|
Gola People
The Gola or Gula are a West African ethnic group who share a common cultural heritage, language and history and who live primarily in western/northwestern Liberia and Eastern Sierra Leone. The Gola language is an isolate within the Niger–Congo language family. , it is spoken by about 278,000 people. The name ''Gola'' is a possible source for the name of the Gullah, a people of African origin living on the islands and coastal regions of Georgia and South Carolina, in the southeastern United States. Gola historical figures * Zolu Duma (aka King Peter) ruled the Gola and Vai areas in the early 19th century. He participated in negotiations with American settlers of Liberia in 1821. * Charles Taylor, who ruled Liberia between 1997 and 2003, is of mixed Gola and Americo-Liberian ancestry. * Ellen Johnson Sirleaf, who was Liberia's president from 2006 to 2018, whose father was Gola, and mother was mixed with Kru and German ancestry. Sande and Poro There has always been S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gola Language
Gola is a language of Liberia and Sierra Leone. It was traditionally classified as an Atlantic language, but this is no longer accepted in more recent studies. Classification Gola is not closely related to other languages and appears to form its own branch of the Niger–Congo language family. However, '' Ethnologue'' lists Gola as a Mel language. Fields (2004) classifies Gola as a Mel language most closely related to Bullom and Kisi.Fields, Edda LBefore "Baga": Settlement Chronologies of the Coastal Rio Nunez Region, Earliest Times to c.1000 CE In: ''The International Journal of African Historical Studies'', Vol. 37, No. 2 (2004), pp. 229-253. Boston University African Studies Center. Distribution According to '' Ethnologue'', Gola is spoken in widespread regions across Liberia. It is spoken in Gbarpolu County, Grand Cape Mount County, and Lofa County (between the Mano River and Saint Paul River), as well as in inland areas of Bomi County and Montserrado County Montserr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kru People
The Kru, Kroo, Krou or Kuru are a West African ethnic group who are indigenous to western Ivory Coast and eastern Liberia. They migrated and settled along various points of the West African coast, notably Freetown, Sierra Leone, but also the Ivorian and Nigerian coasts. The Kru people are a large ethnic group that is made up of several sub-ethnic groups in Liberia and Ivory Coast. These tribes include Bété, Bassa, Krumen, Guéré, Grebo, Klao, Krahn people and, Jabo people. The kru people were more valuable as traders and sailors on slave ships than as slave labor. To ensure their status as “freemen,” they initiated the practice of tattooing their foreheads and the bridge of their nose with indigo dye to distinguish them from slave labor. Part of the Grebo people were called Krumen and hired as free sailors on European ships, initially engaged in the slave trade, and then when that ended in the coastal trade in goods. The Krumen were famous for their skills in navig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gola People
The Gola or Gula are a West African ethnic group who share a common cultural heritage, language and history and who live primarily in western/northwestern Liberia and Eastern Sierra Leone. The Gola language is an isolate within the Niger–Congo language family. , it is spoken by about 278,000 people. The name ''Gola'' is a possible source for the name of the Gullah, a people of African origin living on the islands and coastal regions of Georgia and South Carolina, in the southeastern United States. Gola historical figures * Zolu Duma (aka King Peter) ruled the Gola and Vai areas in the early 19th century. He participated in negotiations with American settlers of Liberia in 1821. * Charles Taylor, who ruled Liberia between 1997 and 2003, is of mixed Gola and Americo-Liberian ancestry. * Ellen Johnson Sirleaf, who was Liberia's president from 2006 to 2018, whose father was Gola, and mother was mixed with Kru and German ancestry. Sande and Poro There has always been S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malinke
Maninka (also known as Malinke), or more precisely Eastern Maninka, is the name of several closely related languages and dialects of the southeastern Manding subgroup of the Mande language family. It is the mother tongue of the Malinké people in Guinea, where it is spoken by 3,300,000 people and is the main language in the Upper Guinea region, and in Mali, where the closely related Bambara is a national language, as well as in Liberia, Senegal, Sierra Leone and Ivory Coast, where it has no official status. It was the language of court and government during the Mali Empire. Phonology The Wudala dialect of Eastern Maninka, spoken in the central highlands of Guinea and comprehensible to speakers of all dialects in that country, has the following phonemic inventory.Mamadou Camara (1999) ''Parlons Malinké'' (Apart from tone, which is not written, sounds are given in orthography, as IPA values are not certain.) Tones There are two moraic tones, high and low, which in combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula People
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people ( ff, Fulɓe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 40 million people worldwide. A significant proportion of the Fula – a third, or an estimated 12 to 13 million – are pastoralists, and their ethnic group has the largest nomadic pastoral community in the world., Quote: The Fulani form the largest pastoral nomadic group in the world. The Bororo'en are noted for the size of their cattle herds. In addition to fully nomadic groups, however, there are also semisedentary Fulani —Fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loma People
The Loma people, sometimes called Loghoma, Looma, Lorma or Toma, are a West African ethnic group living primarily in mountainous, sparsely populated regions near the border between Guinea and Liberia. Their population was estimated at 330,000 in the two countries in 2010. They are closely related to the Mende people. The Loma speak a language in the Southwestern branch of the Mande languages, belonging to the Niger-Congo family of languages. The language is similar to the Kpelle, Mende, Gola, Vai, and Bandi languages. The Loma refer to their language as Löömàgòòi or Löghömàgòòi ). The Loma people, led by Wido Zobo and assisted by a Loma weaver named Moriba, developed a writing script for their language in the 1930s. This writing script contains at least 185 characters. The Mandinka, Koniaka, and Kissi refer to the Loma as ''Toma''. Loma refer to themselves as Löömàgìtì (, or Löghömagiti in Guinea). They have retained their Traditional Religion, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kpelle People
The Kpelle people (also known as the ''Guerze, Kpwesi, Kpessi, Sprd, Mpessi, Berlu, Gbelle, Bere, Gizima,'' or ''Buni'') are the largest ethnic group in Liberia. They are located primarily in an area of central Liberia extending into Guinea. They speak the Kpelle language, which belongs to the Mande language family. Despite their yearly heavy rainfalls and rough land, Kpelle survive mostly on their staple crop of rice. Traditionally organized under several paramount chiefs who serve as mediators for the public, preserve order and settle disputes, the Kpelle are arguably the most rural and conservative of the major ethnic groups in Liberia. The Kpelle people are also referred to as Gberese, Gbese, Gbeze, Gerse, Gerze, Kpelli, Kpese, Kpwele, Ngere, and Nguere. History The Kpelle or Guerze lived in North Sudan during the sixteenth-century, before fleeing to other parts of Northwest Africa into what is now Mali. Their flight was due to internal conflicts between the tribes from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mende People
The Mende are one of the two largest ethnic groups in Sierra Leone; their neighbours, the Temne people, constitute the largest ethnic group at 35.5% of the total population, which is slightly larger than the Mende at 31.2%. The Mende are predominantly found in the Southern Province and the Eastern Province. The Mende are mostly farmers and hunters. Some of the major cities with significant Mende populations include Bo, Kenema, Kailahun, and Moyamba. Like a majority of African nations, Sierra Leone's political parties are often tied to specific ethnic groups and have been dominated by the Mende, on the one hand, and the Temne and their long-time political allies, the Limba, on the other. The Mende are known to typically support the Sierra Leone People's Party (SLPP), while the Temnes and Limbas are associated with the All People's Congress party (APC). History Regional warfare throughout the 19th century led to the capture and sale of many Mende-speakers into sla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vai People
The Vai are a Mande-speaking ethnic group that live mostly in Liberia, with a small minority living in south-eastern Sierra Leone. The Vai are known for their indigenous syllabic writing system known as Vai syllabary, developed in the 1820s by Momolu Duwalu Bukele and other Vai elders. Over the course of the 19th century, literacy in the writing system became widespread. Its use declined over the 20th century, but modern computer technology may enable a revival. The Vai people speak the Vai language, which is of the Mande languages. The Sierra Leonean Vai are predominantly found in Pujehun District (around the Liberian border). Many Sierra Leonean villages that border Liberia are populated by the Vai. In total only about 1200 Vai live in Sierra Leone. History The earliest written documentation of the Vai is by Dutch merchants sometime in the first half of the 17th century, denoting a political group near Cape Mount. The Vai likely settled there as part of the Mane inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
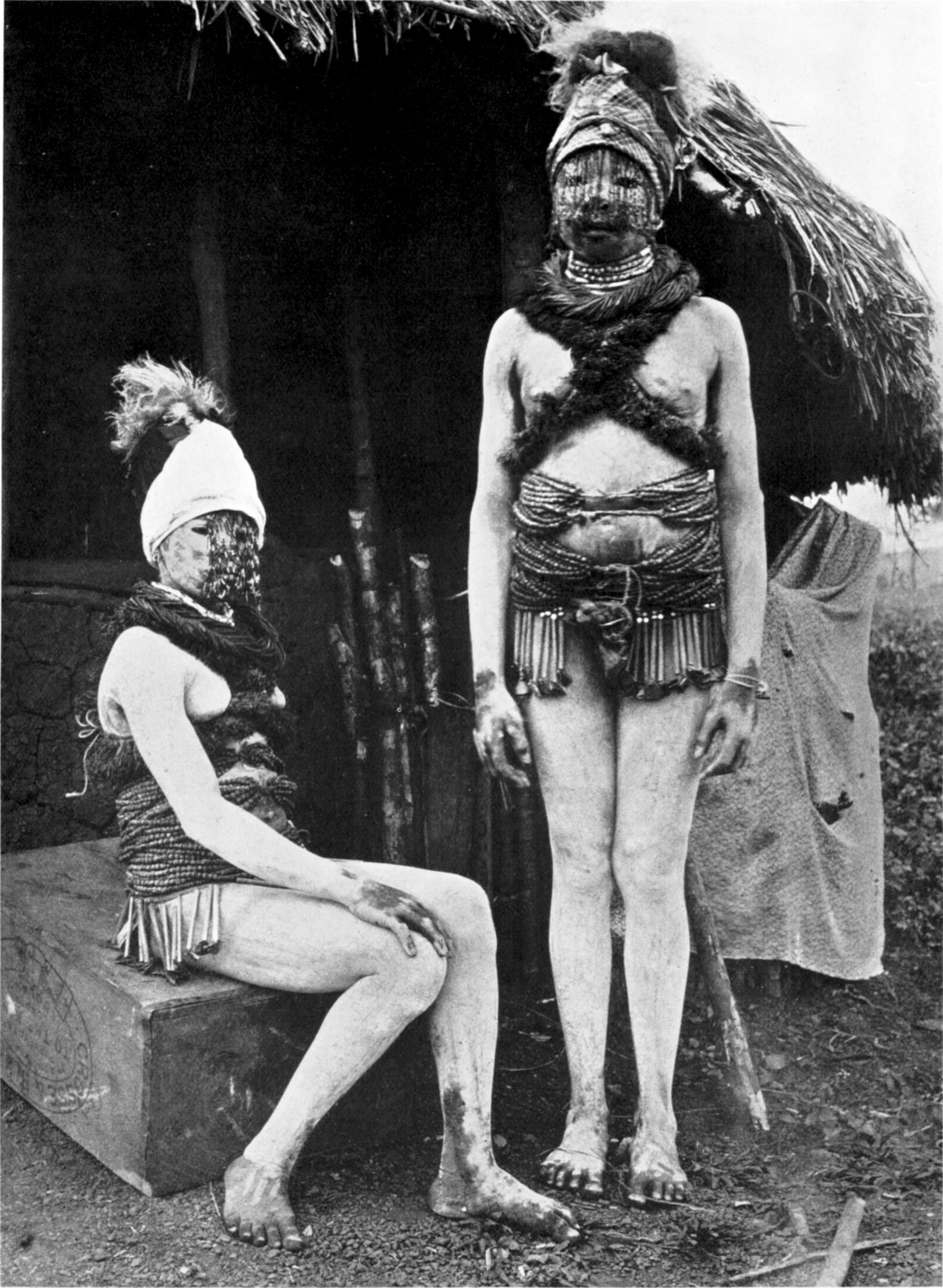
Poro
The Poro, or Purrah or Purroh, is a men's secret society in Sierra Leone, Liberia, Guinea, and the Ivory Coast, introduced by the Mane people. It is sometimes referred to as a hunting society and only males are admitted to its ranks. The female counterpart of the Poro society is the Sande society. Structure The Poro society was part of the culture introduced by Mane people, migrants to the region as early as 1000 AD.Fyfe, Christopher"Weighing the Probabilities."Review: ''Landlords and Strangers: Ecology, Society and Trade in Western Africa, 1000–1630.'' By George E. Brooks. Boulder, CO: Westview Press, 1994. Two affiliated and secret associations exist in Sierra Leone, the Yassi and the Bundu. The first is nominally reserved for females, but members of the Poro are admitted to certain ceremonies. All the female members of the Yassi must be also members of the Bundu, which is strictly reserved to women. In Liberia, the female equivalent of the Poro is the Sande soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sande Society
Sande, also known as zadεgi, bundu, bundo and bondo, is a women's initiation society in Liberia, Sierra Leone, Guinea and the Ivory Coast. The Sande society initiates girls into adulthood by rituals including female genital mutilation. It is said by its supporters to confer fertility, to instill notions of morality and proper sexual comportment, and to maintain an interest in the well-being of its members throughout their lives. In addition, Sande champions women's social and political interests and promotes their solidarity vis-a-vis the Poro, a complementary institution for men. The Sande society masquerade is a rare and perhaps unique African example of a wooden face mask controlled exclusively by women – a feature that highlights the extraordinary social position of women in this geographical region. Geographic extent The Sande society is found throughout the Central West Atlantic Region, an ethnically plural and linguistically diverse region that lies within the littor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
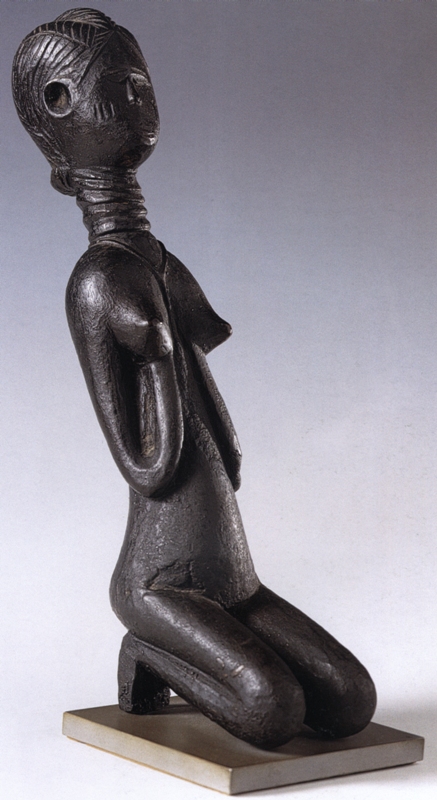
Gola Helmet Mask (Gbetu) With Raffia Costume Brooklyn Museum
Gola may refer to: Groups and tribes *Gola people, a tribal people and language in Liberia *Gola (community/surname), part of Kumhar community in North India. Geography Poland * Gola Dzierżoniowska in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (south-west Poland) * Gola, Lubin County in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (south-west Poland) * Gola, Trzebnica County in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (south-west Poland) * Gola, Łódź Voivodeship (central Poland) * Gola, Gostyń County in Greater Poland Voivodeship (west-central Poland) * Gola, Grodzisk Wielkopolski County in Greater Poland Voivodeship (west-central Poland) * Gola, Jarocin County in Greater Poland Voivodeship (west-central Poland) * Gola, Kępno County in Greater Poland Voivodeship (west-central Poland) * Gola, Krosno Odrzańskie County in Lubusz Voivodeship (west Poland) * Gola, Gmina Sława in Lubusz Voivodeship (west Poland) * Gola, Gmina Szlichtyngowa in Lubusz Voivodeship (west Poland) * Gola, Namysłów County in Opole Voivodeship (sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_Vai_Woman.jpg)