|
Grandes (islands)
Grandes ( el, Γκράντες) is a group of three small islands off the east coast of Crete. Administratively it comes within the Itanos municipality in Lasithi. Grandes can be seen from the Minoan site of Roussolakkos near Palekastro as can the island of Elasa Elasa ( el, Ελάσα) is an island that can be found northeast of Crete in the Aegean Sea, about from the palm tree forest of Vai. It is rocky and uninhabited covering . Its highest point is above sea level. Administratively it comes within t .... {{Aegean Sea Landforms of Lasithi Uninhabited islands of Crete Islands of Greece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
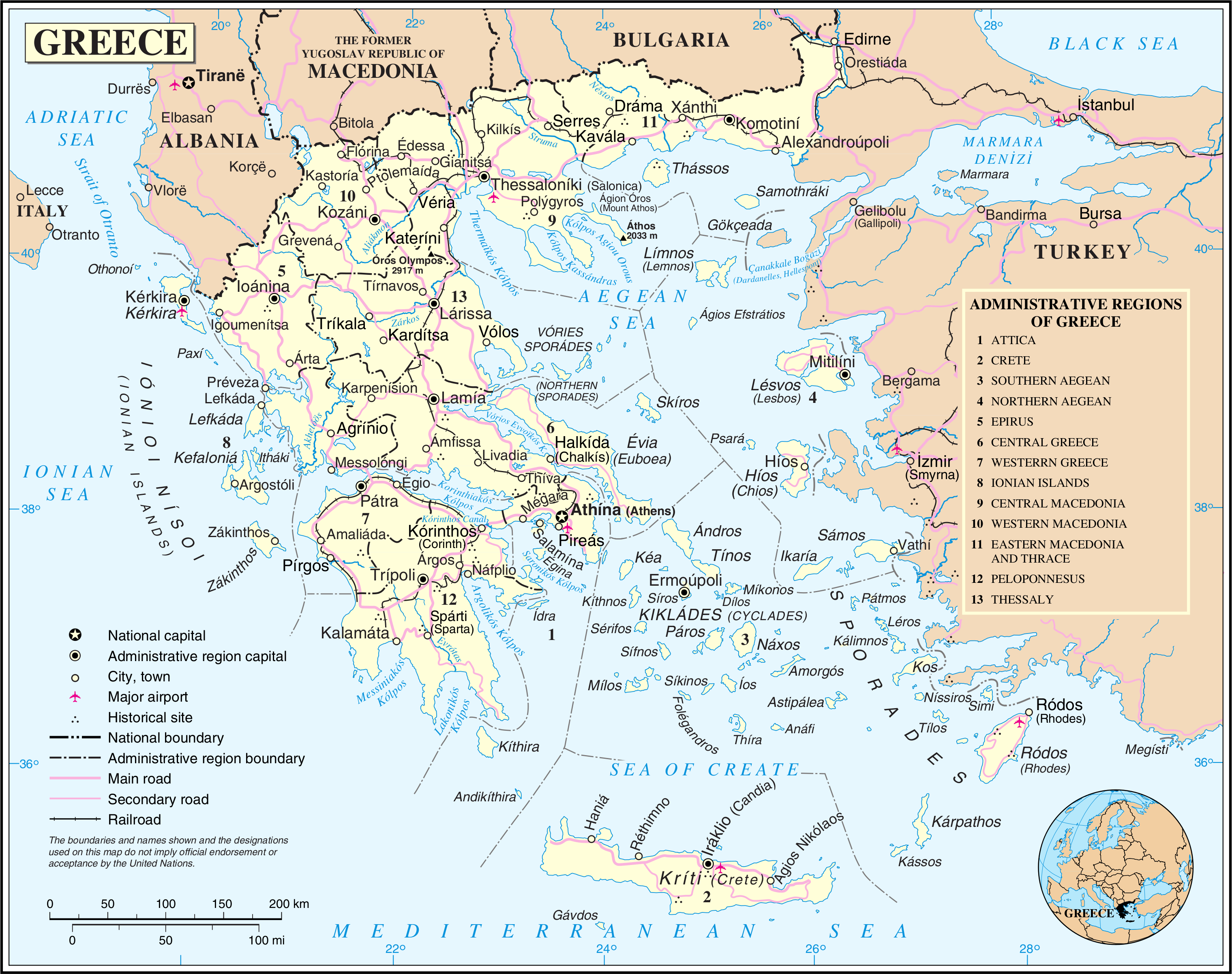
Modern Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece ( el, περιφέρειες, translit=periféries) are the country's thirteen first-level administrative entities, each comprising several second-level units, originally known as prefectures and, since 2011, as regional units. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the prefectures (Law 1622/1986). Ν.1622/86 "Τοπική Αυτοδιοίκηση - Περιφερειακή Ανάπτυξη - Δημοκρατικός Προγραμματισμός", (ΦΕΚ 92/τ.Α΄/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad historical–geographical regions (γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα), which, however, was often arbitrary; not all of the pre-1986 traditional historical-geographic regions had official administrative bodie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete rests about south of the Greek mainland, and about southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete (or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the Libyan Sea (or South Cretan Sea) to the south. Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete ( el, Περιφέρεια Κρήτης, links=no), which is the southernmost of the 13 top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most populous of Greece's regions. Its capital and largest city is Heraklion, on the north shore of the island. , the region had a population of 636,504. The Dodecanese are located to the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Units Of Greece
The 74 regional units of Greece ( el, περιφερειακές ενότητες, ; sing. , ) are the country's Seventy-four second-level administrative units. They are divisions of the country's 13 regions, and are further divided into municipalities. They were introduced as part of the Kallikratis administrative reform on 1 January 2011 and are comparable in area and, in the mainland, coterminous with the 'pre-Kallikratis' prefectures of Greece During the first administrative division of independent Greece in 1833–1836 and again from 1845 until their abolition with the Kallikratis reform in 2010, the prefectures ( el, νομοί, sing. νομός, translit=nomoi, sing. nomós) were .... List References {{Articles on second-level administrative divisions of European countries Regional units Greece transport-related lists Subdivisions of Greece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lasithi
Lasithi ( el, Λασίθι) is the easternmost regional unit on the island of Crete, to the east of Heraklion. Its capital is Agios Nikolaos, the other major towns being Ierapetra and Sitia. The mountains include the Dikti in the west and the Thrypti in the east. The Sea of Crete lies to the north and the Libyan Sea to the south. To the east of the village of Elounda lies the island of Spinalonga, formerly a Venetian fortress and a leper colony. On the foot of Mount Dikti lies the Lasithi Plateau, famous for its windmills. Vai is well known for its datepalm forest. Thanks to its beaches and its mild climate year-long, Lasithi attracts many tourists. Mass tourism is served by places like Vai, Agios Nikolaos and the island of Chrissi. More off-beat tourism can be found in villages on the south coast like Myrtos, Makrys Gialos or Makrigialos, Xerokambos and Koutsouras. Lasithi is home to a number of ancient remains. Vasiliki, Fournou Korifi, Pyrgos, Zakros and Gournia are ruin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itanos
Itanos ( el, Ίτανος) is a municipal unit (demotike enoteta) of the municipality (demos} Siteia in the Lasithi regional unit, eastern Crete, Greece. A former municipality itself, it was included in Siteia as part of the 2011 local government reform. The municipal unit has an area of . The population was 2,164 in 2011, the time of the reorganization. The seat of the municipality was in Palaikastro, but now all municipal units are administered from the municipal seat, Siteia. Until 2017 Itanos comprised four local communities (topika koinoteta): Palaikastro, Karydi, Zakros, and Mitato (Μητάτο). Subsequently by Presidential Decree No. 70/207, on recommendation of the Minister of the Interior, and approval by Sitia and Palaikastro, Mitato was abolished, due to its seriously declining population (being a few mountain communities) and its settlements were turned over to Palaikastro. Etymological speculations Unlike most Greek demes (municipalities) Itanos did not have a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minoan Civilization
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450BC until it ended around 1100BC, during the early Greek Dark Ages, part of a wider bronze age collapse around the Mediterranean. It represents the first advanced civilization in Europe, leaving behind a number of massive building complexes, Minoan art, sophisticated art, and writing systems. Its economy benefited from a network of trade around much of the Mediterranean. The civilization was rediscovered at the beginning of the 20th century through the work of British archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans. The name "Minoan" derives from the mythical Minos, King Minos and was coined by Evans, who identified the site at Knossos with the labyrinth of the Minotaur. The Minoan civilization has been described as the earliest of its kind in Europe, and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roussolakkos
Roussolakkos is the site of a Minoan city, located near Palekastro, Crete. The Bronze Age town was occupied from Early Minoan IIA to Late Minoan IIIB, and its remains are relatively well preserved. A later Greek temple to Diktaian Zeus was built at the nearby Elaea promontory. In Greek mythology, the site was regarded as the birthplace of ''Diktaian Zeus''. and the location where Jason and the Argonauts confronted Talos, the man of bronze, a generation before the Trojan War. Bronze age settlement The earliest written records documenting the worship of Diktaian Zeus at Roussolakkos come from the Mycenaean Greek Linear B archives at Knossos and date to the close of the Cretan Bronze Age (ca. 1300 BC), however, sacred art and architecture dating from all periods have been found, suggesting that the site was hallowed throughout its history. Among the most beautiful artifacts attesting the worship of Diktaian Zeus is a unique gold and ivory statuette of the god made ca. 1500 BC. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palekastro
Palaikastro or Palekastro ( el, Παλαίκαστρο, officially el, Παλαίκαστρον), with the Godart and Olivier Cretan hieroglyphs are a hieroglyphic writing system used in early Bronze Age Crete, during the Minoan era. They predate Linear A by about a century, but the two writing systems continued to be used in parallel for most of their history. , they ... abbreviation PK, is a thriving town, geographic heir to a long line of settlements extending back into prehistoric times, at the east end of the Mediterranean island Crete. The Kallikratis Programme implemented starting 2011 made the town into a local community (topiki koinoteta) under jurisdiction of the next-highest levels, chained as follows: municipal unit (demotike enoteta) Itanos, municipality (demos) Sitia, regional unit (periphereiakes enotetas) Lasithi, region (periphereia) Crete. Until 2017 Palaikastro shared Itanos with Karydi, Itanos, Karydi, Zakros, and Mitato (Μητάτο). The latter was lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasa
Elasa ( el, Ελάσα) is an island that can be found northeast of Crete in the Aegean Sea, about from the palm tree forest of Vai. It is rocky and uninhabited covering . Its highest point is above sea level. Administratively it comes within the Itanos municipality in Lasithi. Environmentally protected area Elasa is a neighbour of the Dionysades islands and is part of an environmentally protected area with many rare plants and animals including the Mediterranean monk seal. See also * |
Landforms Of Lasithi
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uninhabited Islands Of Crete
The list of uninhabited regions includes a number of places around the globe. The list changes year over year as human beings migrate into formerly uninhabited regions, or migrate out of formerly inhabited regions. List As a group, the list of uninhabited places are called the "nonecumene". This is a special geography term which means the uninhabited area of the world. * Virtually all of the Ocean *Virtually all of Antarctica *Most of The Arctic *Most of Greenland *Most of The Sahara * Antipodes Islands * Ashmore and Cartier Islands * Bajo Nuevo Bank * Baker Island * Ball's Pyramid * Balleny Islands * Big Major Cay * Bouvet Island * Much of the interior of Brazil * Caroline Island * Clipperton Island * The semi-arid regions and deserts of Australia * Devon Island * Much of Eastern Oregon * Elephant Island * Elobey Chico * Ernst Thälmann Island * Much of Fiordland, New Zealand * Goa Island * Gough Island * Hans Island * Harmil * Hashima Island * Hatutu * Heard Island and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)
