|
Goldschmidtfjella
Goldschmidtfjella is a mountain in Oscar II Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It forms a 6 kilometer long nunatak in the glacier Osbornebreen, north of the head of St. Jonsfjorden, and reaches an altitude of 581 meters. The mountain is named after geologist and mineralogist Victor Moritz Goldschmidt. Nearby mountains are Carlsfjella to the west and Devikfjellet Devikfjellet is a mountain in Oscar II Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It is located between the glaciers Osbornebreen and Devikbreen, northeast of the head of St. Jonsfjorden, and has an altitude of 860 meters. The mountain is named after physicist ... to the east. References Mountains of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-mountain-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osbornebreen
Osbornebreen is a glacier in Oscar II Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard, Norway. It has a length of 21 kilometers, merges with the glaciers Devikbreen, Klampebreen and Vintervegen Vintervegen (Winter Road) is a glacier in Oscar II Land Oscar II Land is the land area between Isfjorden and Kongsfjorden on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The long glacier Sveabreen divides Oscar II Land from James I Land. The area is named after Osc ..., and debouches into St. Jonsfjorden. The mountain ridge Goldschmidtfjella forms a six kilometer long nunatak in the glacier. References Glaciers of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Moritz Goldschmidt
Victor Moritz Goldschmidt (27 January 1888 in Zürich – 20 March 1947 in Oslo) was a Norwegian mineralogist considered (together with Vladimir Vernadsky) to be the founder of modern geochemistry and crystal chemistry, developer of the Goldschmidt Classification of elements. Early life and education Goldschmidt was born in Zürich, Switzerland on 27 January 1888. His father, Heinrich Jacob Goldschmidt, (1857–1937) was a physical chemist at the Eidgenössisches Polytechnikum and his mother, Amelie Koehne (1864–1929), was the daughter of a lumber merchant. They named him Viktor after a colleague of Heinrich, Victor Meyer. His father's family was Jewish back to at least 1600 and mostly highly educated, with rabbis, judges, lawyers and military officers among their numbers. As his father's career progressed, the family moved first to Amsterdam in 1893, to Heidelberg in 1896, and finally to Kristiania (later Oslo), Norway in 1901, where he took over the physical chemist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
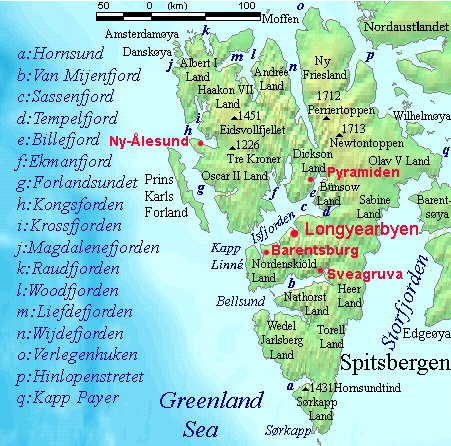
Oscar II Land
Oscar II Land is the land area between Isfjorden and Kongsfjorden on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The long glacier Sveabreen divides Oscar II Land from James I Land. The area is named after Oscar II of Sweden. Older name variants are ''Oscar II's Land'' and ''Terre Oscar II''. The Hofgaardtoppen Hofgaardtoppen is a mountain in Oscar II Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the no ... mountain is the highest peak in Oscar II Land. References Geography of Svalbard Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlsfjella
Carlsfjella is a mountain ridge in Oscar II Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The ridge has a length of 14 kilometers, is located between St. Jonsfjorden and Løvenskioldfonna, and includes Valentinryggen, Patronen, Knausen and Haraldfjellet. The ridge is named after land owner Carl Otto Løvenskiold Carl Otto Løvenskiold (23 December 1839 – 1 October 1916) was a Norwegian naval officer, business executive and landowner. He served as the Norwegian prime minister in Stockholm during 1884. By birth, he is a member of Løvenskiold family, L .... References Mountains of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-mountain-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devikfjellet
Devikfjellet is a mountain in Oscar II Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It is located between the glaciers Osbornebreen and Devikbreen, northeast of the head of St. Jonsfjorden, and has an altitude of 860 meters. The mountain is named after physicist Olaf Devik. Nearby mountains are Krymlefjellet Krymlefjellet (The Bended Mountain) is a mountain in Oscar II Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has a height of 1,085 m.a.s.l. and is located between the mountains of Bognutane and Devikfjellet. It is separated from Devikfjellet by Devikbreen Dev ... to the north and Klampen to the south. References Mountains of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-mountain-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Polar Institute
The Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI; no, Norsk Polarinstitutt) is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Environment. The institute advises Norwegian authorities on matters concerning polar environmental management and is the official environmental management body for Norwegian activities in Antarctica. Activities The institute's activities are focused on environmental research and management in the polar regions. The NPI's researchers investigate biodiversity, climate and environmental toxins in the Arctic and Antarctic, and in this context the institute equips and organizes large-scale expeditions to both polar regions. The institute contributes to national and international climate work, and is an active contact point for the international scientific community. The institute collects and analyses data on the environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |