|
Grandfather Ivan
Grandfather Ivan ( bg, Дядо Иван) is a folklore image of Russia in the minds of Bulgarians from the times of the Bulgarian National Revival, portraying Russia as a benevolent, protective force. Ivan is a Slavic form of the biblical name Joan (John). The apparition of the myth of "Grandfather Ivan" is associated with the marriage of Ivan III to the niece of the last Byzantine emperor, Sophia Palaiologina, in 1472. Through this marriage, Ivan III was formally entitled to ascend to the throne of the already nonexisting Byzantine Empire and also received the moral obligation to liberate the Balkan Orthodox peoples from the Ottoman invaders. "Grandfather Ivan" was accepted as an "old clever patron". This vision was applied not only to the Tsar but also to the Russian people. Sometime in the 18th century, during the Bulgarian National Awakening, the Bulgarians came to the conclusion that "Grandfather Ivan" should come to set them free from the Ottoman rule.Асен Димов, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Of Ivan 3 (reverse)
Seal may refer to any of the following: Common uses * Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly: ** Earless seal, or "true seal" ** Fur seal * Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of authentication, on paper, wax, clay or another medium (the impression is also called a seal) * Seal (mechanical), a device which helps prevent leakage, contain pressure, or exclude contamination where two systems join Arts, entertainment and media * ''Seal'' (1991 album), by Seal * ''Seal'' (1994 album), sometimes referred to as ''Seal II'', by Seal * ''Seal IV'', a 2003 album by Seal * ''Seal Online'', a 2003 massively multiplayer online role-playing game Law * Seal (contract law), a legal formality for contracts and other instruments * Seal (East Asia), a stamp used in East Asia as a form of a signature * Record sealing Military * ''Fairey Seal'', a 1930s British carrier-borne torpedo bomber aircra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
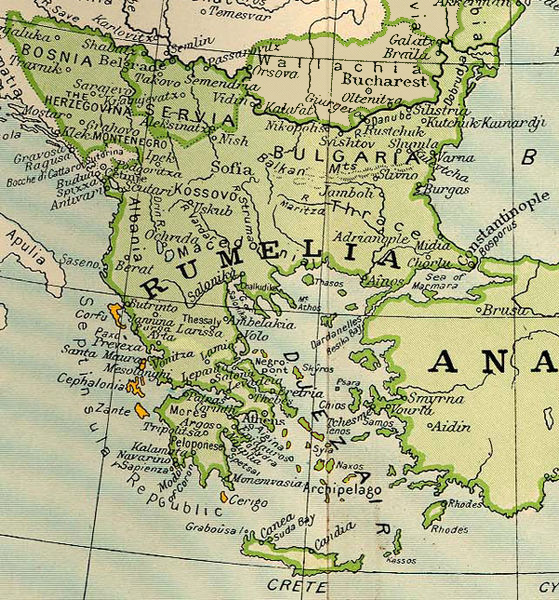
Ottoman Balkans
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the Byzantine rite, was the name of a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and vassals in Europe that would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans". During the period of its existence, it was more often known in English as Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means "Greek", or a Christian Greek speaker and ''ėli'' means "land" and ''Rumelia'' ( ota, روم ايلى, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans, which formerly belonged to the Byzantine Empire, known by its contemporaries as the Roman E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Folklore
The main Bulgarian celebration events are : * Martenitsa, all of March, beginning with the 1st of march * Nestinari * Kukeri * Koleda (Christmas), Koledari * Velikden (Easter) * Name Days * International Mother's Day, March 8 * Independence Day, March 3 * Sveti, Sveti Kiril i Metodii, May 24 Other Bulgarian customs, specific for Bulgaria, worship God, the saints, the nature, the health, and chase away bad spirits : * St. Andrew's Day - 30 November * Antonovden - 17 January * Archangelden - 8 November * Christmas Eve * Budnik * Easter * Valtchi praznici * St George's Day * German * Dragon chasing * Gorestnici - 28,29,30 July * Dimitrovden - 26 October * St John's Eve - 24 June * Need-fire * Trifon Zarezan - 1 February / 14 February * Horse riding Todorovden - 1st Saturday of Lent * Feast of the Cross - 14 September * Lazarice (Lazarus Saturday) - 8 days before Easter in the name of Lazarus * Maccabees - ab 1 August for 12 days, to remember the Maccabees * Mratinci - Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878)
The Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878 ( tr, 93 Harbi, lit=War of ’93, named for the year 1293 in the Islamic calendar; russian: Русско-турецкая война, Russko-turetskaya voyna, "Russian–Turkish war") was a conflict between the Ottoman Empire and a coalition led by the Russian Empire, and including Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, and Montenegro. Fought in the Balkans and in the Caucasus, it originated in emerging 19th century Balkan nationalism. Additional factors included the Russian goals of recovering territorial losses endured during the Crimean War of 1853–56, re-establishing itself in the Black Sea and supporting the political movement attempting to free Balkan nations from the Ottoman Empire. The Russian-led coalition won the war, pushing the Ottomans back all the way to the gates of Constantinople, leading to the intervention of the western European great powers. As a result, Russia succeeded in claiming provinces in the Caucasus, namely Kars and Batum, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russophilia
Russophilia (literally love of Russia or Russians) is admiration and fondness of Russia (including the era of the Soviet Union and/or the Russian Empire), Russian history and Russian culture. The antonym is Russophobia. In the 19th Century, Russophilia was often linked to variants of Pan-Slavism, since the Russian Empire and the autonomous Serbia were the only two slav-associated sovereign states during and after Spring of Nations. Russophilia in Europe American author Robert Alexander wrote: "I love Russians for their dramatic, emotional nature. They're not afraid to love, not afraid to get hurt, not afraid to exaggerate or act impulsively." Russophilia in Serbia Russia is hugely popular in Serbia, and Serbs have always traditionally seen Russia as a close ally due to shared Slavic heritage, culture, and Orthodox faith. According to European Council on Foreign Relations, 54% of Serbians see Russia as an ally. In comparison, 11% see European Union as an ally, and onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow, Third Rome
Moscow, third Rome (; ) is a theological and political concept asserting Moscow as the successor to ancient Rome, with the Russian world carrying forward the legacy of the Roman Empire. The term "third Rome" refers to a historical topic of debate in European culture: the question of the successor city to the "first Rome" (Rome, within the Western Roman Empire) and the "second Rome" (Constantinople, within the Eastern Roman Empire). Concept "Moscow, Third Rome" is a theological and a political concept which was formulated in the 15th–16th centuries in the Tsardom of Rus. In this concept, three interrelated and interpenetrating fields of ideas can be found: ;Theology: that is linked with justification of necessity and inevitability of the unity of the Eastern Orthodox Church. ;Social policy: derived out of the feeling of unity in East Slavic territories being historically tied through Christian Eastern Orthodox faith and Slavic culture. ;State doctrine: according to which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Bulgaria
The history of Ottoman Bulgaria spans nearly 500 years, from the conquest by the Ottoman Empire of the smaller kingdoms emerging from the disintegrating Second Bulgarian Empire in the late 14th century, to the Liberation of Bulgaria in 1878. As a result of the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878), the Principality of Bulgaria, a self-governing Ottoman vassal state that was functionally independent, was created. In 1885 the Ottoman autonomous province of Eastern Rumelia came under the control of and was unified with the Principality of Bulgaria. Bulgaria declared independence in 1908. Administrative organization The Ottomans reorganised the Bulgarian territories, dividing them into several vilayets, each ruled by a Sanjakbey or Subasi accountable to the Beylerbey. Significant parts of the conquered land were parcelled out to the Sultan's followers, who held it as benefices or fiefs (small ''timars'', medium ''ziyamet'' and large ''hases'') directly from him, or from the Beylerbeys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian National Awakening
The Bulgarian National Awakening ( bg, Ранно възраждане) is the initial period of the Bulgarian National Revival in the history of Bulgaria, from the Treaty of Karlowitz to the Ottoman coups of 1807–08. During this historical period of enlightenment (''The Age of Enlightenment''), the interest in self-identification and self-knowledge was aroused and revived in the conditions of the gradual decline of the Ottoman Empire, especially after the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca. Background Ottoman Bulgaria, administratively formed as Rumelia Eyalet, is the foundation on which the Ottoman Empire stepped for its establishment, consolidation and conquest in Europe until the two battles of Vienna ( Siege of Vienna and Battle of Vienna). Previously, the two battles at Mohács marked the beginning and end of the Ottoman presence in Central Europe. The period of the 16th and 17th centuries until the Great Turkish War were a time of all-round prosperity without wars in the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian People
, native_name_lang = ru , image = , caption = , population = , popplace = 118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate) , region1 = , pop1 = approx. 7,500,000 (including Russian Jews and Russian Germans) , ref1 = , region2 = , pop2 = 7,170,000 (2018) ''including Crimea'' , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 3,512,925 (2020) , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 3,072,756 (2009)(including Russian Jews and Russian Germans) , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 1,800,000 (2010)(Russian ancestry and Russian Germans and Jews) , ref5 = 35,000 (2018)(born in Russia) , region6 = , pop6 = 938,500 (2011)(including Russian Jews) , ref6 = , region7 = , pop7 = 809,530 (2019) , ref7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsardom Of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I in 1721. From 1551 to 1700, Russia grew by 35,000 km2 per year. The period includes the upheavals of the transition from the Rurik to the Romanov dynasties, wars with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Sweden and the Ottoman Empire, and the Russian conquest of Siberia, to the reign of Peter the Great, who took power in 1689 and transformed the Tsardom into the Russian Empire. During the Great Northern War, he implemented substantial reforms and proclaimed the Russian Empire after victory over Sweden in 1721. Name While the oldest endonyms of the Grand Duchy of Moscow used in its documents were "Rus'" () and the "Russian land" (), a new form of its name, ''Rusia'' or ''Russia'', appeared and became common in the 15th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |