|
Gohliser Schlösschen
The Gohlis Palace (in German: ''Gohliser Schlösschen'') is a Rococo building in the Leipzig borough of Gohlis, Germany, built as a representative bourgeois country house. It is one of the city's sights. Location The plot of the Gohlis Palace stretches between the streets named Menckestrasse (courtyard side) and Poetenweg (garden side) in Leipzig-Gohlis. It is about from the city center and only from the Rosental landscape park via Turmgutstrasse and the Parthe Bridge (''Parthenbrücke''). History In 1755/56, the Leipzig councillor and council architect Johann Caspar Richter (1708–1770) had a summer palace built in the then village of Gohlis, northwest of Leipzig. The plot of land on which the building was constructed was created by merging two adjacent farms that belonged to Christiana Regina Richter (1724–1780), the owner's wife. Comparative studies suggest that the Leipzig municipal architect Friedrich Seltendorff (1686–1752), who was influenced by the Dresden arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
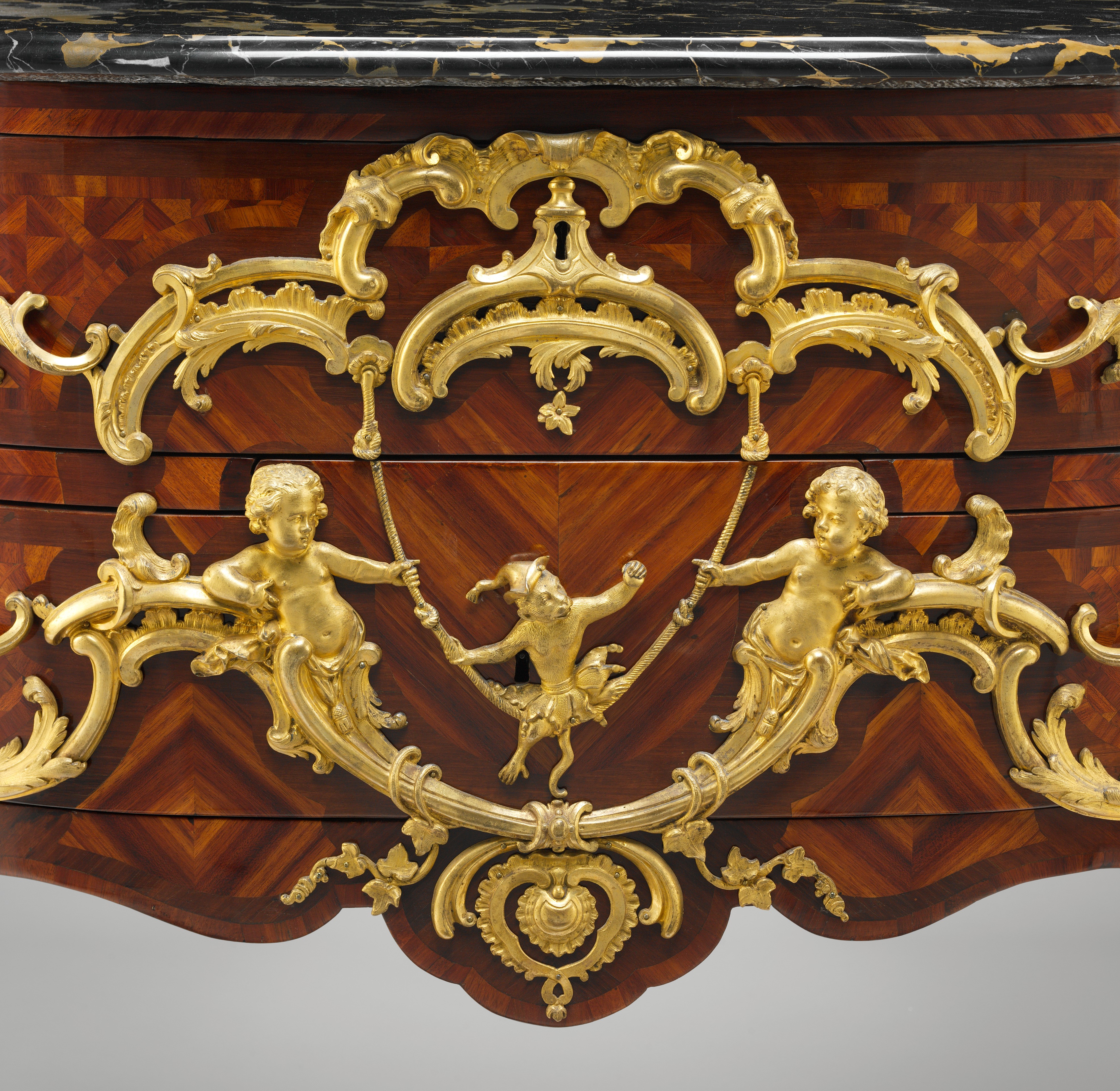
Rococo Architecture
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, and ''trompe-l'œil'' frescoes to create surprise and the illusion of motion and drama. It is often described as the final expression of the Baroque art, Baroque movement. The Rococo style began in France in the 1730s as a reaction against the more formal and geometric Louis XIV style. It was known as the "style Rocaille", or "Rocaille style". It soon spread to other parts of Europe, particularly northern Italy, Austria, southern Germany, Central Europe and Russia. It also came to influence the other arts, particularly sculpture, furniture, silverware, glassware, painting, music, and theatre. Although originally a secular style primarily used for interiors of private residences, the Rococo had a spiritual aspect to it which led to its wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Schiller
Johann Christoph Friedrich von Schiller (, short: ; 10 November 17599 May 1805) was a German playwright, poet, and philosopher. During the last seventeen years of his life (1788–1805), Schiller developed a productive, if complicated, friendship with the already famous and influential Johann Wolfgang von Goethe. They frequently discussed issues concerning aesthetics, and Schiller encouraged Goethe to finish works that he had left as sketches. This relationship and these discussions led to a period now referred to as Weimar Classicism. They also worked together on ''Xenien'', a collection of short satirical poems in which both Schiller and Goethe challenge opponents of their philosophical vision. Early life and career Friedrich Schiller was born on 10 November 1759, in Marbach, Württemberg, as the only son of military doctor Johann Kaspar Schiller (1733–1796) and Elisabetha Dorothea Schiller (1732–1802). They also had five daughters, including Christophine, the eldest. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orangery
An orangery or orangerie was a room or a dedicated building on the grounds of fashionable residences of Northern Europe from the 17th to the 19th centuries where orange and other fruit trees were protected during the winter, as a very large form of greenhouse or conservatory. The orangery provided a luxurious extension of the normal range and season of woody plants, extending the protection which had long been afforded by the warmth offered from a masonry fruit wall. During the 17th century, fruits like orange, pomegranate, and bananas arrived in huge quantities to European ports. Since these plants were not adapted to the harsh European winters, orangeries were invented to protect and sustain them. The high cost of glass made orangeries a status symbol showing wealth and luxury. Gradually, due to technological advancements, orangeries became more of a classic architectural structure that enhanced the beauty of an estate garden, rather than a room used for wintering pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billiard Table
A billiard table or billiards table is a bounded table on which cue sports are played. In the modern era, all billiards tables (whether for carom billiards, pool, pyramid or snooker) provide a flat surface usually made of quarried slate, that is covered with cloth (usually of a tightly woven worsted wool called baize), and surrounded by vulcanized rubber cushions, with the whole thing elevated above the floor. More specific terms are used for specific sports, such as snooker table and pool table, and different-sized billiard balls are used on these table types. An obsolete term is billiard board, used in the 16th and 17th centuries. Parts and equipment Cushions Cushions (also sometimes called "rail cushions", "cushion rubber", or rarely "bumpers") are located on the inner sides of a table's wooden . There are several different materials and design philosophies associated with cushion rubber. These cushions are made from an elastic material such as vulcanized rubber (gum or sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowling Alley
A bowling alley (also known as a bowling center, bowling lounge, bowling arena, or historically bowling club) is a facility where the sport of bowling is played. It can be a dedicated facility or part of another, such as a Meetinghouse, clubhouse or dwelling house. History By the late 1830s, the Knickerbocker Hotel's bowling alley had opened, with three lanes. Instead of wood, this indoor alley used clay for the bowling lane. By 1850, there were more than 400 bowling alleys in New York City, which earned it the title "bowling capital of North America". Because early versions of bowling were difficult and there were concerns about gambling, the sport faltered. Several cities in the United States regulated bowling due to its association with gambling. In the late 19th century, bowling was revived in many U.S. cities. Alleys were often located in saloon basements and provided a place for working-class men to meet, socialize, and drink alcohol. Bars were and still are a principal fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
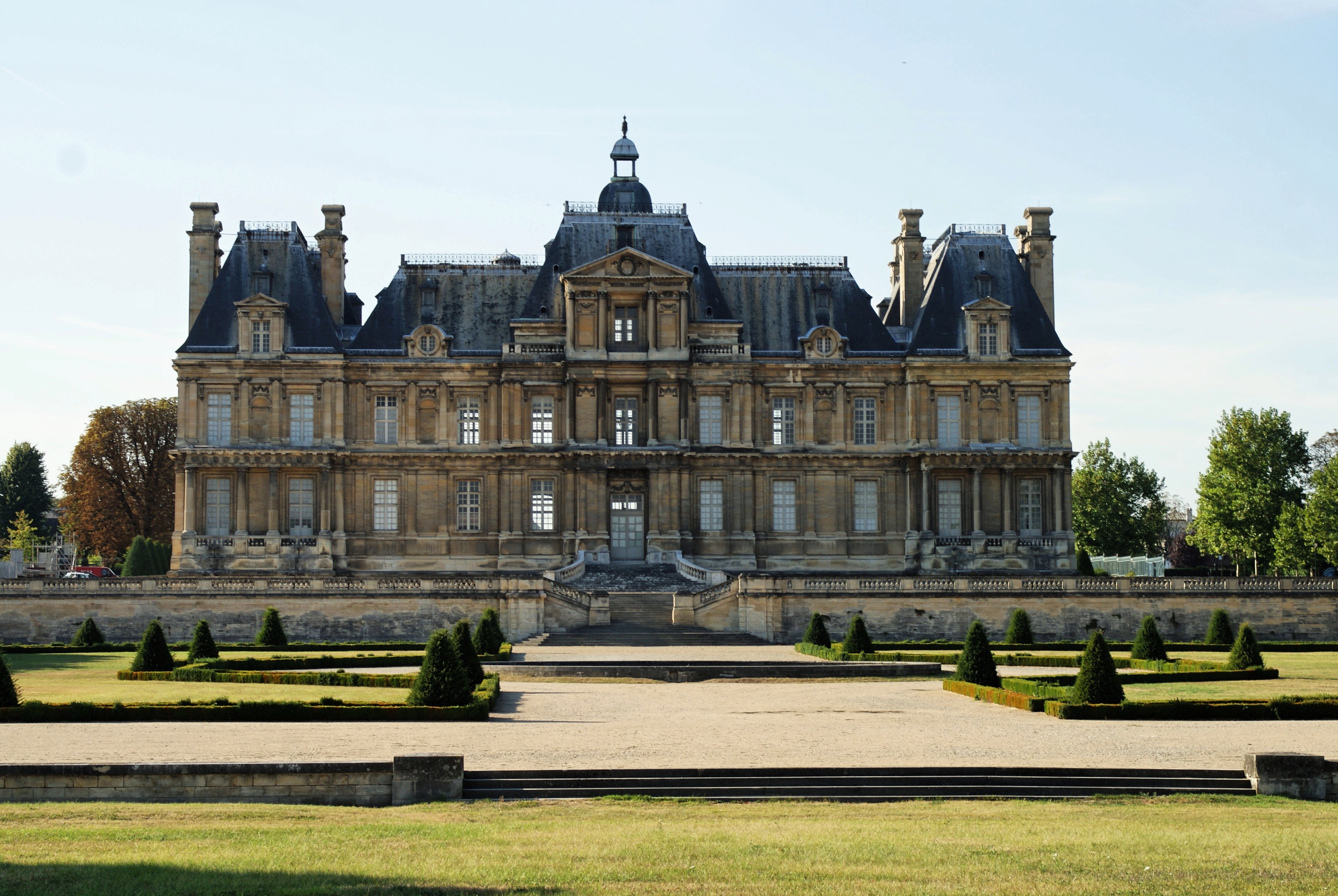
Classicism (architecture)
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psyche (mythology)
Psyche (; el, Ψυχή, Psukhḗ ; ) is the Greek goddess A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of de ... of the soul and often represented with butterfly wings. Psyche was commonly referred to as such in Roman mythology as well, though direct translation is ''Anima (other), Anima'' (Latin word for "soul"). She was born a mortal woman, with beauty that rivaled Aphrodite. Psyche is known from the novel called ''The Golden Ass'', written by the Roman philosopher and orator Apuleius in the 2nd century. Mythology Early life Psyche was the youngest daughter of a Greek king and queen, with two beautiful elder sisters. Her beauty surpassed that of her sisters and people, including priests, compared her to Aphrodite (referred to as Venus (mythology), Venus in ''The Gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceiling Painting
A painted ceiling is a ceiling covered with an artistic mural or painting. They are usually decorated with fresco painting, mosaic tiles and other surface treatments. While hard to execute (at least in situ) a decorated ceiling has the advantage that it is largely protected from damage by fingers and dust. In the past, however, this was more than compensated for by the damage from smoke from candles or a fireplace. Many historic buildings have celebrated ceilings, perhaps the most famous in the world is the Sistine Chapel ceiling by Michelangelo. See also * Dropped ceiling * Coffered ceiling * Camp ceiling * Cove ceiling * Beam ceiling * Scottish Renaissance painted ceilings Scottish renaissance painted ceilings are decorated ceilings in Scottish houses and castles built between 1540 and 1640. This is a distinctive national style, though there is common ground with similar work elsewhere, especially in France, Spain ... {{art-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocaille
Rocaille ( , ) was a French style of exuberant decoration, with an abundance of curves, counter-curves, undulations and elements modeled on nature, that appeared in furniture and interior decoration during the early reign of Louis XV of France. It was a reaction against the heaviness and formality of the Louis XIV style. It began in about 1710, reached its peak in the 1730s, and came to an end in the late 1750s, replaced by Neoclassicism. It was the beginning of the French Baroque movement in furniture and design, and also marked the beginning of the Rococo movement, which spread to Italy, Bavaria and Austria by the mid-18th century. Overview Rocaille was exuberant and inspired by nature like Rococo, but, unlike Rococo, it was usually symmetrical and not overloaded with decoration. It took its name from the mixture of rock, seashell and plaster that was used to create a picturesque effect in grottos during the Renaissance, and from the name of a seashell-shaped ornament which wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesene
A lesene, also called a pilaster strip, is an architectural term for a narrow, low-relief vertical pillar on a wall. It resembles a pilaster, but does not have a base or capital. It is typical in Lombardic and Rijnlandish architectural building styles. Function Lesenes are used in architecture to vertically divide a façade or other wall surface optically. However, unlike pilasters, lesenes are simpler, having no bases or capitals. Their function is ornamental, not just to decorate the plain surface of a wall but, in the case of corner lesenes (at the edges of a façade), to emphasise the edges of a building. Gallery File:Lisene2.jpg, Lesenes and Lombard band (arches) on a chapel File:Lisene-Ravenna.jpg, Lesenes forming blind arcades, Mausoleum of Galla Placidia, Ravenna (); dentils under the eaves. File:Gernrode-Lisene.jpg, Lesene on the staircase tower, Gernrode collegiate church (pre-1000) File:Maria Laach.jpg, Lesenes on the Maria Laach Abbey (1156) File:Saxon tower - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risalit
An ''avant-corps'' ( it, avancorpo or , plural , german: Risalit, pl, ryzalit), a French term literally meaning "fore-body", is a part of a building, such as a porch or pavilion, that juts out from the ''corps de logis'', often taller than other parts of the building. It is common in façades in French Baroque architecture. Particularly in German architecture, a corner ''Risalit'' is where two wings meet at right-angles. Baroque three-winged constructions often incorporate a median ''Risalit'' in a main hall or a stairwell, such as in Weißenstein Palace Weißenstein ( sl, Bilšak) is a town in the district of Villach-Land in the Austrian state of Carinthia. Geography Weißenstein lies in the lower Drau valley northwest of Villach. The highest point in the municipality is the Spitzeck at 1517 ... and the . Terms By position to the building A central avant-corps stands in the middle of the facade. A side projection is positioned off-centre. Two wings (usually) runn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Garden
The Baroque garden was a style of garden based upon symmetry and the principle of imposing order on nature. The style originated in the late-16th century in Italy, in the gardens of the Vatican and the Villa Borghese gardens in Rome and in the gardens of the Villa d'Este in Tivoli, and then spread to France, where it became known as the ''jardin à la française'' or French formal garden. The grandest example is found in the Gardens of Versailles designed during the 17th century by the landscape architect André Le Nôtre for Louis XIV. In the 18th century, in imitation of Versailles, very ornate Baroque gardens were built in other parts of Europe, including Germany, Austria, Spain, and in Saint-Petersburg, Russia. In the mid-18th century the style was replaced by the less geometric and more natural English landscape garden. Characteristics Baroque gardens were intended to illustrate the mastery of man over nature. They were often designed to be seen from above and from a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)





