|
Godfrey Benson, 1st Baron Charnwood
Godfrey Rathbone Benson, 1st Baron Charnwood (6 November 1864 – 3 February 1945), was an English author, academic, Liberal politician and philanthropist. Benson was born in Alresford, Hampshire, the fourth son of William Benson, a barrister, and Elizabeth Soulsby Smith. The actor-manager Sir Frank Benson and the designer William Arthur Smith Benson were his brothers. He was educated at Winchester and Balliol College, Oxford, graduating in 1887 with a First in '' literae humaniores'', and would later become a Philosophy lecturer at Balliol. He was called to the bar by the Inner Temple in 1898. Benson was involved in Liberal politics and represented Woodstock in the House of Commons from 1892 to 1895, when he was defeated. He then unsuccessfully stood in St. Pancras West in 1900 and Worcestershire West in 1906. He served as Mayor of Lichfield between 1909 and 1911. In the latter year Benson was raised to the peerage as Baron Charnwood, of Castle Donington in the County of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberal Party (UK)
The Liberal Party was one of the two major political parties in the United Kingdom, along with the Conservative Party, in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Beginning as an alliance of Whigs, free trade–supporting Peelites and reformist Radicals in the 1850s, by the end of the 19th century it had formed four governments under William Gladstone. Despite being divided over the issue of Irish Home Rule, the party returned to government in 1905 and won a landslide victory in the 1906 general election. Under prime ministers Henry Campbell-Bannerman (1905–1908) and H. H. Asquith (1908–1916), the Liberal Party passed reforms that created a basic welfare state. Although Asquith was the party leader, its dominant figure was David Lloyd George. Asquith was overwhelmed by the wartime role of coalition prime minister and Lloyd George replaced him in late 1916, but Asquith remained as Liberal Party leader. The split between Lloyd George's breakaway faction and Asquith's official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
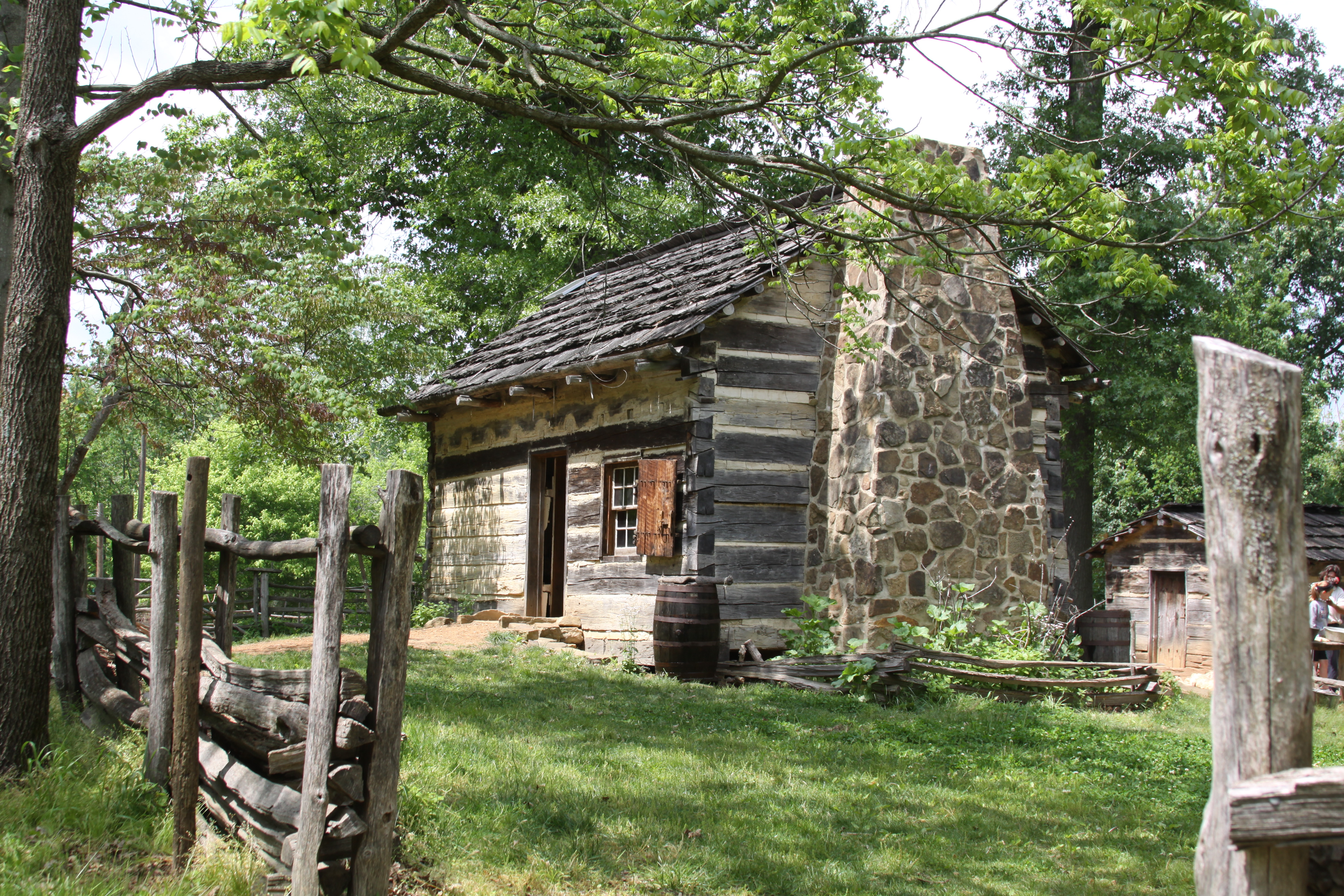
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation through the American Civil War and succeeded in preserving the Union, abolishing slavery, bolstering the federal government, and modernizing the U.S. economy. Lincoln was born into poverty in a log cabin in Kentucky and was raised on the frontier, primarily in Indiana. He was self-educated and became a lawyer, Whig Party leader, Illinois state legislator, and U.S. Congressman from Illinois. In 1849, he returned to his successful law practice in central Illinois. In 1854, he was angered by the Kansas–Nebraska Act, which opened the territories to slavery, and he re-entered politics. He soon became a leader of the new Republican Party. He reached a national audience in the 1858 Senate campaign debates against Stephen A. Douglas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Benson, 2nd Baron Charnwood
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Herbert Morrell
George Herbert Morrell MA, MP, JP, DL (1845, Adderbury – 30 September 1906, Bad Nauheim) was an English politician and lawyer. George Herbert Morrell was the son of the Rev. G. K. Morrell, fellow of St John's College, Oxford.'Mr G. H. Morrell', ''The Times'', 2 October 1906 He was educated at Rugby School and Exeter College, Oxford, where he took honours in natural science as well as a B.C.L. in 1870. Morrell became a demonstrator in physiology at the Oxford university museum under George Rolleston. In 1874 he married his third cousin, Emilia Alicia Morrell (1854–1938), granddaughter of one of the founder of Morrells Brewery and the richest heiress in Oxfordshire.Brigid Allen‘Morrell family (per. c.1790–1965)’ ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online edn, May 2005 , accessed 13 Jan 2009 He was the Conservative Member of Parliament for Woodstock Woodstock Music and Art Fair, commonly referred to as Woodstock, was a mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Macdonald (British Politician, Born 1854)
John Archibald Murray Macdonald (9 October 1854 – 16 January 1939) was a Scottish Liberal Party politician. Biography The fourth son of the Rev. H. F. Macdonald DD, Strachur, Argyllshire, he was educated at Glasgow High School, the University of Glasgow and the University of Edinburgh. In 1885 he married Alice Mary Noel, daughter of Edward H. Noel. He was Liberal Member of Parliament for Bow and Bromley from 1892 to 1895, for Falkirk Burghs from 1906 to 1918 and for Stirling and Falkirk Burghs from 1918 to 1922. He was also an elected member of the London School Board for Marylebone in 1897 and 1900, resigning in 1902. In 1911, he addressed a meeting of the Young Scots Society in Clydebank and advocated for devolution of political power to Scotland due to what he saw as the congestion of business at Westminster, claiming that Parliament was no longer "a deliberative assembly in the true sense."The Scotsman 29 Nov 1911: 13 He was appointed a Privy Counsellor The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm Muggeridge
Thomas Malcolm Muggeridge (24 March 1903 – 14 November 1990) was an English journalist and satirist. His father, H. T. Muggeridge, was a socialist politician and one of the early Labour Party Members of Parliament (for Romford, in Essex). In his twenties, Muggeridge was attracted to communism and went to live in the Soviet Union in the 1930s, and the experience turned him into an anti-communist. During World War II, he worked for the British government as a soldier and a spy, first in East Africa for two years and then in Paris. In the aftermath of the war, he converted to Christianity under the influence of Hugh Kingsmill and helped to bring Mother Teresa to popular attention in the West. He was also a critic of the sexual revolution and of drug use. Muggeridge kept detailed diaries for much of his life, which were published in 1981 under the title ''Like It Was: The Diaries of Malcolm Muggeridge'', and he developed them into two volumes of an uncompleted autobiography ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Henry Chamberlin
William Henry Chamberlin (February 17, 1897 – September 12, 1969) was an American historian and journalist. He was the author of several books about the Cold War, communism, and foreign policy, including ''The Russian Revolution 1917-1921'' (1935), which was written in Russia between 1922 and 1934 while he was the Moscow correspondent of ''The Christian Science Monitor''. He had communist sympathies until he lived in the Soviet Union, when he gradually turned anticommunist. He predicted that intervention in World War II would help communism in Europe and in Asia and so he was a non-interventionist. Early life and education Chamberlin was born in Brooklyn and educated in Pennsylvania schools and later at Haverford College. At 25, he moved to Greenwich Village and was deeply affected by the cultural bohemianism and Bolshevik politics there. He worked for Heywood Broun, the book editor of the ''New York Tribune''. He also published under the pseudonym of A.C. Freeman and was a soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Innitzer
Theodor Innitzer (25 December 1875 – 9 October 1955) was Archbishop of Vienna and a cardinal of the Catholic Church. Early life Innitzer was born in Neugeschrei (Nové Zvolání), part of the town Weipert (Vejprty) in Bohemia, at that time Austria-Hungary, (now Czech Republic). He was the son of a passementier Wilhelm Innitzer in Vejprty, House Nr. 362, later a textile factory worker, and his wife Maria born Seidl, daughter of a mining clerk. After completing the minimum mandatory school, Innitzer became an apprentice in a textile factory. The dean of his home parish supported the young Theodor, which allowed him to attend a gymnasium (1890–1892 Communal-Gymnasium), and Staatsgymnasium (1892–1898) in Kaaden (Kadaň). Ecclesiastical career *1898 – entered the seminary in Vienna *1902 – became a priest *1906 – received his Dr. theol. (Doctorate in Theology) *1908 to 1911 Privatdozent at the University of Vienna *1911 to 1932 professor and (from 1913) Chair for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
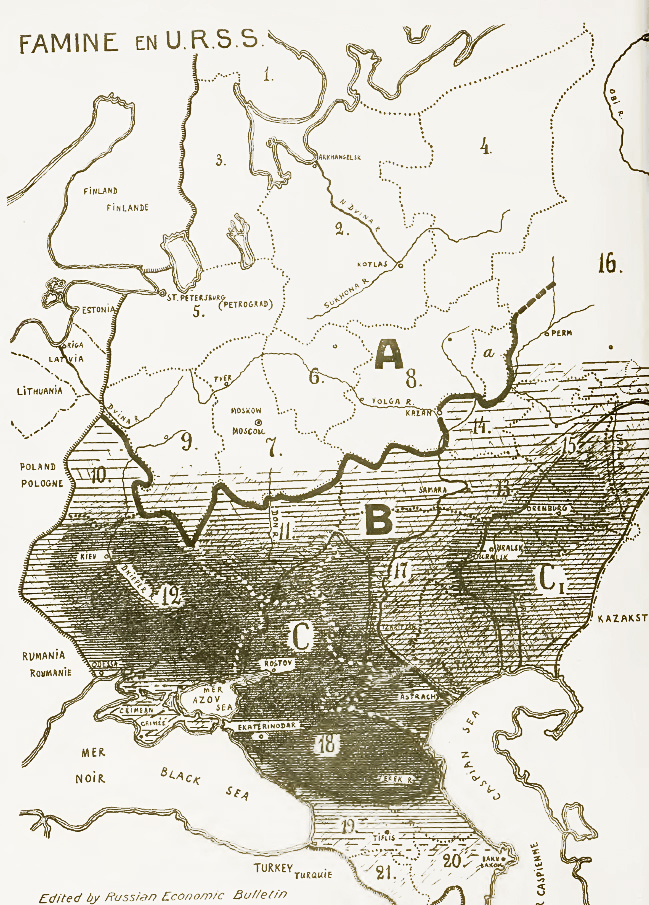
Holodomor
The Holodomor ( uk, Голодомо́р, Holodomor, ; derived from uk, морити голодом, lit=to kill by starvation, translit=moryty holodom, label=none), also known as the Terror-Famine or the Great Famine, was a man-made famine in Soviet Ukraine from 1932 to 1933 that killed millions of Ukrainians. The Holodomor was part of the wider Soviet famine of 1932–1933 which affected the major grain-producing areas of the Soviet Union. While scholars universally agree that the cause of the famine was man-made, whether the Holodomor constitutes a genocide remains in dispute. Some historians conclude that the famine was planned and exacerbated by Joseph Stalin in order to eliminate a Ukrainian independence movement. This conclusion is supported by Raphael Lemkin. Others suggest that the famine arose because of rapid Soviet industrialisation and collectivization of agriculture. Ukraine was one of the largest grain-producing states in the USSR and was subject to u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Ridding
George Ridding (16 March 1828 – 30 August 1904) was an English headmaster and bishop. Life He was born at Winchester College, of which his father, the Rev. Charles Ridding, vicar of Andover, was a fellow. He was educated at Winchester College and at Balliol College, Oxford. He became a fellow of Exeter College and was a tutor from 1853 to 1863. In 1853 he married Mary Louisa Moberly, who died within a year of her marriage. Ordained Priest by Bishop of Oxford 20 September 1856 in St John Baptist Church, Oxford.Oxford University & City Herald, 27/09/1856 He was appointed second master of Winchester College in 1863, and on the retirement of his father-in-law, George Moberly, he succeeded to the headmastership. The gate between College Meads and Lavender Meads bears his name. During the tenure of this office (1867–1884) he carried out successfully a series of radical reforms in the organization of the school, resulting in a great increase both in its reputation and numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Criticism
Biblical criticism is the use of critical analysis to understand and explain the Bible. During the eighteenth century, when it began as ''historical-biblical criticism,'' it was based on two distinguishing characteristics: (1) the concern to avoid dogma and bias by applying a neutral, non-sectarian, reason-based judgment to the study of the Bible, and (2) the belief that the reconstruction of the historical events behind the texts, as well as the history of how the texts themselves developed, would lead to a correct understanding of the Bible. This sets it apart from earlier, pre-critical methods; from the anti-critical methods of those who oppose criticism-based study; from later post-critical orientation, and from the many different types of criticism which biblical criticism transformed into in the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries. Most scholars believe the German Enlightenment () led to the creation of biblical criticism, although some assert that its roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)