|
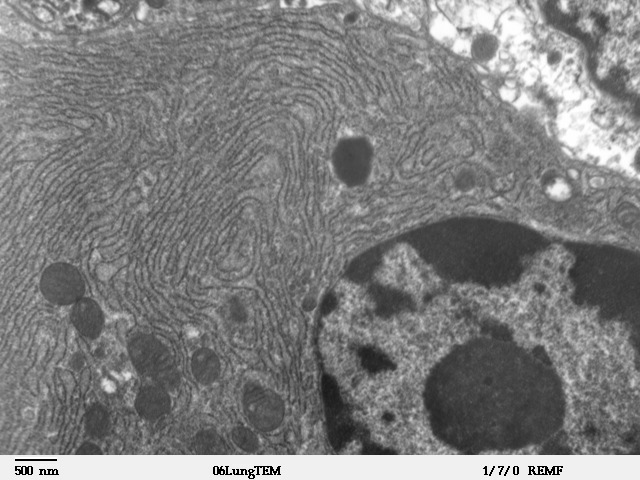
Granular Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or plasma m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clara Cell Lung - TEM
Clara may refer to: Organizations * CLARA, Latin American academic computer network organization * Clara.Net, a European ISP * Consolidated Land and Rail Australia, a property development consortium People * Clara (given name), a feminine given name (includes a list of people and fictional characters with this name) * Saint Clara or Clare of Assisi ; Surname * Florian Clara (born 1988), Italian luger * Roland Clara (born 1982), Italian cross country skier Places France * Clara, Pyrénées-Orientales, a commune of the Pyrénées-Orientales ''département'' in southwestern France Ireland * Clara, County Kilkenny, a parish * Clara, County Offaly, a town in Ireland ** Clara Bog, a wetland near the town of Clara, County Offaly * Clara, County Wicklow, sometimes referred to as the "smallest village in Ireland" United Kingdom *Clara Vale, a village in Tyne and Wear, England United States *Clara, Florida, area on the border of Taylor County and Dixie County * Clara City, Minnesota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detoxification
Detoxification or detoxication (detox for short) is the physiological or medicinal removal of toxic substances from a living organism, including the human body, which is mainly carried out by the liver. Additionally, it can refer to the period of drug withdrawal during which an organism returns to homeostasis after long-term use of an addictive substance. In medicine, detoxification can be achieved by decontamination of poison ingestion and the use of antidotes as well as techniques such as dialysis and (in a limited number of cases) chelation therapy. Many alternative medicine practitioners promote various types of detoxification such as detoxification diets. Scientists have described these as a "waste of time and money". Sense About Science, a UK-based charitable trust, determined that most such dietary "detox" claims lack any supporting evidence. The liver and kidney are naturally capable of detox, as are intracellular (specifically, inner membrane of mitochondria or in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Translation
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later folds into an active protein and performs its functions in the cell. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of complementary tRNA anticodon sequences to mRNA codons. The tRNAs carry specific amino acids that are chained together into a polypeptide as the mRNA passes through and is "read" by the ribosome. Translation proceeds in three phases: # Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the target mRNA. The first tRNA is attached at the start codon. # Elongation: The last tRNA validated by the small ribosomal subunit (''acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perinuclear Space
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material. The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membranes: an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. The space between the membranes is called the perinuclear space. It is usually about 10–50 nm wide. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The nuclear envelope has many nuclear pores that allow materials to move between the cytosol and the nucleus. Intermediate filament proteins called lamins form a structure called the nuclear lamina on the inner aspect of the inner nuclear membrane and give structural support to the nucleus. Structure The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes, an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores. Two sets of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipid Membrane
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer, as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus, and membranes of the membrane-bound organelles in the cell. The lipid bilayer is the barrier that keeps ions, proteins and other molecules where they are needed and prevents them from diffusing into areas where they should not be. Lipid bilayers are ideally suited to this role, even though they are only a few nanometers in width, because they are impermeable to most water-soluble (hydrophilic) molecules. Bilayers are particularly impermeable to ions, which allows cells to regulate salt concentrations and pH by transporting ions across their membranes using proteins called ion pumps. Biological bilayers are usually composed of amphiphilic phospholip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. It is composed of three main components, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules, and these are all capable of rapid growth or disassembly dependent on the cell's requirements. A multitude of functions can be performed by the cytoskeleton. Its primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, and through association with extracellular connective tissue and other cells it stabilizes entire tissues. The cytoskeleton can also contract, thereby deforming the cell and the cell's environment and allowing cells to migrate. Moreover, it is involved in many cell signaling pathways and in the uptake of extracellular material ( endocytosis), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blausen 0350 EndoplasmicReticulum
Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. is the creator and owner of a library of two- and three-dimensional medical and scientific images and animations, a developer of information technology allowing access to that content, and a business focused on licensing and distributing the content. It was founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas, in 1991, and is privately held. Background Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. (BMC) is a privately held company founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas in 1991. BMC created and owns a library of medical and scientific images and animations, and has developed information technology tools allowing access to the library; as well, it licenses and otherwise works to distribute the content. As of this date, BMC's animation library comprised approximately 1,500 animations and over 27,000 two- and three-dimensional images designed for point-of-care patient education, which could be accessed by consumers or professional caregivers (primarily via h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus ER Golgi
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to: *Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom *Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA Nucleus may also refer to: Science, technology, and mathematics Astronomy *Active galactic nucleus in astronomy *Comet nucleus, the solid, central part of a comet Biology *Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA *Nucleus (neuroanatomy), a cluster of cell bodies of neurons in the central nervous system *Nucleus that forms in the eye in nuclear sclerosis (early cataracts) *''Nucleus'', a scientific journal concerned with the cell nucleus; published by Taylor & Francis *Nucleus, a small colony of honeybees, induced to raise a new queen by the beekeeper Computer systems * Nucleus (operating system), sometimes a synonym for kernel * Nucleus CMS, a weblog system * Nucleus RTOS, a real-time operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reticulum
Reticulum is a small, faint constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for a small net, or reticle—a net of crosshairs at the focus of a telescope eyepiece that is used to measure star positions. The constellation is best viewed between October and December, and save for one main star visible in ideal conditions, cannot be seen from north of the 30th parallel north. History A constellation in this area was introduced by Isaac Habrecht II in his celestial globe in 1621, who named it ''Rhombus''. It was replaced with a somewhat different constellation by the French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in the eighteenth century; during his stay at the Cape of Good Hope, he named the constellation le Réticule Rhomboide to commemorate the reticle in his telescope eyepiece. The name was later Latinized to Reticulum in his star catalogue ''Coelum Australe Stelliferum''. In 1810, the stars of Reticulum were used by William Croswell to produce the constellation '' Marmor Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Claude
Albert Claude (; 24 August 1899 – 22 May 1983) was a Belgian- American cell biologist and medical doctor who shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1974 with Christian de Duve and George Emil Palade. His elementary education started in a comprehensive primary school at Longlier, his birthplace. He served in the British Intelligence Service during the First World War, and got imprisoned in concentration camps twice. In recognition of his service, he was granted enrolment at the University of Liège in Belgium to study medicine without any formal education required for the course. He earned his Doctor of Medicine degree in 1928. Devoted to medical research, he initially joined German institutes in Berlin. In 1929 he found an opportunity to join the Rockefeller Institute in New York. At Rockefeller University he made his most groundbreaking achievements in cell biology. In 1930 he developed the technique of cell fractionation, by which he discovered the agent of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keith R
Keith may refer to: People and fictional characters * Keith (given name), includes a list of people and fictional characters * Keith (surname) * Keith (singer), American singer James Keefer (born 1949) * Baron Keith, a line of Scottish barons in the late 18th century * Clan Keith, a Scottish clan associated with lands in northeastern and northwestern Scotland Places Australia * Keith, South Australia, a town and locality Scotland * Keith, Moray, a town ** Keith railway station * Keith Marischal, East Lothian United States * Keith, Georgia, an unincorporated community * Keith, Ohio, an unincorporated community * Keith, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Keith, Wisconsin, a ghost town * Keith County, Nebraska Other uses * Keith F.C., a football team based in Keith, Scotland * , a ship of the British Royal Navy * Hurricane Keith, a 2000 hurricane that caused extensive damage in Central America * ''Keith'' (film), a 2008 independent film directed by Todd Kessler * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a higher resolving power than light microscopes and can reveal the structure of smaller objects. A scanning transmission electron microscope has achieved better than 50 pm resolution in annular dark-field imaging mode and magnifications of up to about 10,000,000× whereas most light microscopes are limited by diffraction to about 200 nm resolution and useful magnifications below 2000×. Electron microscopes use shaped magnetic fields to form electron optical lens systems that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope. Electron microscopes are used to investigate the ultrastructure of a wide range of biological and inorganic specimens including microorganisms, cells, large molecules, biopsy samples, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |