|
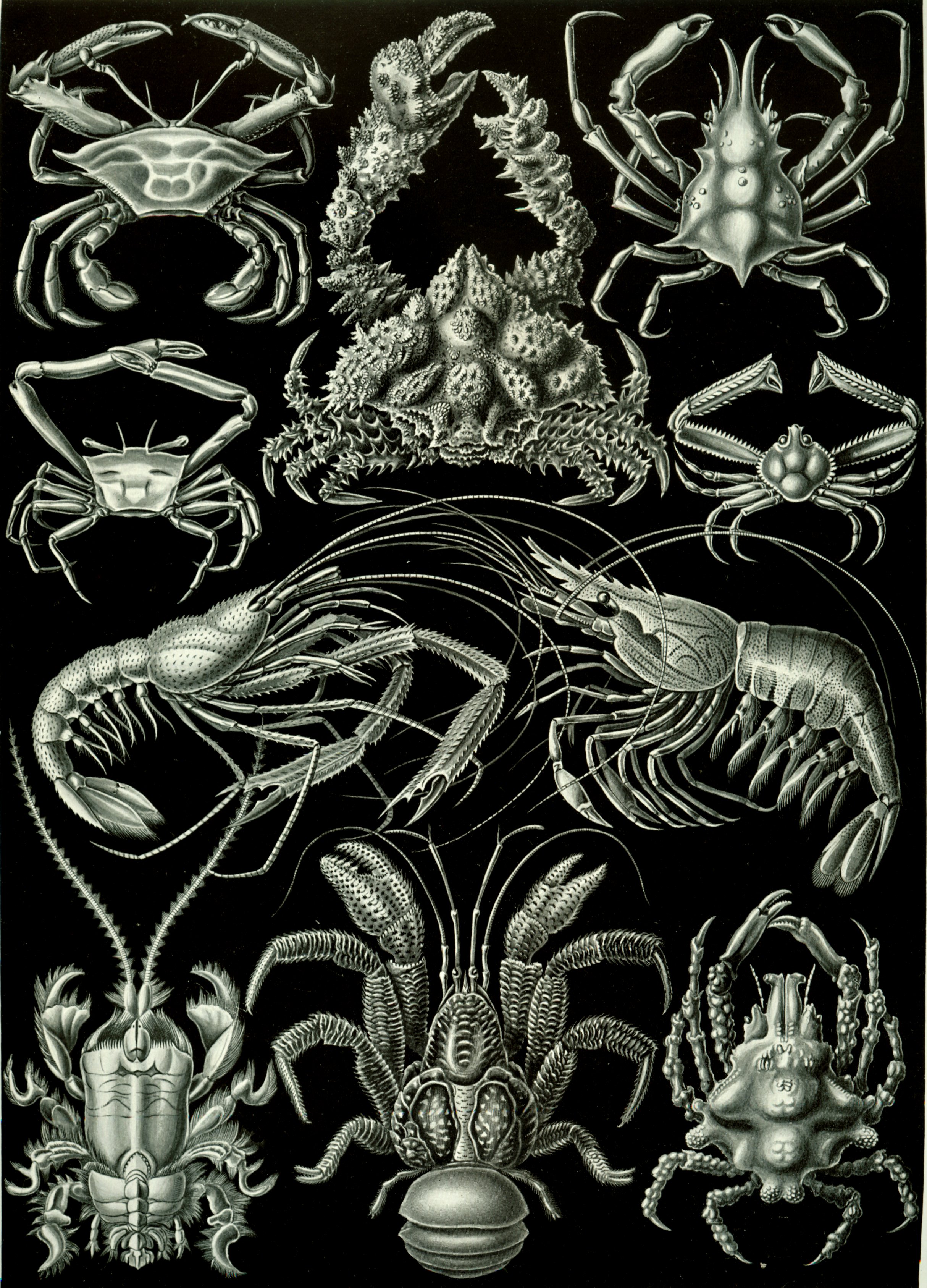
Grapsus Albolineatus
''Grapsus albolineatus'' is a species of decapod crustacean in the family Grapsidae, native to the Indo-Pacific. Description Its carapace, or upper shell, is flat, circular, and rough with arched lateral margins, and may be up to 37 mm in length. Its chelae, or claws, are short, small, and flattened. Its pereiopods, or legs, are long with a tapered end. The margin of the inferior extremity of its last pair of legs is serrate. Males have bigger claws than females. This species is red, blue, or green in color. Its legs are the same color and have irregular dark-brown mottling. Habitat and distribution This species occurs in rocky depths and in coral reefs. It is found in the Indo-Pacific from the East African coast to the Chilean coast. This includes the waters of the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, India, Indonesia, Pakistan, Japan, Australia, and the tropical islands of the Pacific Ocean (such as Hawaii). Diet The species consumes a mostly herbivorous diet but also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre André Latreille
Pierre André Latreille (; 29 November 1762 – 6 February 1833) was a French zoologist, specialising in arthropods. Having trained as a Roman Catholic priest before the French Revolution, Latreille was imprisoned, and only regained his freedom after recognising a rare beetle species he found in the prison, ''Necrobia ruficollis''. He published his first important work in 1796 (), and was eventually employed by the . His foresighted work on arthropod systematics and taxonomy gained him respect and accolades, including being asked to write the volume on arthropods for George Cuvier's monumental work, , the only part not by Cuvier himself. Latreille was considered the foremost entomologist of his time, and was described by one of his pupils as "the prince of entomologists". Biography Early life Pierre André Latreille was born on 29 November 1762 in the town of Brive, then in the province of Limousin, as the illegitimate child of Jean Joseph Sahuguet d'Amarzit, général ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grapsidae
The Grapsidae are a family of crabs known variously as marsh crabs, shore crabs, or talon crabs. The family has not been confirmed to form a monophyletic group and some taxa may belong in other families. They are found along the shore among rocks, in estuaries, marshes, and in some cases pelagic among drifting seaweeds and flotsam. Genera A number of taxa, formerly treated as subfamilies of the family Grapsidae are now considered families in their own right, including the Varunidae and Plagusiidae. Ten genera remain in the family, two of them known only from fossils: *''Geograpsus'' Stimpson, 1858 *'' Goniopsis'' De Haan, 1833 *''Grapsus'' Lamarck, 1801 *'' Leptograpsodes'' Montgomery, 1931 *''Leptograpsus'' H. Milne Edwards, 1853 *'' Litograpsus'' † Schweitzer & Karasawa, 2004 *''Metopograpsus'' H. Milne Edwards, 1853 *'' Miograpsus'' † Fleming, 1981 *''Pachygrapsus'' Randall, 1840 *''Planes Plane(s) most often refers to: * Aero- or airplane, a powered, fixed-wing aircra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baa Atoll
Baa Atoll (includes Southern Maalhosmadulu Atoll or Maalhosmadulu Dhekunuburi, Fasdhūtherē Atoll, and Goifulhafehendhu Atoll) is an administrative division of the Maldives. It consists of three separate natural atolls, namely southern Maalhosmadulu Atoll (which is 42 km long and 32 km wide and consists of 9 inhabited islands), the Fasdūtherē Atoll (wedged in between the two Maalhosmadulu Atolls and separated from north Maalhosmasdulu Atoll by Hani Kandu or Moresby Channel) and the smaller natural atoll known as Goifulhafehendhu Atoll (Horsburgh Atoll in the Admiralty charts). Situated on the west of the Maldives atoll chain, it consists of 75 islands of which 13 are inhabited with a population of over 11,000 people. The remaining 57 islands are uninhabited, in addition to eight islands being developed as resorts. Thulhaadhoo Island is traditionally well known for being the only island making lacquerwork handicrafts. Haa Alifu, Haa Dhaalu, Shaviyani, Noonu, Raa, Baa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
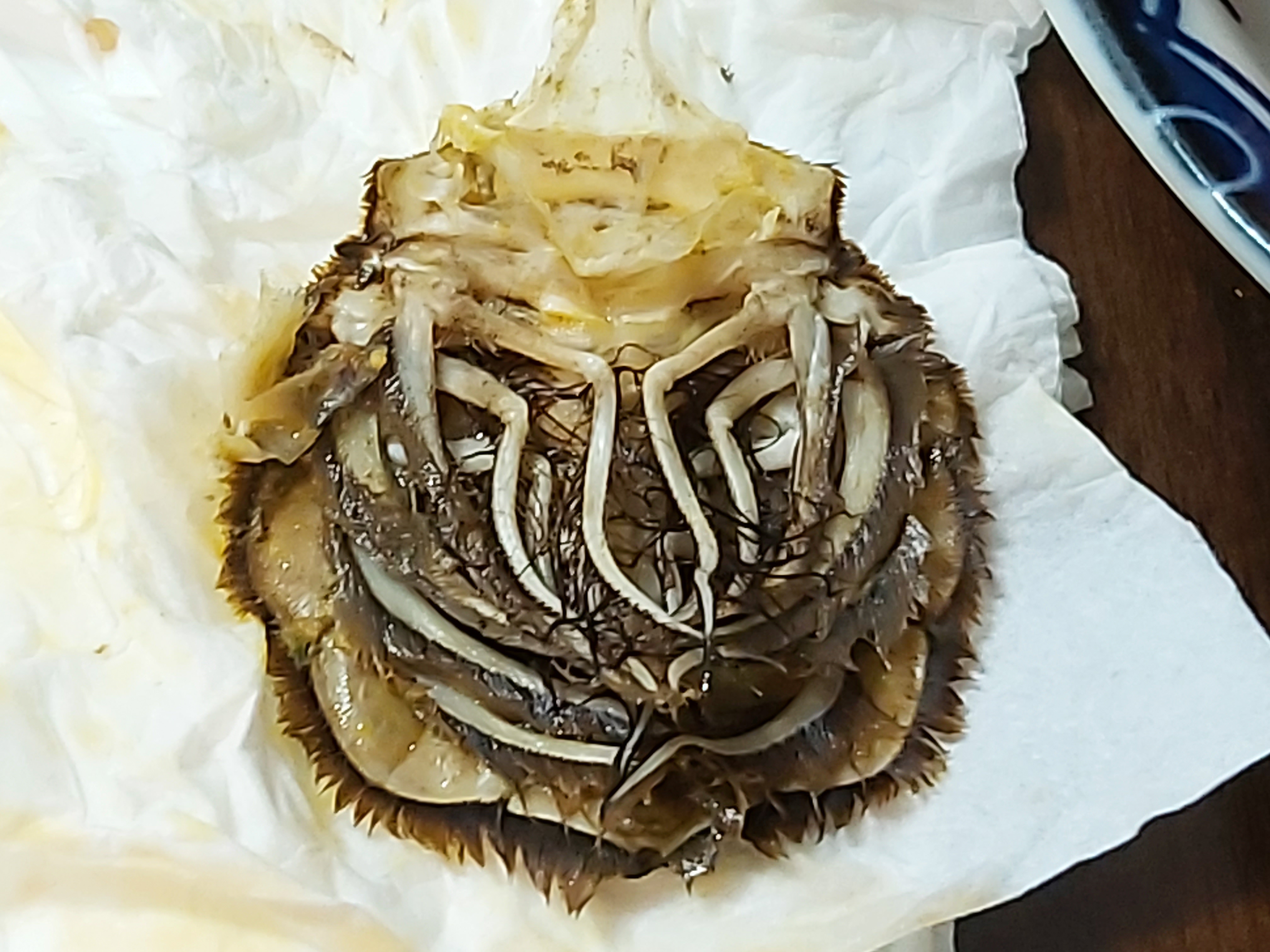
Crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the world's oceans, in freshwater, and on land, are generally covered with a thick exoskeleton, and have a single pair of pincers. They first appeared during the Jurassic Period. Description Crabs are generally covered with a thick exoskeleton, composed primarily of highly mineralized chitin, and armed with a pair of chelae (claws). Crabs vary in size from the pea crab, a few millimeters wide, to the Japanese spider crab, with a leg span up to . Several other groups of crustaceans with similar appearances – such as king crabs and porcelain crabs – are not true crabs, but have evolved features similar to true crabs through a process known as carcinisation. Environment Crabs are found in all of the world's oceans, as well as in fresh w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two in the general area of Indonesia. It does not include the temperate and polar regions of the Indian and Pacific oceans, nor the Tropical Eastern Pacific, along the Pacific coast of the Americas, which is also a distinct marine realm. The term is especially useful in marine biology, ichthyology, and similar fields, since many marine habitats are continuously connected from Madagascar to Japan and Oceania, and a number of species occur over that range, but are not found in the Atlantic Ocean. The region has an exceptionally high species richness, with the world's highest species richness being found in at its heart in the Coral Triangle, and a remarkable gradient of decreasing species richness radiating outward in al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decapod Anatomy
The decapod (crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. They are, from head to tail: Cephalothorax Head # antennules # antennae #mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelae
A chela ()also called a claw, nipper, or pinceris a pincer (biology), pincer-like organ at the end of certain limbs of some arthropods. The name comes from Ancient Greek , through New Latin '. The plural form is chelae. Legs bearing a chela are called chelipeds. Another name is ''claw'' because most chelae are curved and have a sharp point like a claw. Chelae can be present at the tips of arthropod legs as well as their pedipalps. Chelae are distinct from spider chelicerae in that they do not contain venomous glands and cannot distribute venom. See also * Pincer (biology) * Pincer (tool) References Arthropod anatomy {{Arthropod-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carapace
A carapace is a Dorsum (biology), dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the underside is called the plastron. Crustaceans In crustaceans, the carapace functions as a protective cover over the cephalothorax (i.e., the fused head and thorax, as distinct from the abdomen behind). Where it projects forward beyond the eyes, this projection is called a rostrum (anatomy), rostrum. The carapace is Calcification, calcified to varying degrees in different crustaceans. Zooplankton within the phylum Crustacea also have a carapace. These include Cladocera, ostracods, and Isopoda, isopods, but isopods only have a developed "cephalic shield" carapace covering the head. Arachnids In arachnids, the carapace is formed by the fusion of prosomal tergites into a single Plate (animal anatomy), plate which carries the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques-Gérard Milbert
Jacques-Gérard Milbert (18 November 1766 – 5 June 1840) was a French naturalist and artist. Milbert was a pupil of the landscape art, landscape painter Pierre-Henri de Valenciennes, and went on to teach drawing at the Parisian school of mines – the ' – from 1795. In 1800, Milbert embarked on Nicolas Baudin's Baudin expedition to Australia, voyage to Australia. During the voyage, Milbert and several other artists became ill, and the artists and the captain came into conflict. This caused several artists, including Milbert, to leave the voyage at Mauritius, leaving Charles-Alexandre Lesueur to produce the voyage's scientific drawings. Milbert returned to France, where in 1812 he published a series of views of Mauritius, the Cape Colony and Tenerife, titled ', comprising two octavo volumes of text, and one quarto volume of plates. In 1815, Milbert travelled to the United States, where he would remain for eight years, based in New York City, teaching, and travelling extensiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decapoda
The Decapoda or decapods (literally "ten-footed") are an order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, including many familiar groups, such as crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp and prawns. Most decapods are scavengers. The order is estimated to contain nearly 15,000 species in around 2,700 genera, with around 3,300 fossil species. Nearly half of these species are crabs, with the shrimp (about 3,000 species) and Anomura including hermit crabs, porcelain crabs, squat lobsters (about 2500 species) making up the bulk of the remainder. The earliest fossil decapod is the Devonian ''Palaeopalaemon''. Anatomy Decapods can have as many as 38 appendages, arranged in one pair per body segment. As the name Decapoda (from the Greek , ', "ten", and , '' -pod'', "foot") implies, ten of these appendages are considered legs. They are the pereiopods, found on the last five thoracic segments. In many decapods, one pair of these "legs" has enlarged pincers, called chelae, with the legs be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Milne-Edwards
Henri Milne-Edwards (23 October 1800 – 29 July 1885) was an eminent French zoologist. Biography Henri Milne-Edwards was the 27th child of William Edwards, an English planter and colonel of the militia in Jamaica and Elisabeth Vaux, a Frenchwoman. Henri was born in Bruges, in present-day Belgium, where his parents had retired; Bruges was then a part of the newborn French Republic. His father had been jailed for several years for helping some Englishmen in their escape to their country. Henri spent most of his life in France. He was brought up in Paris by his older brother Guillaume Frederic Edwards (1777–1842), a distinguished physiologist and ethnologist. His father was released after the fall of Napoleon. The whole family then moved to Paris. At first he turned his attention to medicine, in which he graduated as an MD at Paris in 1823. His passion for natural history soon prevailed, and he gave himself up to the study of the lower forms of animal life. He became a stude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)