture. According to this definition, satoyama contains a mosaic of mixed forests, rice paddy fields, dry rice fields, grasslands, streams, ponds, and reservoirs for irrigation. Farmers use the grasslands to feed horses and cattle. Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species have subspecies, but for those that do there must be at least two. Subspecies is abbreviated subsp. or ssp. and the singular and plural forms are the same ("the subspecies is" or "the subspecies are"). In zoology, under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, the subspecies is the only taxonomic rank below that of species that can receive a name. In botany and mycology, under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, other infraspecific ranks, such as variety, may be named. In bacteriology and virology, under standard bacterial nomenclature and virus nomenclature, there are recommendations but not strict requirements for recognizing other important infraspecific ranks. A taxonomist decides whether ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Germain De Lacépède
Bernard-Germain-Étienne de La Ville-sur-Illon, comte de Lacépède or La Cépède (; 26 December 17566 October 1825) was a French naturalist and an active freemason. He is known for his contribution to the Comte de Buffon's great work, the ''Histoire Naturelle''. Biography Lacépède was born at Agen in Guienne. His education was carefully conducted by his father, and the early perusal of Buffon's Natural History ('' Histoire naturelle, générale et particulière'') awakened his interest in that branch of study, which absorbed his chief attention. His leisure he devoted to music, in which, besides becoming a good performer on the piano and organ, he acquired considerable mastery of composition, two of his operas (which were never published) meeting with the high approval of Gluck; in 1781–1785 he also brought out in two volumes his ''Poétique de la musique''. Meantime he wrote two treatises, ''Essai sur l'électricité'' (1781) and ''Physique générale et particuliè ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buteo
''Buteo'' is a genus of medium to fairly large, wide-ranging raptors with a robust body and broad wings. In the Old World, members of this genus are called "buzzards", but "hawk" is used in the New World (Etymology: ''Buteo'' is the Latin name of the common buzzard). As both terms are ambiguous, buteo is sometimes used instead, for example, by the Peregrine Fund. Characteristics Buteos are fairly large birds. Total length can vary from and wingspan can range from . The lightest known species is the roadside hawk, at an average of although the lesser known white-rumped and Ridgway's hawks are similarly small in average wingspan around , and average length around in standard measurements. The largest species in length and wingspan is the upland buzzard, which averages around in length and in wingspan. The upland is rivaled in weight and outsized in foot measurements and bill size by the ferruginous hawk. In both of these largest buteos, adults typically weigh over , and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of wordsGarner's Modern American Usage , p. 644. in which parts of multiple words are combined into a new word, as in ''smog'', coined by blending ''smoke'' and ''fog'', or ''motel'', from ''motor'' and ''hotel''. In , a portmanteau is a single morph that is analyzed as representing two (or more) underlying s. When portmanteaus shorten es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian Houghton Hodgson
Brian Houghton Hodgson (1 February 1800 or more likely 1801 – 23 May 1894) was a pioneer naturalist and ethnologist working in India and Nepal where he was a British Resident. He described numerous species of birds and mammals from the Himalayas, and several birds were named after him by others such as Edward Blyth. He was a scholar of Newar Buddhism and wrote extensively on a range of topics relating to linguistics and religion. He was an opponent of the British proposal to introduce English as the official medium of instruction in Indian schools. Early life Hodgson was the second of seven children of Brian Hodgson (1766–1858) and his wife Catherine (1776–1851), and was born at Lower Beech, Prestbury, Cheshire. His father lost money in a bad bank investment and had to sell their home at Lower Beech. A great-aunt married to Beilby Porteus, the Bishop of London, helped them but the financial difficulties were great. Hodgson's father worked as a warden of the Martello towe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butastur
''Butastur'' is a genus of birds of prey in the family Accipitridae. Taxonomy and species The genus ''Butastur'' was introduced in 1843 by the English naturalist Brian Houghton Hodgson with the white-eyed buzzard as the type species. The genus name is a portmanteau of the genus ''Buteo ''Buteo'' is a genus of medium to fairly large, wide-ranging raptors with a robust body and broad wings. In the Old World, members of this genus are called "buzzards", but " hawk" is used in the New World (Etymology: ''Buteo'' is the Latin na ...'' introduced by Bernard Germain de Lacépède for the buzzards and ''Astur'' introduced by Lacépède for the goshawks. The genus now contains four species. References Bird genera Taxa named by Brian Houghton Hodgson Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Accipitriformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
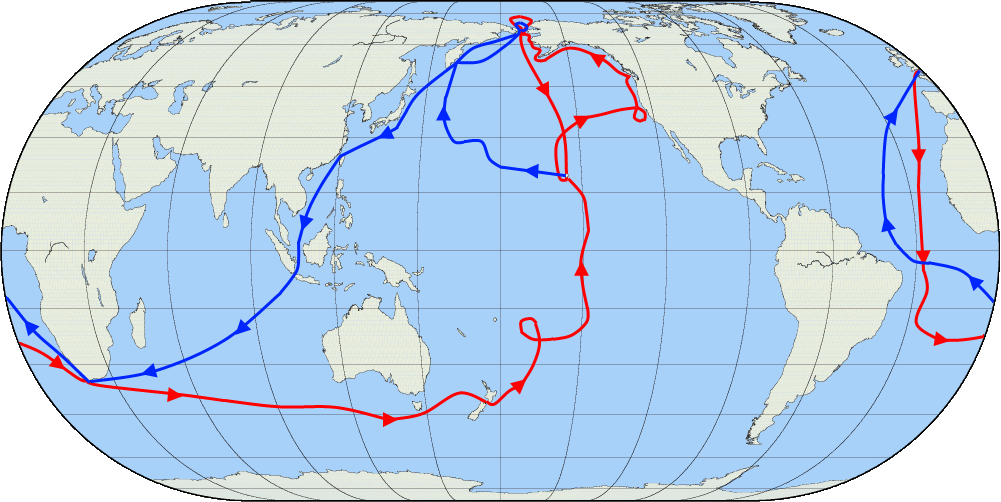
Third Voyage Of James Cook
James Cook's third and final voyage (12 July 1776 – 4 October 1780) took the route from Plymouth via Cape Town and Tenerife to New Zealand and the Hawaiian Islands, and along the North American coast to the Bering Strait. Its ostensible purpose was to return Omai, a young man from Raiatea, to his homeland, but the Admiralty used this as a cover for their plan to send Cook on a voyage to discover the Northwest Passage. HMS ''Resolution'', to be commanded by Cook, and HMS ''Discovery'', commanded by Charles Clerke, were prepared for the voyage which started from Plymouth in 1776. Omai was returned to his homeland and the ships sailed onwards, encountering the Hawaiian Archipelago, before reaching the Pacific coast of North America. The two charted the west coast of the continent and passed through the Bering Strait when they were stopped by ice from sailing either east or west. The vessels returned to the Pacific and called briefly at the Aleutians before retiring towar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(8967632085).jpg)