|
Goniothalamus Velutinus
''Goniothalamus velutinus'' is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Borneo. Herbert Airy Shaw, the English botanist who first formally described the species, named it after the dense velvety ( in Latin) hair on its branchlets and petioles. Description It is a tree reaching 6 meters in height. Its smooth, dark grey to black, young branches are covered in dense, rust-colored, velvety hairs. Its cylindrical petioles are 1.3-2.2 by 0.5-0.8 centimeters and covered in dense, rust-colored, velvety hairs. Its papery to leathery, oblong to lance-shaped leaves are 24-60 by 6.5-12.5 centimeters with rounded apices that end in an abrupt, tapering tip and pointed bases. The leaves have margins that are curved toward underside with upper surfaces that are brown to green and covered in fine hairs, and lower surfaces that are green to brown and covered in dense, matted, woolly hairs. The leaf midribs are sunken, grooved and covered with hair on the upper surface; rais ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Kenneth Airy Shaw
Herbert Kenneth Airy Shaw (7 April 1902 – 1985) was a notable English botanist and classicist. Airy Shaw was born at The Mount, Grange Road, Woodbridge, Suffolk to a father serving as Second Master at the Woodbridge Grammar School and a mother descended from George Biddell Airy, Astronomer Royal (1835–1881). In 1921 he entered Corpus Christi College, Cambridge University, to read classics, but he switched to natural sciences, taking his degree in 1924 and finishing in 1925, then taking a position at Kew Gardens. He became an expert on tropical Asian botany and on entomology Entomology () is the science, scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology. In the past the term "insect" was less specific, and historically the definition of entomology would also include the study of animals in other arthropod groups, such .... Selected works * ''The Euphorbiaceae of Borneo'', Her Majesty's Stationery Office, 1975. . * ''The Euphorbiaceae of New Guinea'', Her Majesty's Station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stigma (botany)
The stigma () is the receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. Description The stigma, together with the style and ovary (typically called the stigma-style-ovary system) comprises the pistil, which is part of the gynoecium or female reproductive organ of a plant. The stigma itself forms the distal portion of the style, or stylodia, and is composed of , the cells of which are receptive to pollen. These may be restricted to the apex of the style or, especially in wind pollinated species, cover a wide surface. The stigma receives pollen and it is on the stigma that the pollen grain germinates. Often sticky, the stigma is adapted in various ways to catch and trap pollen with various hairs, flaps, or sculpturings. The pollen may be captured from the air (wind-borne pollen, anemophily), from visiting insects or other animals ( biotic pollination), or in rare cases from surrounding water (hydrophily). Stigma can vary from long and sle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Borneo
The flora of Borneo include 15 species of dicot tree, 37 species of non-tree dicot and 49 species of monocot endemic to the rich forest of Brunei Darussalam. Borneo is also home to the world's largest flower, the "corpse flower" (''Rafflesia arnoldii''), which can reach nearly in diameter and up to in weight. Borneo is the third largest island in the world and is divided between three countries: Brunei in the north, the Malaysian constituent states of Sarawak and Sabah, and the 5 Kalimantan provinces of Indonesia (note that in Indonesian, "Kalimantan" refers to the entire island of Borneo). The tallest tropical trees of the world are in Borneo. They are in the family Dipterocarpaceae. See also *Biodiversity of Borneo The island of Borneo is located on the Sunda Shelf, which is an extensive region in Southeast Asia of immense importance in terms of biodiversity, biogeography and phylogeography of fauna and flora that had attracted Alfred Russel Wallace and oth ... * Fauna of Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goniothalamus
''Goniothalamus'' is one of the largest palaeotropical genera of plant in family Annonaceae. Iban people beliefs It is believed by the Iban people that when burnt it repels mosquitoes because of its strong scent and thick smoke it creates. It is also believed to repel evil spirits, it is mostly burned during the night and on days where it is both hot and rainy. Species list It contains the following species (divided according to Floristic Region): Fijian Region ( Fiji and New Hebrides) * ''Goniothalamus monospermus'' (A.Gray) R.M.K.Saunders Indian Region (India and Sri Lanka) * ''Goniothalamus gardneri'' Hook.f. & Thomson * ''Goniothalamus hookeri'' Thwaites * ''Goniothalamus rhynchantherus'' Dunn * ''Goniothalamus salicina'' Hook.f. & Thomson * ''Goniothalamus simonsii'' Hook.f. & Thomson * ''Goniothalamus thwaitesii'' Hook.f. & Thomson * ''Goniothalamus wynaadensis'' Bedd. * ''Goniothalamus meeboldii'' Craib Indochinese Region (South China extending into North Vietnam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytostatic
Cytostasis (cyto – cell; stasis – stoppage) is the inhibition of cell growth and multiplication. Cytostatic refers to a cellular component or medicine that inhibits cell division. Cytostasis is an important prerequisite for structured multicellular organisms. Without regulation of cell growth and division only unorganized heaps of cells would be possible. Chemotherapy of cancer, treatment of skin diseases and treatment of infections are common use cases of cytostatic drugs. Active hygienic products generally contain cytostatic substances. Cytostatic mechanisms and drugs generally occur together with cytotoxic ones. Activators Nitric oxide – activated macrophages produce large amounts of nitric oxide (NO), which induces both cytostasis and cytotoxicity to tumor cells both ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo''. Nitric oxide-induced cytostasis targets ribonucleotide reductase by rapid and reversible inhibition. However, other studies show there could be other targets that are res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteus Mirabilis
''Proteus mirabilis'' is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It shows swarming motility and urease activity. ''P. mirabilis'' causes 90% of all ''Proteus'' infections in humans. It is widely distributed in soil and water. ''Proteus mirabilis'' can migrate across the surface of solid media or devices using a type of cooperative group motility called swarming. ''Proteus mirabilis'' is most frequently associated with infections of the urinary tract, especially in complicated or catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Diagnosis An alkaline urine sample is a possible sign of ''P. mirabilis''. It can be diagnosed in the lab due to characteristic swarming motility, and inability to metabolize lactose (on a MacConkey agar plate, for example). Also ''P. mirabilis'' produces a very distinct fishy odor. Disease This rod-shaped bacterium has the ability to produce high levels of urease, which hydrolyzes urea to ammonia (NH3), so makes the urine more a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
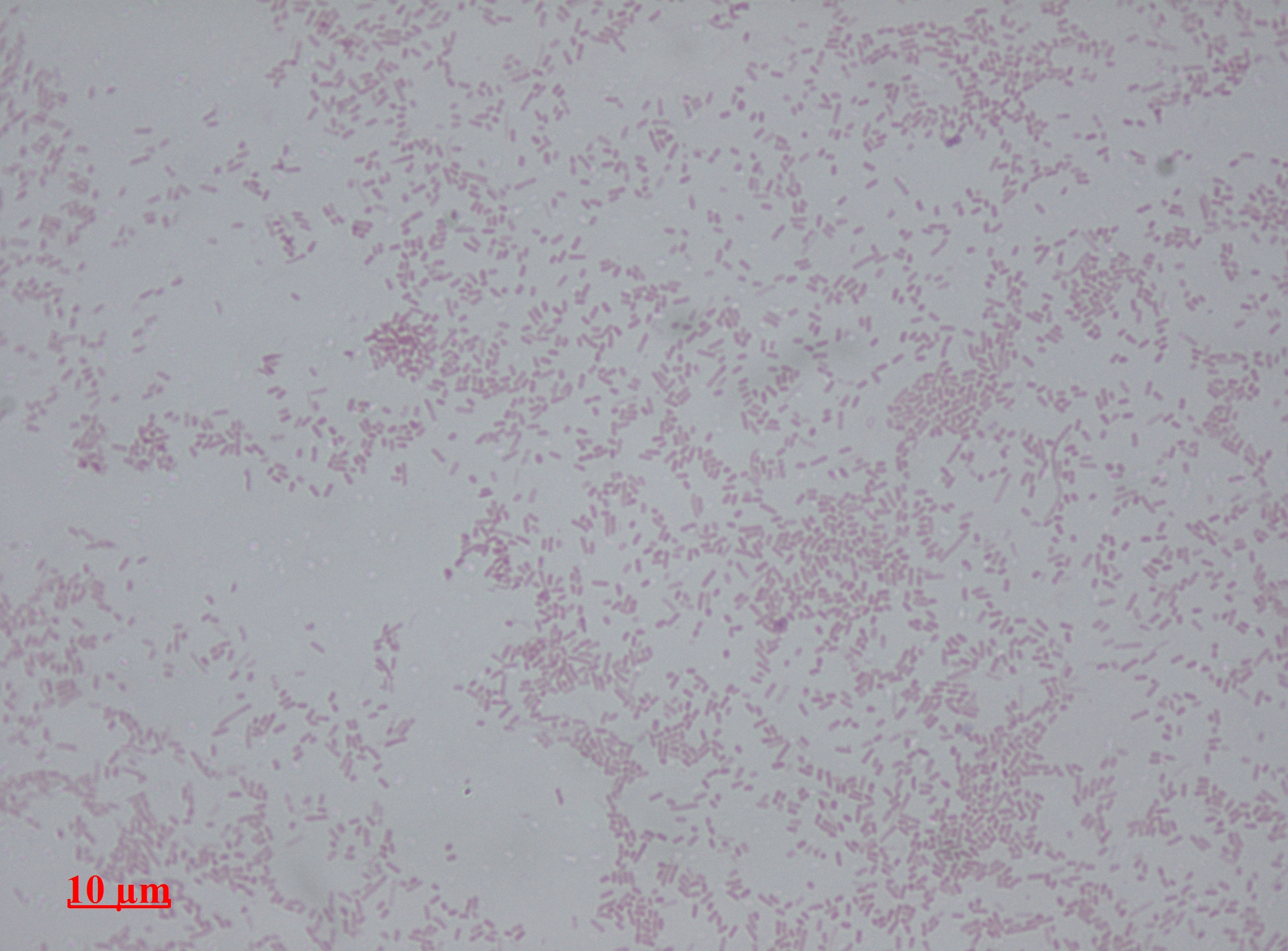
Streptococcus Mutans
''Streptococcus mutans'' is a facultatively anaerobic, gram-positive coccus (round bacterium) commonly found in the human oral cavity and is a significant contributor to tooth decay. It is part of the " streptococci" (plural, non-italic lowercase), an informal general name for all species in the genus ''Streptococcus''. The microbe was first described by James Kilian Clarke in 1924. This bacterium, along with the closely related species ''Streptococcus sobrinus'', can cohabit the mouth: Both contribute to oral disease, and the expense of differentiating them in laboratory testing is often not clinically necessary. Therefore, for clinical purposes they are often considered together as a group, called the mutans streptococci (plural, non-italic due to its being an informal group name). This grouping of similar bacteria with similar tropism can also be seen in the viridans streptococci, another group of ''Streptococcus'' species. Ecology ''S. mutans'' is naturally present in the hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
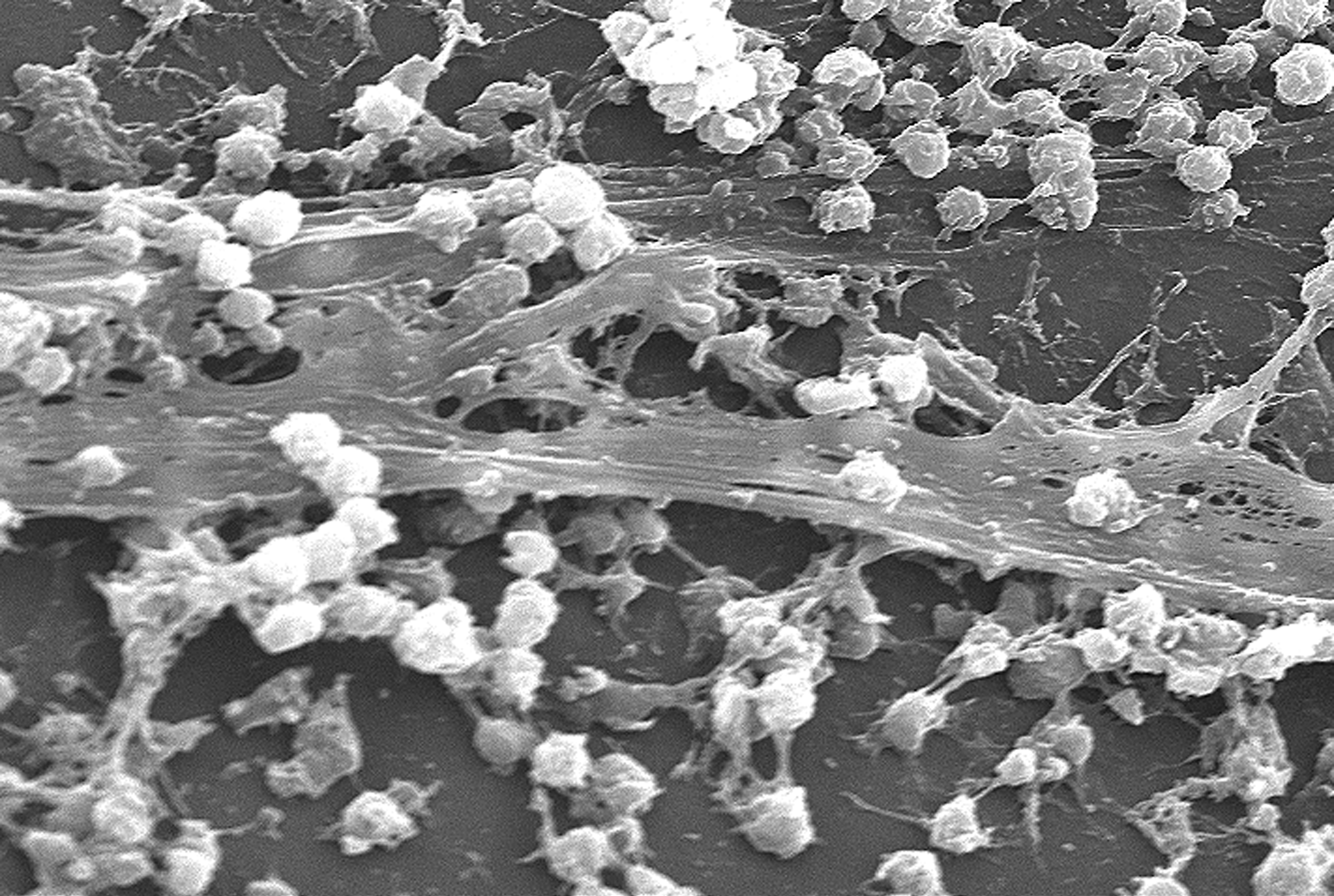
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms can form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubricants, to prevent oxidation, and to foods to prevent spoilage, in particular the rancidification of oils and fats. In cells, antioxidants such as glutathione, mycothiol or bacillithiol, and enzyme systems like superoxide dismutase, can prevent damage from oxidative stress. The only dietary antioxidants are vitamins A, C, and E, but the term ''antioxidant'' has also been applied to numerous other dietary compounds that only have antioxidant properties in vitro, with little evidence for antioxidant properties in vivo. Dietary supplements marketed as antioxidants have not been shown to maintain health or prevent disease in humans. History As part of their adaptation from marine life, terrestrial plants began producing non-marine antioxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynoecium
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) ''pistils'' and is typically surrounded by the pollen-producing reproductive organs, the stamens, collectively called the androecium. The gynoecium is often referred to as the "female" portion of the flower, although rather than directly producing female gametes (i.e. egg cells), the gynoecium produces megaspores, each of which develops into a female gametophyte which then produces egg cells. The term gynoecium is also used by botanists to refer to a cluster of archegonia and any associated modified leaves or stems present on a gametophyte shoot in mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. The corresponding terms for the male parts of those plants are clusters of antheridia within the androecium. Flowers that bear a gynoecium but no stamens are called ''pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamen
The stamen (plural ''stamina'' or ''stamens'') is the pollen-producing reproductive organ of a flower. Collectively the stamens form the androecium., p. 10 Morphology and terminology A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament and an anther which contains ''sporangium, microsporangia''. Most commonly anthers are two-lobed and are attached to the filament either at the base or in the middle area of the anther. The sterile tissue between the lobes is called the connective, an extension of the filament containing conducting strands. It can be seen as an extension on the dorsal side of the anther. A pollen grain develops from a microspore in the microsporangium and contains the male gametophyte. The stamens in a flower are collectively called the androecium. The androecium can consist of as few as one-half stamen (i.e. a single locule) as in ''Canna (plant), Canna'' species or as many as 3,482 stamens which have been counted in the saguaro (''Carnegiea gigantea'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |