|
GnuCash
GnuCash is an accounting program that implements a double-entry bookkeeping system. It was initially aimed at developing capabilities similar to Intuit, Inc.'s Quicken application, but also has features for small business accounting. Recent development has been focused on adapting to modern desktop support-library requirements. GnuCash is part of the GNU Project, and runs on Linux, GNU, OpenBSD, FreeBSD, Solaris, macOS, and other Unix-like platforms. A Microsoft Windows (2000 or newer) port was made available starting with the 2.2.0 series. History Programming on GnuCash began in 1997, and its first stable release was in 1998. Small Business Accounting was added in 2001. A Mac installer became available in 2004. A Windows port was released in 2007. GnuCash for Android/GnuCash Mobile GnuCash for Android was initially developed as part of a Google Summer of Code Project. This was an expense-tracking companion app for GnuCash, as opposed to a stand-alone accounting package, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SourceForge
SourceForge is a web service that offers software consumers a centralized online location to control and manage open-source software projects and research business software. It provides source code repository hosting, bug tracking, mirroring of downloads for load balancing, a wiki for documentation, developer and user mailing lists, user-support forums, user-written reviews and ratings, a news bulletin, micro-blog for publishing project updates, and other features. SourceForge was one of the first to offer this service free of charge to open-source projects. Since 2012, the website has run on Apache Allura software. SourceForge offers free hosting and free access to tools for developers of free and open-source software. , the SourceForge repository claimed to host more than 502,000 projects and had more than 3.7 million registered users. Concept SourceForge is a web-based source code repository. It acts as a centralized location for free and open-source software pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-entry Bookkeeping System
Double-entry bookkeeping, also known as double-entry accounting, is a method of bookkeeping that relies on a two-sided accounting entry to maintain financial information. Every entry to an account requires a corresponding and opposite entry to a different account. The double-entry system has two equal and corresponding sides known as debit and credit. A transaction in double-entry bookkeeping always affects at least two accounts, always includes at least one debit and one credit, and always has total debits and total credits that are equal. The purpose of double-entry bookkeeping is to allow the detection of financial errors and fraud. For example, if a business takes out a bank loan for $10,000, recording the transaction would require a debit of $10,000 to an asset account called "Cash", as well as a credit of $10,000 to a liability account called "Notes Payable". The basic entry to record this transaction in a general ledger will look like this: Double-entry bookkeeping is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quicken Interchange Format
Quicken Interchange Format (QIF) is an open specification for reading and writing financial data to media (i.e. files). Background Although still widely used, QIF is a format older than Open Financial Exchange (OFX). The inability to reconcile imported transactions against the current account information is one of the primary shortcomings of QIF. Most personal money management software, such as Microsoft Money, GnuCash and Quicken's low end products (e.g. Quicken Personal and Quicken Personal Plus), can read QIF files to import information. Intuit's Quicken used to be able to import QIF, too, but with its 2006 version it dropped that support for several important account types, including checking, savings, and credit card accounts. The Australian version of Quicken still allows the importing of QIF files for these account types. However, unlike the American version, it is not possible to export data to QIF or any other file type for any account type. The QIF format does not allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-entry Bookkeeping System
Double-entry bookkeeping, also known as double-entry accounting, is a method of bookkeeping that relies on a two-sided accounting entry to maintain financial information. Every entry to an account requires a corresponding and opposite entry to a different account. The double-entry system has two equal and corresponding sides known as debit and credit. A transaction in double-entry bookkeeping always affects at least two accounts, always includes at least one debit and one credit, and always has total debits and total credits that are equal. The purpose of double-entry bookkeeping is to allow the detection of financial errors and fraud. For example, if a business takes out a bank loan for $10,000, recording the transaction would require a debit of $10,000 to an asset account called "Cash", as well as a credit of $10,000 to a liability account called "Notes Payable". The basic entry to record this transaction in a general ledger will look like this: Double-entry bookkeeping is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheme (programming Language)
Scheme is a dialect of the Lisp family of programming languages. Scheme was created during the 1970s at the MIT AI Lab and released by its developers, Guy L. Steele and Gerald Jay Sussman, via a series of memos now known as the Lambda Papers. It was the first dialect of Lisp to choose lexical scope and the first to require implementations to perform tail-call optimization, giving stronger support for functional programming and associated techniques such as recursive algorithms. It was also one of the first programming languages to support first-class continuations. It had a significant influence on the effort that led to the development of Common Lisp.Common LISP: The Language, 2nd Ed., Guy L. Steele Jr. Digital Press; 1981. . "Common Lisp is a new dialect of Lisp, a successor to MacLisp, influenced strongly by ZetaLisp and to some extent by Scheme and InterLisp." The Scheme language is standardized in the official IEEE standard1178-1990 (Reaff 2008) IEEE Standard for the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed-point Arithmetic
In computing, fixed-point is a method of representing fractional (non-integer) numbers by storing a fixed number of digits of their fractional part. Dollar amounts, for example, are often stored with exactly two fractional digits, representing the cents (1/100 of dollar). More generally, the term may refer to representing fractional values as integer multiples of some fixed small unit, e.g. a fractional amount of hours as an integer multiple of ten-minute intervals. Fixed-point number representation is often contrasted to the more complicated and computationally demanding floating-point representation. In the fixed-point representation, the fraction is often expressed in the same number base as the integer part, but using negative powers of the base ''b''. The most common variants are decimal (base 10) and binary (base 2). The latter is commonly known also as binary scaling. Thus, if ''n'' fraction digits are stored, the value will always be an integer multiple of ''b' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced like the letter c'') is a General-purpose language, general-purpose computer programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie, and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems, device drivers, protocol stacks, though decreasingly for application software. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the measuring programming language popularity, most widely used programming languages, with C compilers avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minnesota State Bar Association
The Minnesota State Bar Association is a voluntary bar association for the state of Minnesota, whose members include lawyers, judges, and other legal practitioners, such as clerks, registrars, and paralegals. The MSBA is one of the oldest state bar associations in the United States. Membership is not required to practice law in Minnesota. Purposes The MSBA states the following goals: * To aid the courts in the administration of justice. * To apply the knowledge and experience of the profession to the public good. * To maintain in the profession high standards of learning, competence, ethics, and public service. * To conduct a program of continuing legal education. * To organize into the MSBA the entire Bench and Bar of Minnesota and correlate the activities of affiliated associations. * To provide a forum for the discussion of subjects pertaining to the practice of law, the science of jurisprudence and law reform, and to publish information relating thereof. * To cooperate with ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
501(c)3
A 501(c)(3) organization is a United States corporation, trust, unincorporated association or other type of organization exempt from federal income tax under section 501(c)(3) of Title 26 of the United States Code. It is one of the 29 types of 501(c) nonprofit organizations in the US. 501(c)(3) tax-exemptions apply to entities that are organized and operated exclusively for religious, charitable, scientific, literary or educational purposes, for testing for public safety, to foster national or international amateur sports competition, or for the prevention of cruelty to children or animals. 501(c)(3) exemption applies also for any non-incorporated community chest, fund, cooperating association or foundation organized and operated exclusively for those purposes.IR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floating-point Arithmetic
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can be represented as a base-ten floating-point number: 12.345 = \underbrace_\text \times \underbrace_\text\!\!\!\!\!\!^ In practice, most floating-point systems use base two, though base ten (decimal floating point) is also common. The term ''floating point'' refers to the fact that the number's radix point can "float" anywhere to the left, right, or between the significant digits of the number. This position is indicated by the exponent, so floating point can be considered a form of scientific notation. A floating-point system can be used to represent, with a fixed number of digits, numbers of very different orders of magnitude — such as the number of meters between galaxies or between protons in an atom. For this reason, floating-poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
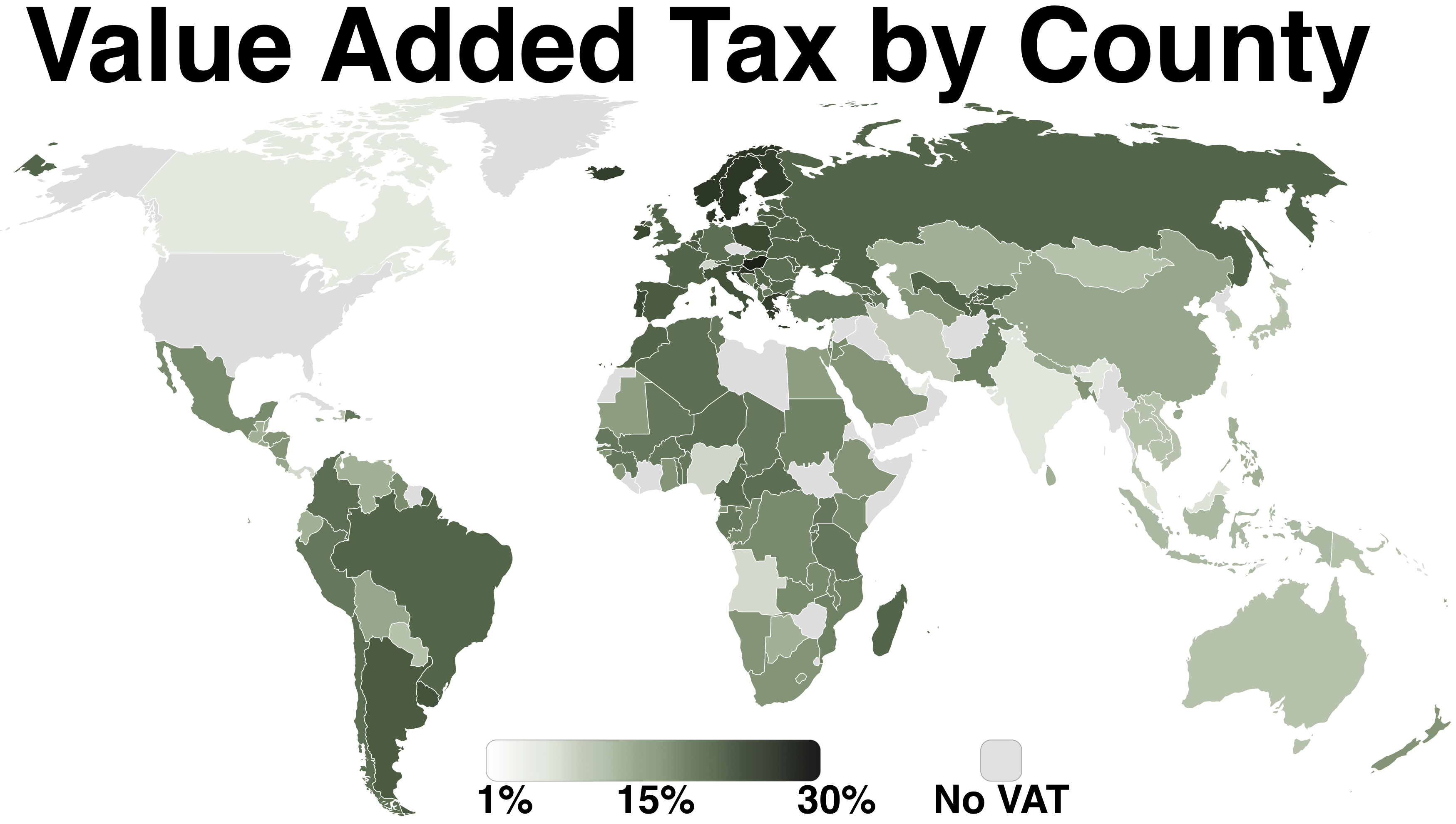
Value-added Tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the end consumer. If the ultimate consumer is a business that collects and pays to the government VAT on its products or services, it can reclaim the tax paid. It is similar to, and is often compared with, a sales tax. VAT is an indirect tax because the person who ultimately bears the burden of the tax is not necessarily the same person as the one who pays the tax to the tax authorities. Not all localities require VAT to be charged, and exports are often exempt. VAT is usually implemented as a destination-based tax, where the tax rate is based on the location of the consumer and applied to the sales price. The terms VAT, GST, and the more general consumption tax are sometimes used interchangeably. VAT raises about a fifth of total tax revenues bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FinTS
FinTS (Financial Transaction Services), formerly known as HBCI (Home Banking Computer Interface), is a bank-independent protocol for online banking, developed and used by German banks. HBCI was originally designed by Germany's three banking "pillar" networks, namely the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe, German Cooperative Financial Group, and Association of German Banks. The result of this effort was an open protocol specification, which is publicly available. The standardisation effort was necessary to replace the huge number of deprecated homemade software clients and servers (some of them still using BTX emulation). While IFX (Interactive Financial Exchange), OFX (Open Financial Exchange) and SET (Secure Electronic Transaction) are tailored for the North American market, HBCI is designed to meet the requirements of the European market. The FinTS-specification is publicly available on a website run by the ZKA ( Central Credit Committee). Features * Support for online-banking using PIN/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |