|
Graham Passage
Murray Island, also sometimes known as Bluff Island, is an island 6 mile long lying at the south-west side of Hughes Bay, off the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. The feature has been known to sealers operating in the area since the 1820s, although it was shown on charts as part of the mainland. In 1922 the whale catcher ''Graham'' passed through the channel separating it from the mainland, proving its insularity. It was named in association with Cape Murray, the seaward extremity of the island. Important Bird Area A 98 ha ice-free site on the western side of a small peninsula on the northern coast of the island was designated the Bluff Island Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because, in 1989, it supported a breeding colony of about 180 pairs of Antarctic shag The Antarctic shag (''Leucocarbo bransfieldensis''), sometimes referred to as the imperial cormorant, king cormorant, imperial shag, blue-eyed shag or Antarctic cormorant, is the only s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
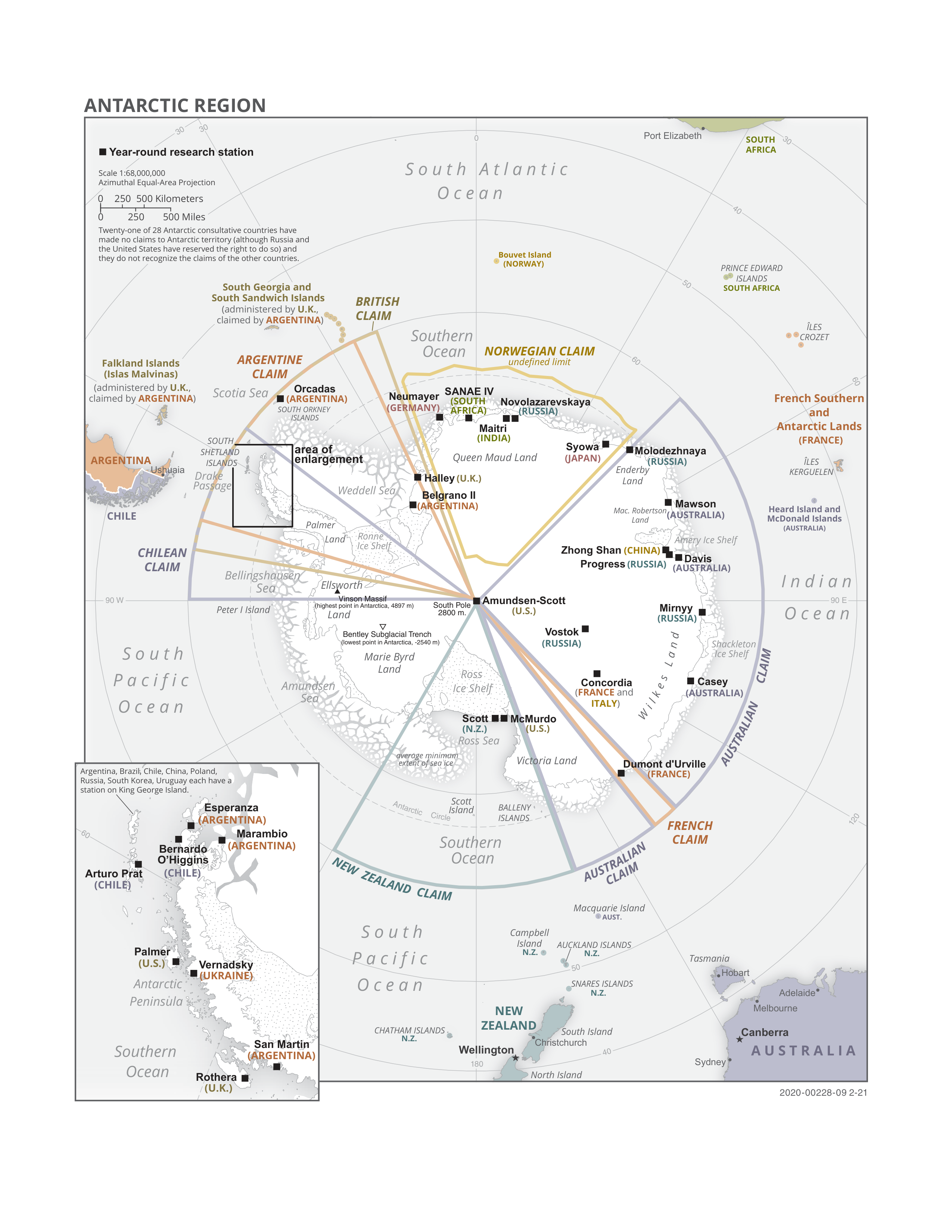
Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hughes Bay
Hughes Bay is a bay lying between Cape Sterneck and Cape Murray along the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. It is wide and lies south of Chavdar Peninsula and north of Pefaur (Ventimiglia) Peninsula, indenting the Danco Coast on the west side of Graham Land for . History The name has appeared on maps for over 100 years, and commemorates Edward Hughes, master of the ''Sprightly'', a sealing vessel owned by the London whaling company Samuel Enderby & Sons, which explored in this area in 1824–25. Hughes Bay may have been site of the first landing on the Antarctic mainland, by sealers from the U.S. sealing vessel ''Cecilia'' under Captain John Davis on February 7, 1821. SCAR |
Graham Land
Graham Land is the portion of the Antarctic Peninsula that lies north of a line joining Cape Jeremy and Cape Agassiz. This description of Graham Land is consistent with the 1964 agreement between the British Antarctic Place-names Committee and the US Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names, in which the name "Antarctic Peninsula" was approved for the major peninsula of Antarctica, and the names Graham Land and Palmer Land for the northern and southern portions, respectively. The line dividing them is roughly 69 degrees south. Graham Land is named after Sir James R. G. Graham, First Lord of the Admiralty at the time of John Biscoe's exploration of the west side of Graham Land in 1832. It is claimed by Argentina (as part of Argentine Antarctica), Britain (as part of the British Antarctic Territory) and Chile (as part of the Chilean Antarctic Territory). Graham Land is the closest part of Antarctica to South America. Thus it is the usual destination for small ships taking paying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Hunting
Seal hunting, or sealing, is the personal or commercial hunting of seals. Seal hunting is currently practiced in ten countries: United States (above the Arctic Circle in Alaska), Canada, Namibia, Denmark (in self-governing Greenland only), Iceland, Norway, Russia, Finland and Sweden. Most of the world's seal hunting takes place in Canada and Greenland. The Canadian Department of Fisheries and Oceans (DFO) regulates the seal hunt in Canada. It sets quotas (total allowable catch – TAC), monitors the hunt, studies the seal population, works with the Canadian Sealers' Association to train sealers on new regulations, and promotes sealing through its website and spokespeople. The DFO set harvest quotas of over 90,000 seals in 2007; 275,000 in 2008; 280,000 in 2009; and 330,000 in 2010. The actual kills in recent years have been less than the quotas: 82,800 in 2007; 217,800 in 2008; 72,400 in 2009; and 67,000 in 2010. In 2007, Norway claimed that 29,000 harp seals were killed, Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Murray, Graham Land
Cape Murray is a cape forming the western end of Murray Island just off the west coast of Pefaur (Ventimiglia) Peninsula in Graham Land, Antarctica, separating Hughes Bay to the northeast from Charlotte Bay Charlotte Bay is a bay on the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula indenting the west coast of Graham Land in a southeast direction for , between Reclus Peninsula and Cape Murray. Its head is fed by the glaciers Nobile, Bozhinov, Krebs, We ... to the south. First charted by the 1897-99 Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Lt. Adrien de Gerlache, and considered at the time as joined to the mainland. Named by Gerlache, presumably for Sir John Murray, British marine zoologist and oceanographer, an ardent advocate of Antarctic research. Location Cape Murray is located at . British mapping in 1978. Map * British Antarctic Territory. Scale 1:200000 topographic map. DOS 610 Series, Sheet W 64 60. Directorate of Overseas Surveys, Tolworth, UK, 1978. References SCAR Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations. IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife International. There are over 13,000 IBAs worldwide. These sites are small enough to be entirely conserved and differ in their character, habitat or ornithological importance from the surrounding habitat. In the United States the Program is administered by the National Audubon Society. Often IBAs form part of a country's existing protected area network, and so are protected under national legislation. Legal recognition and protection of IBAs that are not within existing protected areas varies within different countries. Some countries have a National IBA Conservation Strategy, whereas in others protection is completely lacking. History In 1985, following a specific request from the European Economic Community, Birdlife International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding important sites for birds, maintaining and restoring key bird habitats, and empowering conservationists worldwide. It has a membership of more than 2.5 million people across 116 country partner organizations, including the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, the Wild Bird Society of Japan, the National Audubon Society and American Bird Conservancy. BirdLife International has identified 13,000 Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas and is the official International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Red List authority for birds. As of 2015, BirdLife International has established that 1,375 bird species (13% of the total) are threatened with extinction ( critically endangered, endangered or vulnerable). BirdLife International p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Colony
A bird colony is a large congregation of individuals of one or more species of bird that nest or roost in proximity at a particular location. Many kinds of birds are known to congregate in groups of varying size; a congregation of nesting birds is called a breeding colony. Colonial nesting birds include seabirds such as auks and albatrosses; wetland species such as herons; and a few passerines such as weaverbirds, certain blackbirds, and some swallows. A group of birds congregating for rest is called a communal roost. Evidence of colonial nesting has been found in non- neornithine birds ( Enantiornithes), in sediments from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of Romania. Variations on colonial nesting in birds Approximately 13% of all bird species nest colonially. Nesting colonies are very common among seabirds on cliffs and islands. Nearly 95% of seabirds are colonial, leading to the usage, seabird colony, sometimes called a rookery. Many species of terns nest in colonie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Shag
The Antarctic shag (''Leucocarbo bransfieldensis''), sometimes referred to as the imperial cormorant, king cormorant, imperial shag, blue-eyed shag or Antarctic cormorant, is the only species of the cormorant family found in the Antarctic. It is sometimes considered conspecific with the Imperial shag (''Leucocarbo atriceps''). Description The adult Antarctic shag is about 75–77 cm tall, has a wingspan of 124 cm, and weighs 1.5-3.5 kg. When looking at individuals within this species, the most defining characteristic is the warty yellow caruncle found on the forehead. Additionally, the blue "eye", which is actually blue skin surrounding the eye, is a distinct trait that stands out. The head, wings, and outside of the thighs are black. While the underparts and central back are white. White is also found on the wing bars that line the upper wing. The bill is dark ranging from brown to yellow. As the bill hooks, the lower mandible becomes lighter. The species has nak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islands Of Graham Land
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |