|
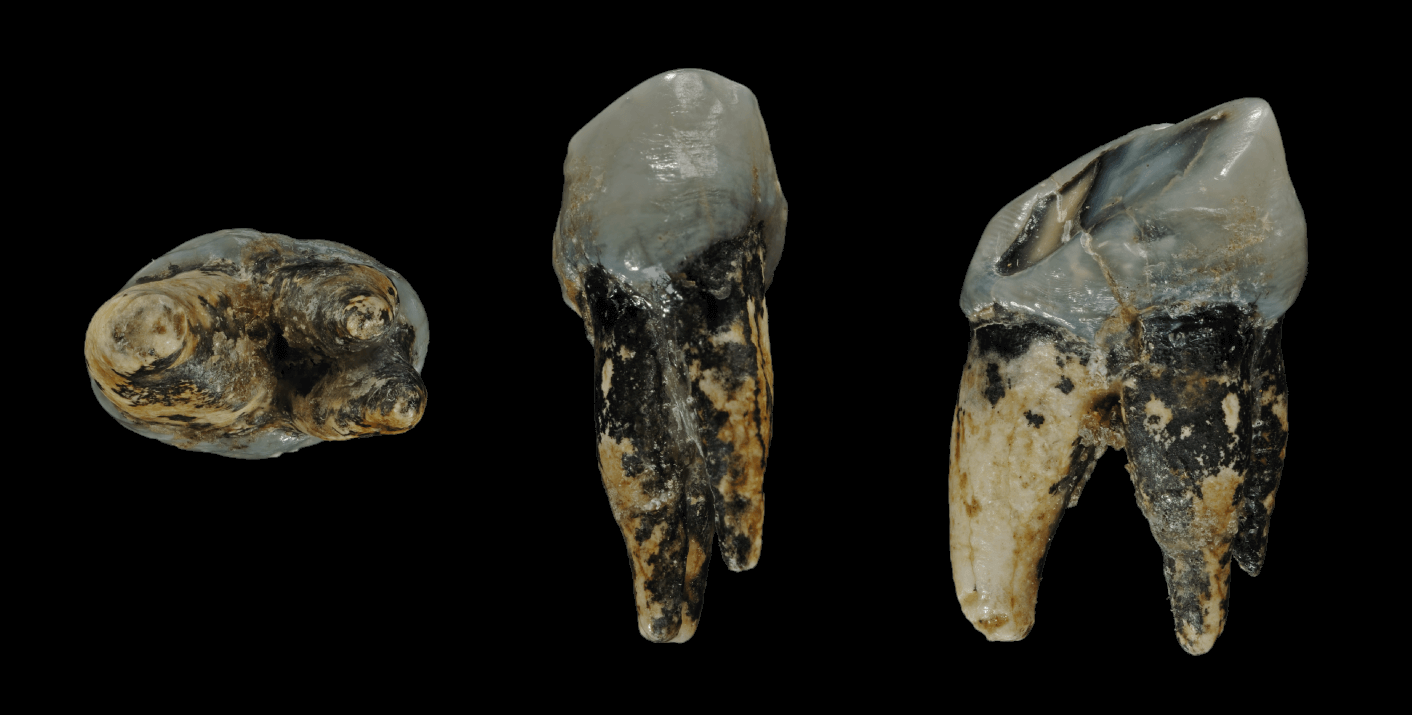
Graecopithecus Tooth
''Graecopithecus'' is an extinct species of Hominidae, hominid that lived in southeast Europe during the late Miocene around 7.2 million years ago. Originally identified by a single Mandible, lower jaw bone bearing a Molar teeth, molar tooth found in Pyrgos Vasilissis, Athens, Greece, in 1944, other tooth specimens were discovered from Azmaka quarry in Bulgaria in 2012. With only little and badly preserved materials to reveal its nature, it is considered as "the most poorly known European Miocene Ape, hominoids." The creature was popularly nicknamed 'El Graeco' (word play on the Spanish painter El Greco) by scientists. In 2017, an international team of palaeontologists led by Madelaine Böhme of the Eberhard Karls University, Tübingen, Eberhard-Karls-University Tübingen, Germany, published a detailed analysis of the teeth and age of the specimens, and came to the conclusion that it could be the oldest hominin, meaning that it could be the oldest direct ancestors of humans after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Priority
270px, '' valid name. Priority is a fundamental principle of modern botanical nomenclature and zoological nomenclature. Essentially, it is the principle of recognising the first valid application of a name to a plant or animal. There are two aspects to this: # The first formal scientific name given to a plant or animal taxon shall be the name that is to be used, called the valid name in zoology and correct name in botany (principle of synonymy). # Once a name has been used, no subsequent publication of that name for another taxon shall be valid (zoology) or validly published (botany) (principle of homonymy). Note that nomenclature for botany and zoology is independent, and the rules of priority regarding homonyms operate within each discipline but not between them. There are formal provisions for making exceptions to the principle of priority under each of the Codes. If an archaic or obscure prior name is discovered for an established taxon, the current name can be declared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sivapithecus
''Sivapithecus'' () (syn: ''Ramapithecus)'' is a genus of extinct apes. Fossil remains of animals now assigned to this genus, dated from 12.2 million years old in the Miocene, have been found since the 19th century in the Siwalik Hills The Sivalik Hills, also known as the Shivalik Hills and Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas that stretches over about from the Indus River eastwards close to the Brahmaputra River, spanning the northern parts of the Indian ... of the Indian subcontinent as well as in Kutch. Any one of the species in this genus may have been the ancestor to the modern orangutans. Some early discoveries were given the separate names ''Ramapithecus'' (Rama's Ape) and ''Bramapithecus'' (Brahma's Ape), and were thought to be possible ancestors of humans. Discovery The first incomplete specimens of ''Sivapithecus'' were found in northern India in the late 19th century. Another find was made in Nepal on the bank of the Tinau River situated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouranopithecus Macedoniensis
''Ouranopithecus macedoniensis'' is a prehistoric species of ''Ouranopithecus'' from the Late Miocene of Greece. See more detail at ''Ouranopithecus''. This species is known from three localities in Northern Greece. The type location is Ravin de la Pluie. The other localities are Chalkidiki and Xirochori. It is known from a large collection of cranial fossils and few postcranial. The material has been dated to the late Miocene 9.6 – 8.7 million years old, so slightly earlier than '' O. turkae''. To some this suggests ''O. turkae'' is the direct descendant of ''O. macedoniensis'', although it is generally accepted that they are sister taxa. Etymology The specific epithet ''macedoniensis'' is due to the holotype fossil's discovery location in Macedonia, Greece. Habitat Examination of dental remains of ''O. macedoniensis'' and associated bovid species indicate a habitat of low tree cover and a rich herbaceous layer. Morphology ''O. macedoniensis'' had a large, broad face with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-dimensional Matching
In the mathematical discipline of graph theory, a 3-dimensional matching is a generalization of bipartite matching (also known as 2-dimensional matching) to 3-partite hypergraphs, which consist of hyperedges each of which contains 3 vertices (instead of edges containing 2 vertices in a usual graph). 3-dimensional matching, often abbreviated as 3DM, is also the name of a well-known computational problem: finding a largest 3-dimensional matching in a given hypergraph. 3DM is one of the first problems that were proved to be NP-hard. Definition Let ''X'', ''Y'', and ''Z'' be finite sets, and let ''T'' be a subset of ''X'' × ''Y'' × ''Z''. That is, ''T'' consists of triples (''x'', ''y'', ''z'') such that ''x'' ∈ ''X'', ''y'' ∈ ''Y'', and ''z'' ∈ ''Z''. Now ''M'' ⊆ ''T'' is a 3-dimensional matching if the following holds: for any two distinct triples (''x''1, ''y''1, ''z''1) ∈ ''M'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Microtomography
X-ray microtomography, like tomography and X-ray computed tomography, uses X-rays to create cross-sections of a physical object that can be used to recreate a virtual model ( 3D model) without destroying the original object. The prefix ''micro-'' (symbol: µ) is used to indicate that the pixel sizes of the cross-sections are in the micrometre range. These pixel sizes have also resulted in the terms high-resolution X-ray tomography, micro–computed tomography (micro-CT or µCT), and similar terms. Sometimes the terms high-resolution CT (HRCT) and micro-CT are differentiated, but in other cases the term high-resolution micro-CT is used. Virtually all tomography today is computed tomography. Micro-CT has applications both in medical imaging and in industrial computed tomography. In general, there are two types of scanner setups. In one setup, the X-ray source and detector are typically stationary during the scan while the sample/animal rotates. The second setup, much more like a cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enamel Organ
The enamel organ, also known as the dental organ, is a cellular aggregation seen in a developing tooth and it lies above the dental papilla. The enamel organ which is differentiated from the primitive oral epithelium lining the stomodeum.The enamel organ is responsible for the formation of enamel, initiation of dentine formation, establishment of the shape of a tooth's crown, and establishment of the dentoenamel junction. The enamel organ has four layers; the inner enamel epithelium, outer enamel epithelium, stratum intermedium, and the stellate reticulum. The dental papilla, the differentiated ectomesenchyme deep to the enamel organ, will produce dentin and the dental pulp. The surrounding ectomesenchyme tissue, the dental follicle, is the primitive cementum, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone beneath the tooth root. The site where the internal enamel epithelium and external enamel epithelium coalesce is the cervical root, important in proliferation of the dental root. Toot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen's Tower (Serpieri)
Queen's Tower ( el, Πύργος Βασιλίσσης, ''Pyrgos Vasilissis'') is a former royal estate near Athens, Greece. The estate, consisting of 200 hectares (494 acres), was purchased by King Otto, the first king of modern Greece. He built there a small neogothic castle for his wife, Queen Amalia. The architecture resembles Hohenschwangau castle in Bavaria, built for Maximilian II of Bavaria, the brother of King Otto. As the castle is only one tower, it is called the Queen's Tower. After the abdication of King Otto, the estate was sold to the Serpieri family, who still own it. They have a dairy farm and wineyard on the estate. The wines bottled on the estate are called "Tour la Reine" (French for Queen's Tower). A nearby station of the Proastiakos The Proastiakos ( el, Προαστιακός; "suburban") is Greece's Commuter rail service, run by Hellenic Train, on rail infrastructure owned by the Hellenic Railways Organisation (OSE) (lines) and GAIAOSE (buildings and Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graecopithecus Tooth
''Graecopithecus'' is an extinct species of Hominidae, hominid that lived in southeast Europe during the late Miocene around 7.2 million years ago. Originally identified by a single Mandible, lower jaw bone bearing a Molar teeth, molar tooth found in Pyrgos Vasilissis, Athens, Greece, in 1944, other tooth specimens were discovered from Azmaka quarry in Bulgaria in 2012. With only little and badly preserved materials to reveal its nature, it is considered as "the most poorly known European Miocene Ape, hominoids." The creature was popularly nicknamed 'El Graeco' (word play on the Spanish painter El Greco) by scientists. In 2017, an international team of palaeontologists led by Madelaine Böhme of the Eberhard Karls University, Tübingen, Eberhard-Karls-University Tübingen, Germany, published a detailed analysis of the teeth and age of the specimens, and came to the conclusion that it could be the oldest hominin, meaning that it could be the oldest direct ancestors of humans after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopithecus
''Mesopithecus'' ("middle monkey" for being between '' Hylobates'' and ''Semnopithecus'' in build) is an extinct genus of Old World monkey that lived in Europe and Asia 7 to 5 million years ago. ''Mesopithecus'' resembled a modern macaque, with a body length of about . It was adapted to both walking and climbing, possessing a slender body with long, muscular limbs and flexible fingers. Its teeth suggest that it primarily ate soft leaves and fruit. It was once thought that these extinct monkeys might be an ancestor of the grey langur, but a study in 2004 suggested that they are more closely related to the snub-nosed monkeys and douc The doucs or douc langurs make up the genus ''Pygathrix''. They are colobine Old World monkeys, native to Southeast Asia, which consists of these 3 species: red-shanked douc, black-shanked douc, and gray-shanked douc. Description The doucs ...s. Gallery Mesopithecus pentelici.JPG, ''Mesopithecus pentelici'' skulls Les ancêtres de nos ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |