|
Gourdou-Leseurre L.2
Gourdou-Leseurre was a French aircraft manufacturer whose founders were Charles Edouard Pierre Gourdou and Jean Adolphe Leseurre. History Engineers Jean Leseurre and his brother-in-law Charles Gourdou founded the ''Établissements Gourdou-Leseurre'' in Saint Maur-des-Fossés, southeast of Paris in 1921. The factory assembled military aircraft under license, such as the Breguet 14, until Gourdou and Leseurre began building their own aircraft as main designers. Between 1925 and 1928, Gourdou-Leseurre was taken over by the Ateliers et Chantiers de la Loire shipyard, together with Loire and Loire-Nieuport. The aircraft produced at that time by the Gourdou-Leseurre company were known as 'Loire-Gourdou', carrying the LGL denomination instead of GL. In the 1930s strong disagreements developed between Charles Gourdou and Jean Adolphe Leseurre. This eventually led to a break-up of their professional relationship and the demise of the company in 1934. Aircraft The company was activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Maur-des-Fossés
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but some are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and consequently a public cult of veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. While the English word ''saint'' originated in Christianity, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special holiness that many religions attribute to certain people", referring to the Jewish tzadik, the Islamic walī, the Hindu rishi o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gourdou-Leseurre GL-430
The Gourdou-Leseurre GL.30 was a racing aircraft built in France in 1920 which formed the basis for a highly successful family of fighter aircraft based on the same design. Development The GL-30 was a parasol-wing monoplane with retractable undercarriage and a Bristol Jupiter engine. Like most of Gordou-Lesserre's earlier aircraft, it was a parasol wing design but its planform was trapezoidal rather than rectangular. In 1923 it flew the Coupe Beaumont course at an impressive . The GL.30 was the basis of a new fighter, the GL.31, which had a greater span, almost double the wing area, a fixed undercarriage, and a Gnome-Rhône 9A engine. It was armed with four machine guns, two in the forward fuselage and two in the wings. The GL. 31 was not flown until 1926 and then abandoned, overtaken by the GL.32, the company's entry in a 1923 ''Aéronautique Militaire'' competition to select a new fighter. It returned to a rectangular plan wing. Operational history By the time this prototype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gourdou-Leseurre GL-821 HY
The Gourdou-Leseurre GL-820 HY family of four-seat single-engined floatplanes were designed and built in France during the latter half of the 1930s by Gourdou-Leseurre. The GL-820 HY and GL-821 HY 02 were shipborne reconnaissance / observation aircraft, while the sole GL-821 HY was built as a torpedo carrier. Design and development The Gl-820 and GL-821 were low-wing monoplane floatplanes with four tandem open cockpits, (the Cockpits on the GL-821 HY 02 were enclosed). The wings, tailplanes and floats were all supported by a system of streamlined struts. Variants ;GL-820 HY:The initial reconnaissance aircraft prototype, powered by a Hispano-Suiza 9Vb driving a two-bladed fixed-pitch wooden propeller. ;GL-821 HY:The second aircraft built as a torpedo carrier, powered by a Gnome & Rhône 9Kfr. ;GL-821 HY 02:The third aircraft, powered by a Gnome & Rhône 9Kfr A gnome is a mythological creature and diminutive spirit in Renaissance magic and alchemy, first introduced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
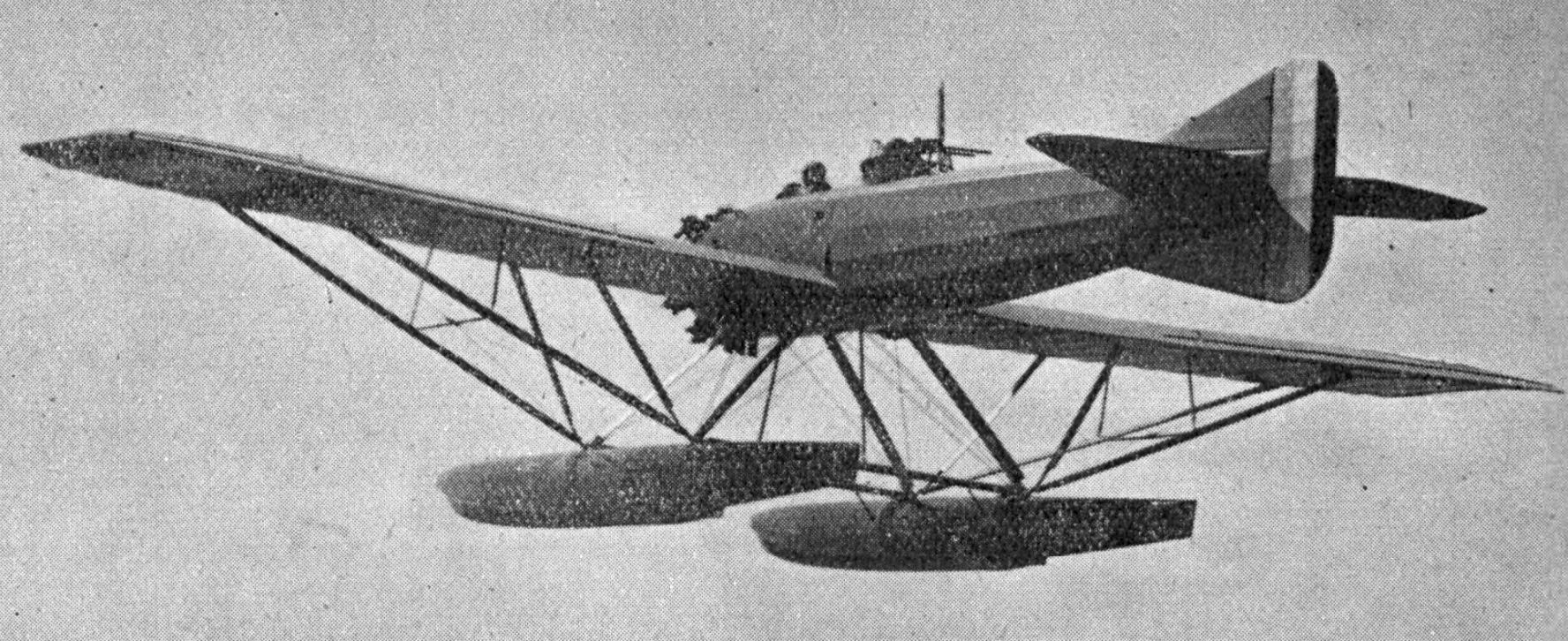
Gourdou-Leseurre GL-813 HY
The Gourdou-Leseurre GL-812 HY was a 3-seat reconnaissance floatplane, built by Gourdou-Leseurre. Development The prototype, called L-2, was built in 1926-27. It has a steel tube fuselage, and rectangular wooden wing. The tail was two fins, one above and one below the fuselage. The entire plane was fabric covered, except the Gnome-Rhône 9A Jupiter engine, which was left uncowled. The prototype was flown to Copenhagen, and demonstrated there to several countries. Six prototype L-3s were constructed. They had a larger Jupiter, steel spars instead of wood, and stronger struts, allowing for shipboard catapult launching. After successfully testing the L-3, the French navy ordered 14 production GL-810 HY aircraft. The first production 810 HY flew on 23 September 1930, taking off from the Seine at Les Mureaux. In 1931, 20 GL-811 HYs were ordered, for operation from the seaplane carrier Commandant Teste and from 1933 to 1934 twenty-nine GL-812 HYs and thirteen GL-813 HYs were order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gourdou-Leseurre GL-633
The Gourdou-Leseurre GL.30 was a racing aircraft built in France in 1920 which formed the basis for a highly successful family of fighter aircraft based on the same design. Development The GL-30 was a parasol-wing monoplane with retractable undercarriage and a Bristol Jupiter engine. Like most of Gordou-Lesserre's earlier aircraft, it was a parasol wing design but its planform was trapezoidal rather than rectangular. In 1923 it flew the Coupe Beaumont course at an impressive . The GL.30 was the basis of a new fighter, the GL.31, which had a greater span, almost double the wing area, a fixed undercarriage, and a Gnome-Rhône 9A engine. It was armed with four machine guns, two in the forward fuselage and two in the wings. The GL. 31 was not flown until 1926 and then abandoned, overtaken by the GL.32, the company's entry in a 1923 ''Aéronautique Militaire'' competition to select a new fighter. It returned to a rectangular plan wing. Operational history By the time this prototype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gourdou-Leseurre GL-51
The Gourdou-Leseurre GL.50, also known as the Gourdou-Leseurre Type F, was a French fighter prototype of the early 1920s. Development In April 1919, General Duval of the French Armée de l'Air set out for the replacement of two of the principal categories of aircraft within the air force - CAP2 (''Chasse, Armée, Biplace'' meaning 'armed two-seat fighter') and CAN2 (''Chasse, Armée, Nuit, Biplace'' meaning 'armed two-seat night fighter'). Gourdou-Leseurre put forward the GL-50 as a submission for the CAP2 category (despite the fact that this categorisation system was removed in 1920). Its 300 hp Hispano-Suiza engine was intended to be fitted with a supercharger In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced indu ..., however this was not fitted, despite the fact it would have incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gourdou-Leseurre GL-50
The Gourdou-Leseurre GL.50, also known as the Gourdou-Leseurre Type F, was a French fighter prototype of the early 1920s. Development In April 1919, General Duval of the French Armée de l'Air set out for the replacement of two of the principal categories of aircraft within the air force - CAP2 (''Chasse, Armée, Biplace'' meaning 'armed two-seat fighter') and CAN2 (''Chasse, Armée, Nuit, Biplace'' meaning 'armed two-seat night fighter'). Gourdou-Leseurre put forward the GL-50 as a submission for the CAP2 category (despite the fact that this categorisation system was removed in 1920). Its 300 hp Hispano-Suiza engine was intended to be fitted with a supercharger, however this was not fitted, despite the fact it would have increased its performance drastically. It was of wooden construction, with a long-span untapered wing, considered unusual at the time, that feature being more in line with single-seat aircraft design, as were the wing bracing struts. Operational history Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |