|
Grasshopper-class Torpedo Gunboats
The ''Grasshopper''-class torpedo gunboat was a class of torpedo gunboat built for the Royal Navy in the late 19th century. All three ships were scrapped before World War I. Design The ''Grasshopper'' class was designed by Nathaniel Barnaby in 1886 and were essentially repeats of the ''Rattlesnake'' of 1886. They had a length between perpendiculars of , a beam of and a displacement of . They were engined with two sets of Maudslay, Sons & Field triple-expansion steam engines, two locomotive boilers, and twin screws. This layout produced with natural draught and with forced draught The difference between atmospheric pressure and the pressure existing in the furnace or flue gas passage of a boiler is termed as draft. Draft can also be referred to as the difference in pressure in the combustion chamber area which results in the ..., giving them a top speed of . They carried 100 tons of coal, giving them a range of about at and were manned by 66 sailors and officers. Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharpshooter-class Torpedo Gunboat
The ''Sharpshooter''-class torpedo gunboat was a class of torpedo gunboat built for the Royal Navy in the late 19th century. One of the class was hulked in 1904, seven were scrapped before World War I and five were converted to minesweepers. Of these minesweepers, ''Seagull'' was lost to a collision in 1918 and the rest survived the war to be broken up in the early 1920s. Design The ''Sharpshooter'' class was designed by Sir William White in 1888. They had a length overall of , a beam of and a displacement of 735 tons. They were engined with two sets of Belliss and Morcom triple-expansion steam engines, two locomotive-type boilers, and twin screws. This layout produced with natural draught and with forced draught, giving them a top speed of . They carried 100 tons of coal, giving them a range of about at and were manned by 91 sailors and officers. The following ''Alarm'' class were essentially an enlarged version of the ''Sharpshooters''. From 1895 to 1898 a series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Rattlesnake (1886)
HMS ''Rattlesnake'' was a unique design of torpedo gunboat of the Royal Navy. A result of the Russian war scare of 1885, she was designed by Nathaniel Barnaby that year and built by Laird Brothers, of Birkenhead. Quickly made obsolete by the new torpedo boat destroyers, she became an experimental submarine target ship in 1906, and was sold in 1910. Design Designed by Nathaniel Barnaby in 1885, ''Rattlesnake'' was, like the larger torpedo cruisers and the s, built in response to the Russian War scare. They were intended as a form of gunboat armed with torpedoes and designed for hunting and destroying smaller torpedo boats. By the end of the 1890s torpedo gunboats were superseded by their more successful contemporaries, the torpedo boat destroyers, and this quickly made ''Rattlesnake'' and her follow-on classes, the s, s, s and s, obsolete. Exactly long and in beam, she displaced 550 tons. Built of steel, ''Rattlesnake'' was un-armoured with the exception of a -inch protectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Classes Of The Royal Navy
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grasshopper-class Torpedo Gunboats
The ''Grasshopper''-class torpedo gunboat was a class of torpedo gunboat built for the Royal Navy in the late 19th century. All three ships were scrapped before World War I. Design The ''Grasshopper'' class was designed by Nathaniel Barnaby in 1886 and were essentially repeats of the ''Rattlesnake'' of 1886. They had a length between perpendiculars of , a beam of and a displacement of . They were engined with two sets of Maudslay, Sons & Field triple-expansion steam engines, two locomotive boilers, and twin screws. This layout produced with natural draught and with forced draught The difference between atmospheric pressure and the pressure existing in the furnace or flue gas passage of a boiler is termed as draft. Draft can also be referred to as the difference in pressure in the combustion chamber area which results in the ..., giving them a top speed of . They carried 100 tons of coal, giving them a range of about at and were manned by 66 sailors and officers. Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Gunboats And Gunvessels Of The Royal Navy
This is a list of gunboat and gunvessel classes of the Royal Navy. For gun-brigs see List of gun-brigs of the Royal Navy. Steam gunboats Wooden paddle gunboats (Indian service) * Wooden paddle gunboats (Great Lakes) Iron paddle gunboat (Great Lakes) * ''Mowhawk'' (1843) Iron paddle despatch vessels/gunboats * (1855) Wooden screw gunboats * ''Gleaner'' (or ''Pelter'') class ** ** ** ** ** ** * ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** * (1855) ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** * ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** * ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** * ** ** ** ** ** ** * ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** ** (or ''Bruizer'') ** (cancelled) ** (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
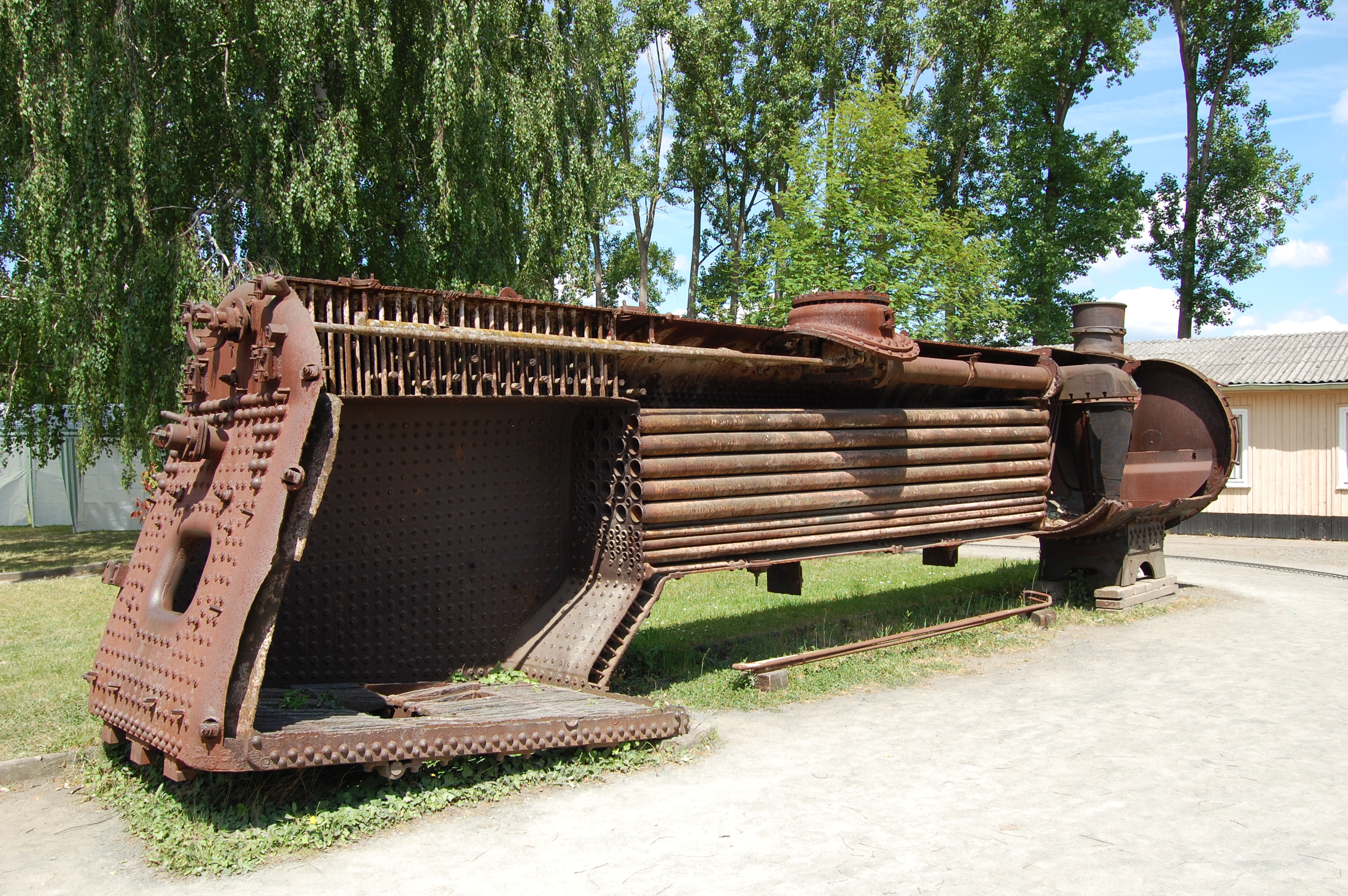
Locomotive Boiler
A fire-tube boiler is a type of boiler in which hot gases pass from a fire through one or more tubes running through a sealed container of water. The heat of the gases is transferred through the walls of the tubes by thermal conduction, heating the water and ultimately creating steam. The fire-tube boiler developed as the third of the four major historical types of boilers: low-pressure tank or "haystack" boilers, flued boilers with one or two large flues, fire-tube boilers with many small tubes, and high-pressure water-tube boilers. Their advantage over flued boilers with a single large flue is that the many small tubes offer far greater heating surface area for the same overall boiler volume. The general construction is as a tank of water penetrated by tubes that carry the hot flue gases from the fire. The tank is usually cylindrical for the most part—being the strongest practical shape for a pressurized container—and this cylindrical tank may be either horizontal or verti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
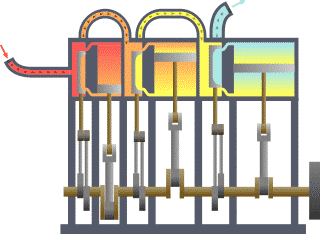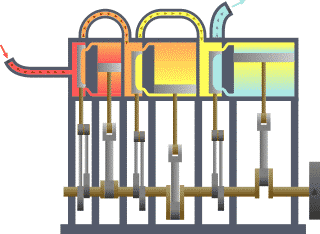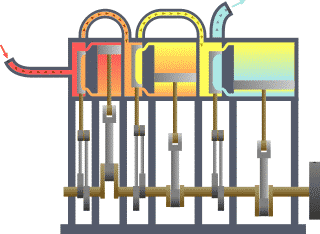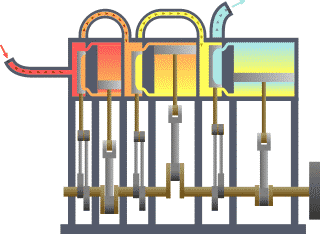
Triple-expansion Steam Engine
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinder, then having given up heat and losing pressure, it exhausts directly into one or more larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinders. Multiple-expansion engines employ additional cylinders, of progressively lower pressure, to extract further energy from the steam. Invented in 1781, this technique was first employed on a Cornish beam engine in 1804. Around 1850, compound engines were first introduced into Lancashire textile mills. Compound systems There are many compound systems and configurations, but there are two basic types, according to how HP and LP piston strokes are phased and hence whether the HP exhaust is able to pass directly from HP to LP ( Woolf compounds) or whether pressure fluctuation necessitates an intermediate "buffer" space in the form of a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maudslay, Sons & Field
Maudslay, Sons and Field was an engineering company based in Lambeth, London. History The company was founded by Henry Maudslay as Henry Maudslay and Company in 1798 and was later reorganised into Maudslay, Sons and Field in 1833 after his sons Thomas and Joseph, as well as Joshua Field joined the company. It specialised in building marine steam engines. The company produced a special steam-powered mill for the 1852 re-cutting of the Koh-i-Noor. See also * Great Wheel The Great Wheel, also known as the Gigantic Wheel, or Graydon Wheel, was built for the Empire of India Exhibition at Earls Court, London, in the United Kingdom. Construction began in March 1894 at the works of Maudslay, Sons and Field in Greenw ... References External links Chronology of the company Defunct shipbuilding companies of England Defunct companies based in London Engineering companies of England 1798 establishments in England Manufacturing companies established in 1798 Manufacturing comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Gunboat
In late 19th-century naval terminology, torpedo gunboats were a form of gunboat armed with torpedoes and designed for hunting and destroying smaller torpedo boats. By the end of the 1890s torpedo gunboats were superseded by their more successful contemporaries, the torpedo boat destroyers. History A number of torpedo gunboats, the prototype ''Rattlesnake'' of 1886 followed by the ''Grasshopper'' class (of 3 vessels), the ''Sharpshooter'' class (13 vessels), the ''Alarm'' class (11 vessels) and the ''Dryad'' class (5 vessels), were built for the Royal Navy during the 1880s and the 1890s; similar vessels were also constructed or otherwise acquired by a number of European nations and Japan. Essentially very small cruisers, torpedo gunboats were typically fitted with locomotive boilers, and were equipped with torpedo tubes and an adequate gun armament, intended for hunting down smaller enemy torpedo boats. In practice they failed in their primary objective, as they were not fas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Gunboat
In late 19th-century naval terminology, torpedo gunboats were a form of gunboat armed with torpedoes and designed for hunting and destroying smaller torpedo boats. By the end of the 1890s torpedo gunboats were superseded by their more successful contemporaries, the torpedo boat destroyers. History A number of torpedo gunboats, the prototype ''Rattlesnake'' of 1886 followed by the ''Grasshopper'' class (of 3 vessels), the ''Sharpshooter'' class (13 vessels), the ''Alarm'' class (11 vessels) and the ''Dryad'' class (5 vessels), were built for the Royal Navy during the 1880s and the 1890s; similar vessels were also constructed or otherwise acquired by a number of European nations and Japan. Essentially very small cruisers, torpedo gunboats were typically fitted with locomotive boilers, and were equipped with torpedo tubes and an adequate gun armament, intended for hunting down smaller enemy torpedo boats. In practice they failed in their primary objective, as they were not fas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |