|
Graphical Output Device
An output device is any piece of computer hardware equipment which converts information into a human-perceptible form or, historically, into a physical machine-readable form for use with other non-computerized equipment. It can be text, graphics, tactile, audio, or video. Examples include monitors, printers, speakers, headphones, projectors, GPS devices, optical mark readers, and braille readers. In an industrial setting, output devices also include "printers" for paper tape and punched cards, especially where the tape or cards are subsequently used to control industrial equipment, such as an industrial loom with electrical robotics which is not fully computerized. Visual A display device is the most common form of output device which presents output visually on computer screen. The output appears temporarily on the screen and can easily be altered or erased. With all-in-one PCs, notebook computers, hand held PCs and other devices; the term display screen is used for the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the case, central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), monitor, mouse, keyboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, speakers and motherboard. By contrast, software is the set of instructions that can be stored and run by hardware. Hardware is so-termed because it is " hard" or rigid with respect to changes, whereas software is "soft" because it is easy to change. Hardware is typically directed by the software to execute any command or instruction. A combination of hardware and software forms a usable computing system, although other systems exist with only hardware. Von Neumann architecture The template for all modern computers is the Von Neumann architecture, detailed in a 1945 paper by Hungarian mathematician John von Neumann. This describes a design architecture for an electronic digital computer with subdivisions of a processing unit consisting of an arithmet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MSI MS-V328 Outputs 20181231
MSI may refer to: Organizations * Marketing Science Institute, a nonprofit learning institution in Cambridge, Massachusetts, US * Media Sport Investment, the international fund of investors that ran Sport Club Corinthians Paulista * Millennium Science Initiative, an international program bringing technology to developing nations * Ministry of Science and Innovation (New Zealand) * Minority-serving institution, in US higher education * MSI Reproductive Choices, an international non-governmental organisation providing contraception and safe abortion services, with a global HQ in London, UK * Museum of Science and Industry (Chicago) * Science and Industry Museum, in Manchester, England * University of Minnesota Supercomputing Institute * Italian Social Movement (''Movimento Sociale Italiano''), a defunct post-fascist party Companies * Micro-Star International, a Taiwanese information technology company * Midwest Scientific Instruments, a defunct American computer company * Morgan S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderbolt (interface)
Thunderbolt is the brand name of a hardware interface for the connection of external peripherals to a computer. It has been developed by Intel, in collaboration with Apple. It was initially marketed under the name Light Peak, and first sold as part of an end-user product on 24 February 2011. Thunderbolt combines PCI Express (PCIe) and DisplayPort (DP) into two serial signals, and additionally provides DC power, all in one cable. Up to six peripherals may be supported by one connector through various topologies. Thunderbolt 1 and 2 use the same connector as Mini DisplayPort (MDP), whereas Thunderbolt 3 and 4 reuse the USB-C connector from USB. Description Thunderbolt controllers multiplex one or more individual data lanes from connected PCIe and DisplayPort devices for transmission via two duplex Thunderbolt lanes, then de-multiplex them for use by PCIe and DisplayPort devices on the other end. A single Thunderbolt port supports up to six Thunderbolt devices via hubs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
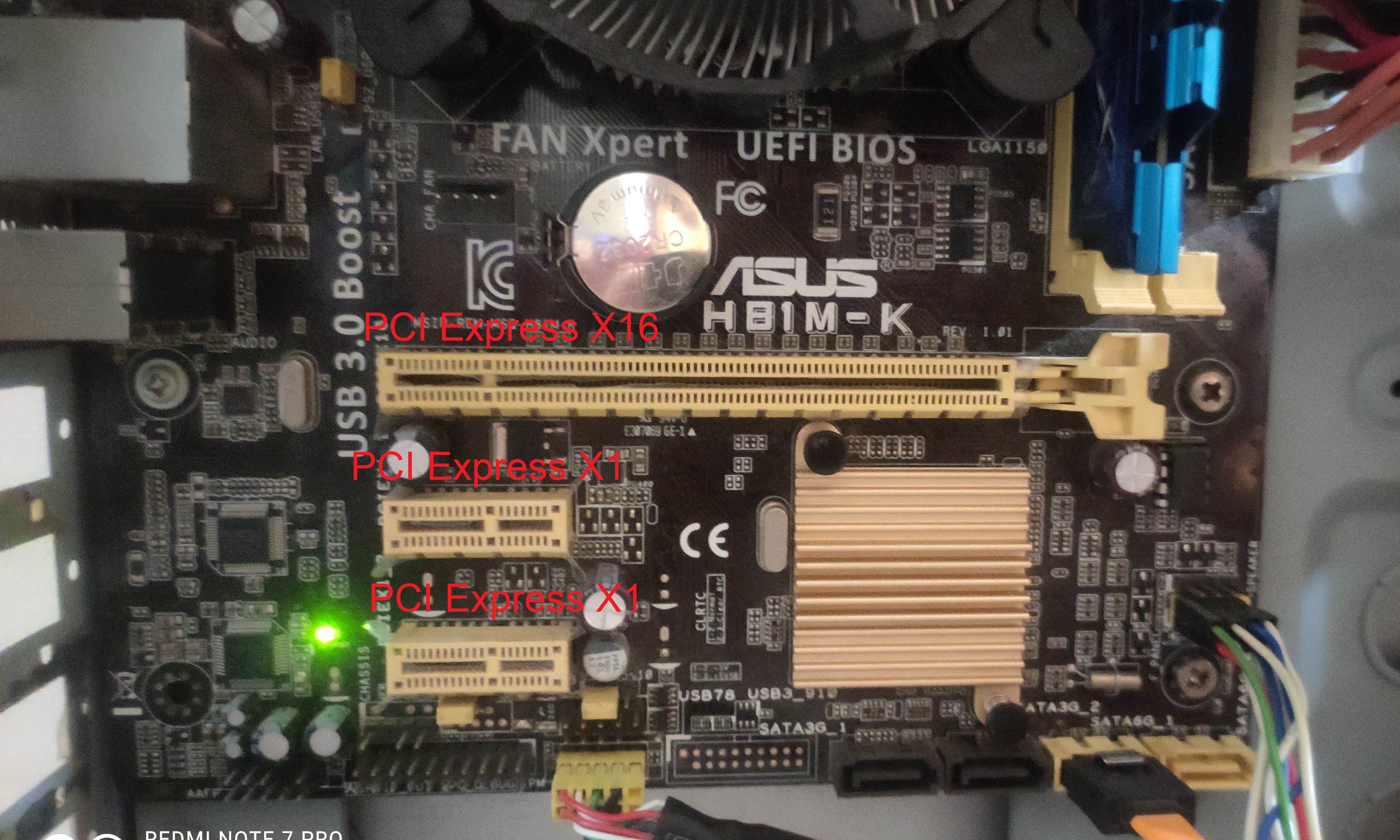
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer and is part of the PCI Local Bus standard. The PCI bus supports the functions found on a processor bus but in a standardized format that is independent of any given processor's native bus. Devices connected to the PCI bus appear to a bus master to be connected directly to its own bus and are assigned addresses in the processor's address space. It is a parallel bus, synchronous to a single bus clock. Attached devices can take either the form of an integrated circuit fitted onto the motherboard (called a ''planar device'' in the PCI specification) or an expansion card that fits into a slot. The PCI Local Bus was first implemented in IBM PC compatibles, where it displaced the combination of several slow Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) slots and one fast VESA Local Bus (VLB) slot as the bus configuration. It has subsequently been adopted for other computer typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerated Graphics Port
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) is a parallel expansion card standard, designed for attaching a video card to a computer system to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. It was originally designed as a successor to PCI-type connections for video cards. Since 2004, AGP was progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express (PCIe), which is serial, as opposed to parallel; by mid-2008, PCI Express cards dominated the market and only a few AGP models were available, with GPU manufacturers and add-in board partners eventually dropping support for the interface in favor of PCI Express. Advantages over PCI AGP is a superset of the PCI standard, designed to overcome PCI's limitations in serving the requirements of the era's high-performance graphics cards. The primary advantage of AGP is that it doesn't share the PCI bus, providing a dedicated, point-to-point pathway between the expansion slot(s) and the motherboard chipset. The direct connection also allows for higher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism (Advanced Error Reporting, AER), and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization. The PCI Express electrical interface is measured by the number of simultaneous lanes. (A lane is a single send/receive line of data. The analogy is a highway with traffic in both direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated GPU
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed to manipulate and alter memory (computing), memory to accelerate the creation of Digital image, images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device. GPUs are used in embedded systems, mobile phones, personal computers, workstations, and game consoles. Modern GPUs are efficient at manipulating computer graphics and image processing. Their Parallel computing, parallel structure makes them more efficient than general-purpose central processing units (CPUs) for algorithms that process large blocks of data in parallel. In a personal computer, a GPU can be present on a video card or embedded on the motherboard. In some CPUs, they are embedded on the CPU Die (integrated circuit), die. In the 1970s, the term "GPU" originally stood for ''graphics processor unit'' and described a programmable processing unit independently working from the CPU and responsible for graphics manipulation and output. Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete GPU
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or mistakenly GPU) is an expansion card which generates a feed of output images to a display device, such as a computer monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called discrete or dedicated graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to integrated graphics. A graphics processing unit that performs the necessary computations is the main component of a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to refer to the graphics card as a whole. Most graphics cards are not limited to simple display output. The graphics processing unit can be used for additional processing, which reduces the load from the central processing unit. Additionally, computing platforms such as OpenCL and CUDA allow using graphics cards for general-purpose computing. Applications of general-purpose computing on graphics cards include AI training, cryptocurrency mining, and mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DisplayPort
DisplayPort (DP) is a digital display interface developed by a consortium of PC and chip manufacturers and standardized by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). It is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor. It can also carry audio, USB, and other forms of data. DisplayPort was designed to replace VGA, FPD-Link, and Digital Visual Interface (DVI). It is backward compatible with other interfaces, such as HDMI and DVI, through the use of either active or passive adapters. It is the first display interface to rely on packetized data transmission, a form of digital communication found in technologies such as Ethernet, USB, and PCI Express. It permits the use of internal and external display connections. Unlike legacy standards that transmit a clock signal with each output, its protocol is based on small data packets known as ''micro packets'', which can embed the clock signal in the data stream, allowing higher resolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an HDMI-compliant source device, such as a display controller, to a compatible computer monitor, video projector, digital television, or digital audio device. HDMI is a digital replacement for analog video standards. HDMI implements the EIA/CEA-861 standards, which define video formats and waveforms, transport of compressed and uncompressed LPCM audio, auxiliary data, and implementations of the VESA EDID. CEA-861 signals carried by HDMI are electrically compatible with the CEA-861 signals used by the Digital Visual Interface (DVI). No signal conversion is necessary, nor is there a loss of video quality when a DVI-to-HDMI adapter is used. The Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) capability allows HDMI devices to control each other when necessary and allows the user to operate multiple devices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Video Connectors
This is a list of physical RF and video connectors and related video signal standards. By signal standard Physical connectors D-subminiature family DVI-related DIN/Mini-DIN The mini-DIN connectors are a family of multi-pin electrical connectors used in a variety of applications. Mini-DIN is similar to the larger, older DIN connector. Design Mini-DIN connectors are in diameter and come in seven patterns, wit ... Others See also * Computer display standard References External linksMonitor PortsPinouts and other technical information; lacks more recent interfaces such as HDMISimple table of PC video standards thru XGA with DB9 pinoutsup to XGAStandard and device-specific video interfaces pinouts Numerous standards described and categorized, including such recent ones as DVI and HDMIList of computer video standards and connectors pinoutsWiki format (including community updates and free redistribution); broad coverage including HDMI {{DEFAULTSORT:Video ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Signal
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems which, in turn, were replaced by flat panel displays of several types. Video systems vary in display resolution, aspect ratio, refresh rate, color capabilities and other qualities. Analog and digital variants exist and can be carried on a variety of media, including radio broadcast, magnetic tape, optical discs, computer files, and network streaming. History Analog video Video technology was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) television systems, but several new technologies for video display devices have since been invented. Video was originally exclusively a live technology. Charles Ginsburg led an Ampex research team developing one of the first practic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |