|
Go-around Switch
A takeoff/go-around switch (TO/GA; ) is a switch on the autothrottle of modern large aircraft, with two modes: takeoff (TO) and go-around (GA). The mode is dependent on the phase of flight; usually, on approach to land, the autopilot will be set to approach mode, therefore if the TO/GA switch is pressed it will activate the go-around mode of the autothrottle; conversely, when takeoff is set on the autopilot, the switch activates takeoff mode of the autothrottle. On Boeing aircraft TO/GA modes are selected by a separate switch near the throttle levers, but on Airbus aircraft it is activated by pushing the thrust levers fully forward to the TO/GA detent. Takeoff Once an aircraft has lined up, the pilots first increase the engine power to 40–60% N1 (low-pressure compressor RPM) on Boeing aircraft, and 50% N1 on Airbus aircraft. Large jet engines accelerate slowly from idle to approximately 40%, and stabilising the engines prior to applying full power prevents a large thrust asymme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autothrottle
An autothrottle (automatic throttle, also known as autothrust, A/T) is a system that allows a pilot to control the power setting of an aircraft's engines by specifying a desired flight characteristic, rather than manually controlling the fuel flow. The autothrottle can greatly reduce the pilots' work load and help conserve fuel and extend engine life by metering the precise amount of fuel required to attain a specific target indicated air speed, or the assigned power for different phases of flight. A/T and AFDS (Auto Flight Director Systems) can work together to fulfill the whole flight plan. Working modes There are two parameters that an A/T can maintain, or try to attain: speed and thrust. In speed mode the throttle is positioned to attain a set target speed. This mode controls aircraft speed within safe operating margins. For example, if the pilot selects a target speed which is slower than stall speed, or a speed faster than maximum speed, the autothrottle system will maint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flex Temp
Flex temp is a technique used to produce cost savings through increased engine life and reduced overhaul and fuel costs for airliners by allowing them to takeoff, take-off at less than rated thrust. For Airbus and Fokker aircraft the technique is known as ''flex temp'' or just ''flex''. Other manufacturers use the terms ''Assumed temperature thrust reduction'', ''Reduced take-off thrust'' or ''Factored take-off thrust''. Technique The runway length required for an aircraft to take off depends on a number of things including aircraft weight, flap setting and environmental conditions. The particular take-off distance required may be less than the available runway length. In this case a lower thrust may be used. Lower thrust settings increase engine life and reduce maintenance costs. The take-off thrust available from a civil engine is a constant value up to a particular ambient temperature. At this temperature the engine is now running at its turbine temperature limit which is displ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas Air Flight 3591
Atlas Air Flight 3591 was a scheduled domestic cargo flight under the Amazon Air banner between Miami International Airport and George Bush Intercontinental Airport in Houston. On February 23, 2019, the Boeing 767-375ER(BCF) used for this flight crashed into Trinity Bay during approach into Houston, killing the two crew members and single passenger on board. The accident occurred near Anahuac, Texas, east of Houston, shortly before 12:45 CST (18:45 UTC). This was the first fatal crash of a Boeing 767 freighter. Investigators attributed the accident to pilot error, finding that the first officer experienced spatial disorientation and inadvertently placed the aircraft in an unrecoverable dive, while the captain failed to adequately monitor the first officer's actions and the flight path of the aircraft. Flight crew training issues at Atlas Air and across the U.S. commercial aviation industry were also implicated. Background Aircraft The Boeing 767-375ER() ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One-Two-GO Airlines Flight 269
One-Two-GO Airlines Flight 269 (OG269) was a scheduled domestic passenger flight from Bangkok to Phuket, Thailand. On 16 September 2007, about 15:41 ICT, the McDonnell Douglas MD-82 operating the flight crashed into an embankment beside runway 27 at Phuket International Airport (HKT) bursting into flames upon impact during an attempted go-around after an aborted landing, killing 90 of the 130 persons on board (this includes one person who died of burn injuries several days after the crash). It is the third deadliest aviation incident to occur in Thailand. The crash report was published by the Aircraft Accident Investigation Committee (AAIC) of the Ministry of Transport. A separate two-year report done by the United States National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) was incorporated into the AAIC report. Both reports found that the captain and first officer had worked hours in excess of the legal flight limits; that the first officer attempted to transfer control to the captain dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Airlines Flight 140
China Airlines Flight 140 was a regularly scheduled passenger flight from Chiang Kai-shek International Airport (serving Taipei, Taiwan) to Nagoya Airport in Nagoya, Japan.China Airlines is based in Taiwan. Air China is the flag carrier for the People's Republic of China. On 26 April 1994, the Airbus A300B4-622R was completing a routine flight and approach, when, just seconds before landing at Nagoya Airport, the takeoff/go-around setting (TO/GA) was inadvertently triggered. The pilots attempted to pitch the aircraft down while the autopilot, which was not disabled, was pitching the aircraft up. The aircraft ultimately stalled and crashed into the ground, killing 264 of the 271 people on board. To date, the accident remains the deadliest accident in the history of China Airlines and the second-deadliest aviation accident on Japanese soil, behind Japan Airlines Flight 123. It is also the third-deadliest aviation accident or incident involving an Airbus A300, after Iran Air Fligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missed Approach
Missed approach is a procedure followed by a pilot when an instrument approach cannot be completed to a full-stop landing. The instructions for the missed approach may be assigned by air traffic control (ATC) prior to the clearance for the approach. If ATC has not issued specific instructions prior to the approach and a missed approach is executed, the pilot must follow the (default) missed approach procedure specified for the approach. Prior to commencing the approach, pilots can make a specific request to ATC if a missed approach may occur. Such a request may include heading and altitude instructions to avoid in-flight delays (such as holds) and efficiently maneuver the aircraft into position for either its next approach or a diversion to an alternate airport. Generally, if a pilot determines by the time the aircraft is at the decision height (for a precision approach) or missed approach point (for a non-precision approach), that the runway or its environment is not in sight, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
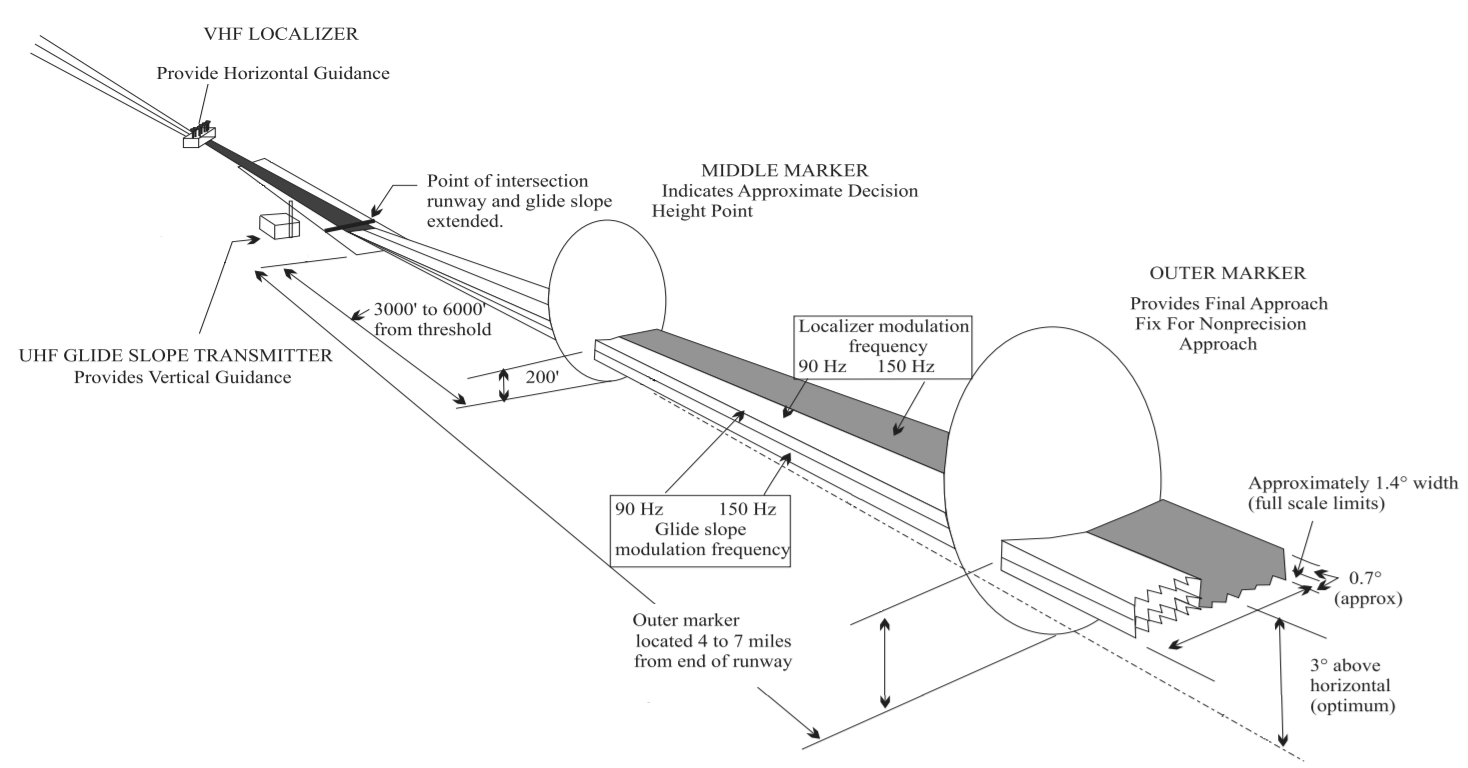
Instrument Landing System Glide Path
Instrument landing system glide path, commonly referred to as a glide path (G/P) or glide slope (G/S), is "a system of vertical guidance embodied in the instrument landing system which indicates the vertical deviation of the aircraft from its optimum path of descent", according to ''Article 1.106'' of the ITU Radio Regulations (ITU RR).ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.106, definition: ''instrument landing system (ILS)'' Principle of operation A glide slope station uses an antenna array sited to one side of the runway touchdown zone. The GS signal is transmitted on a carrier signal using a technique similar to that for the localizer. The centre of the glide slope signal is arranged to define a glide path of approximately 3° above horizontal (ground level). The beam is 1.4° deep (0.7° below the glide-path centre and 0.7° above). The pilot (or the autopilot, if using autoland) controls the aircraft so that the glide slope indicator r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrument Landing System
In aviation, the instrument landing system (ILS) is a precision radio navigation system that provides short-range guidance to aircraft to allow them to approach a runway at night or in bad weather. In its original form, it allows an aircraft to approach until it is over the ground, within a of the runway. At that point the runway should be visible to the pilot; if it is not, they perform a missed approach. Bringing the aircraft this close to the runway dramatically increases the range of weather conditions in which a safe landing can be made. Other versions of the system, or "categories", have further reduced the minimum altitudes, runway visual ranges (RVRs), and transmitter and monitoring configurations designed depending on the normal expected weather patterns and airport safety requirements. ILS uses two directional radio signals, the ''localizer'' (108 to 112 MHz frequency), which provides horizontal guidance, and the ''glideslope'' (329.15 to 335 MHz frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt concrete, asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface (sod, grass, soil, dirt, gravel, ice, sand or road salt, salt). Runways, as well as taxiways and Airport apron, ramps, are sometimes referred to as "tarmac", though very few runways are built using Tarmacadam, tarmac. Takeoff and landing areas defined on the surface of water for seaplanes are generally referred to as waterways. Runway lengths are now International Civil Aviation Organization#Use of the International System of Units, commonly given in meters worldwide, except in North America where feet are commonly used. History In 1916, in a World War I war effort context, the first concrete-paved runway was built in Clermont-Ferrand in France, allowing local company Michelin to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
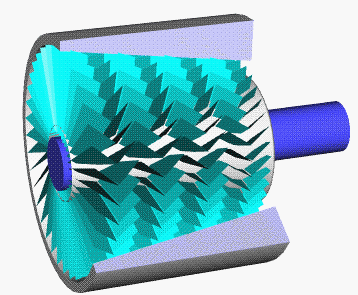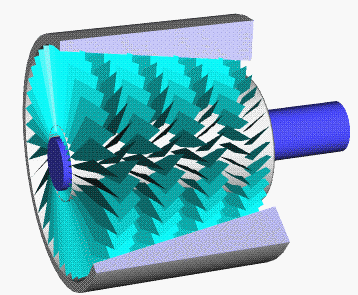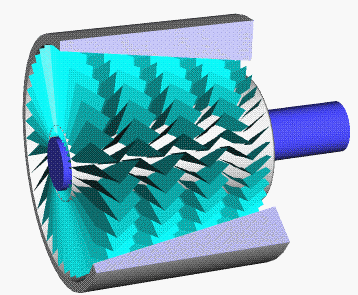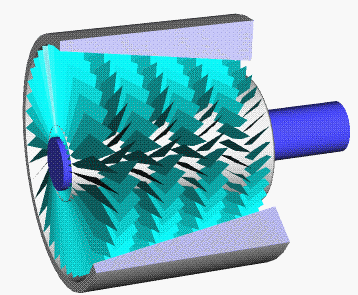
Compressor Stall
A compressor stall is a local disruption of the airflow in the compressor of a gas turbine or turbocharger. A stall that results in the complete disruption of the airflow through the compressor is referred to as a compressor surge. The severity of the phenomenon ranges from a momentary power drop barely registered by the engine instruments to a complete loss of compression in case of a surge, requiring adjustments in the fuel flow to recover normal operation. Compressor stall was a common problem on early jet engines with simple aerodynamics and manual or mechanical fuel control units, but has been virtually eliminated by better design and the use of hydromechanical and electronic control systems such as Full Authority Digital Engine Control. Modern compressors are carefully designed and controlled to avoid or limit stall within an engine's operating range. Types There are two types of compressor stall: Rotating stall Rotating stall is a local disruption of airflow within the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called '' aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jet Engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term typically refers to an internal combustion airbreathing jet engine such as a turbojet, turbofan, ramjet, or pulse jet engine, pulse jet. In general, jet engines are internal combustion engines. Airbreathing jet engines typically feature a Axial compressor, rotating air compressor powered by a turbine, with the leftover power providing thrust through the propelling nozzle—this process is known as the Brayton cycle, Brayton thermodynamic cycle. Jet aircraft use such engines for long-distance travel. Early jet aircraft used turbojet engines that were relatively inefficient for subsonic flight. Most modern subsonic jet aircraft use more complex High-bypass turbofan, high-bypass turbofan engines. They give higher speed and greater fuel eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
_JP6356069.jpg)