|
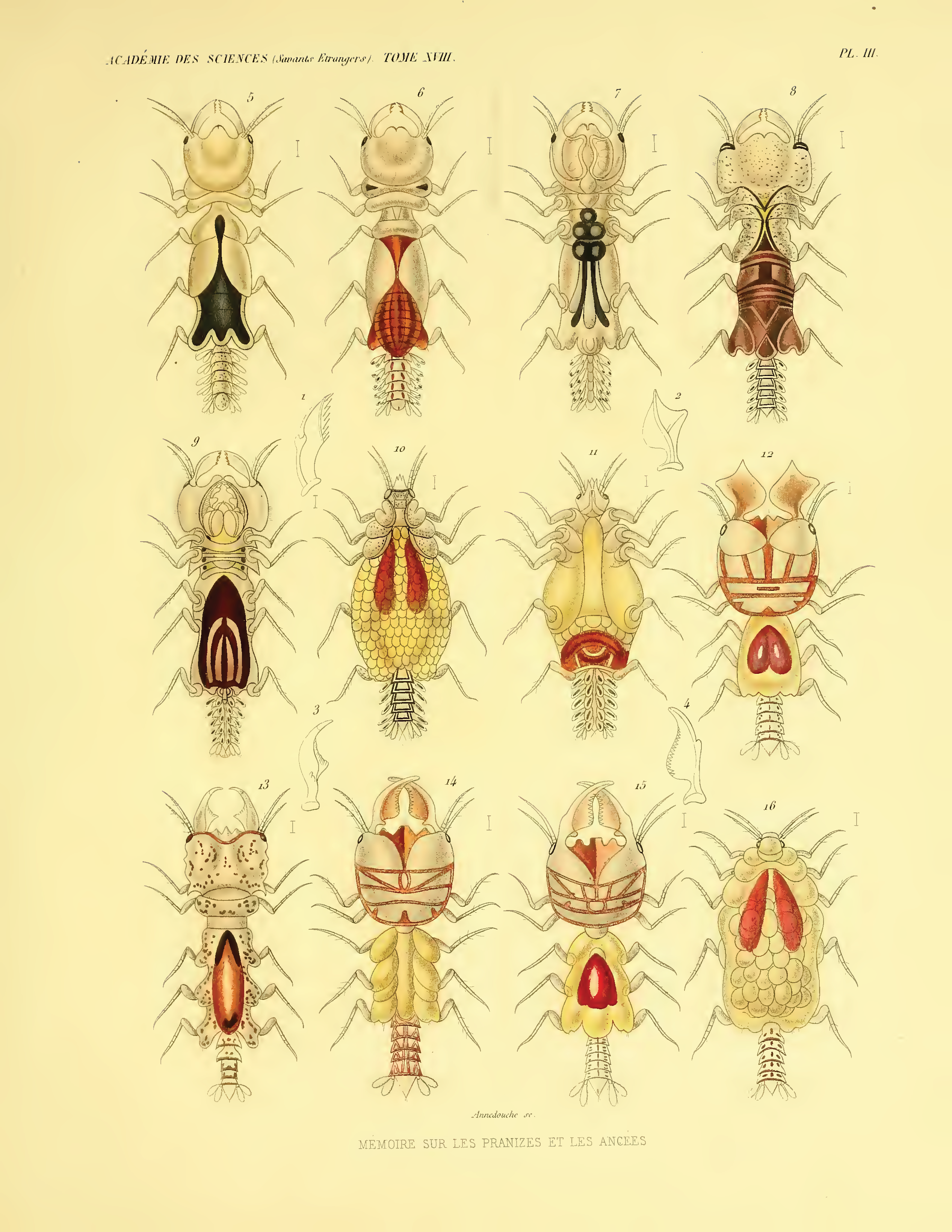
Gnathiidae
The Gnathiidae are a family of isopod crustaceans. They occur in a wide range of depths, from the littoral zone to the deep sea. The adults are associated with sponges and may not feed. The juvenile form is known as a 'praniza', and it is a temporary parasite of marine fish. These forms are not larvae; ''Gnathiidae'' instead become parasitic during the manca stage. Mancae of the ''Gnathiidae'' closely resemble the adult form, however they lack the final pair of pereiopods. Taxonomy in the family relies on male characters, such that females and juveniles cannot be reliably identified. The family contains 182 species, divided among the following genera: *'' Afrignathia'' Hadfield & Smit, 2008 *'' Bathygnathia'' Dollfus, 1901 *'' Bythognathia'' Camp, 1988 *'' Caecognathia'' Dollfus, 1901 *'' Elaphognathia'' Monod, 1926 *'' Euneognathia'' Stebbing, 1893 *'' Gibbagnathia'' Cohen & Poore, 1994 *''Gnathia ''Gnathia'' is a genus of isopod crustaceans, containing the following sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnathia
''Gnathia'' is a genus of isopod crustaceans, containing the following species: *'' Gnathia africana'' Barnard, 1914 *'' Gnathia albescens'' Hansen, 1916 *'' Gnathia alces'' Monod, 1926 *'' Gnathia andrei'' Pires, 1996 *''Gnathia antarctica'' (Studer, 1883) *''Gnathia antonbruunae'' Kensley, Schotte & Poore, 2009 *''Gnathia arabica'' Schotte, 1995 *''Gnathia arctica'' Gurjanova, 1929 *''Gnathia asperifrons'' Holdich & Harrison, 1980 *''Gnathia aureola'' Stebbing, 1900 *''Gnathia aureumaculosa'' Ferreiera, Smit, Grutter & Davies, 2009 *''Gnathia barnardi'' Smit & Basson, 2002 *''Gnathia beethoveni'' Paul & Menzies, 1971 *''Gnathia bengalensis'' Kumari, Hanumantha, Rao & Shyamasundari, 1993 *'' Gnathia biorbis'' Holdich & Harrison, 1980 *'' Gnathia brachyuropus'' Monod, 1926 *''Gnathia brucei'' George, 2003 *'' Gnathia bungoensis'' Nunomura, 1982 *'' Gnathia calamitosa'' Monod, 1926 *'' Gnathia calmani'' Monod, 1926 *'' Gnathia calsi'' Mueller, 1993 *'' Gnathia camponotus'' Cohen & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopoda
Isopoda is an order of crustaceans that includes woodlice and their relatives. Isopods live in the sea, in fresh water, or on land. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons, two pairs of antennae, seven pairs of jointed limbs on the thorax, and five pairs of branching appendages on the abdomen that are used in respiration. Females brood their young in a pouch under their thorax. Isopods have various feeding methods: some eat dead or decaying plant and animal matter, others are grazers, or filter feeders, a few are predators, and some are internal or external parasites, mostly of fish. Aquatic species mostly live on the seabed or bottom of freshwater bodies of water, but some taxa can swim for a short distance. Terrestrial forms move around by crawling and tend to be found in cool, moist places. Some species are able to roll themselves into a ball as a defense mechanism or to conserve moisture. There are over 10,000 identified species of isopod worldwide, with around 4,50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Crustaceans
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host's body; an ect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cymothoida
Cymothoida is the name of a suborder of isopod crustaceans with a mostly carnivorous or parasitic lifestyle. It contains more than 2,700 described species in four superfamilies. Members of the suborder are characterised by their specialised mouthparts which include a mandible with a tooth-like process which is adapted for cutting or slicing. Classification Cymothoida contains these superfamilies and families: *Superfamily Anthuroidea Leach, 1814 ** Antheluridae Poore & Lew Ton, 1988 ** Anthuridae Leach, 1814 ** Expanathuridae Poore, 2001 ** Hyssuridae Wägele, 1981 ** Leptanthuridae Poore, 2001 ** Paranthuridae Menzies & Glynn, 1968 *Superfamily Cymothooidea Leach, 1814 **Aegidae White, 1850 **Anuropidae Stebbing, 1893 ** Barybrotidae Hansen, 1890 **Cirolanidae Dana, 1852 ** Corallanidae Hansen, 1890 ** Cymothoidae Leach, 1818 **Gnathiidae Leach, 1814 ** Protognathiidae Wägele & Brandt, 1988 ** Tridentellidae Bruce, 1984 *Superfamily Cryptoniscoidea Kossmann, 1880 **Asconisc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitism
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted paras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manca
The manca (plural: ''mancae'') is the post- larval juvenile in some crustaceans. The manca stage is the defining characteristic of a clade called Mancoida which comprises all the member of the Peracarida except the Amphipoda. Mancae closely resemble the adult form, but for the absence of the last pair of pereiopods. In some isopods, specifically the family Gnathiidae, the manca stage is a parasite Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ... of fish, and is also known as the praniza. References Crustaceans Developmental biology Larvae {{crustacean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Théodore Monod
Théodore André Monod (9 April 1902 – 22 November 2000) was a French naturalist, humanist, scholar and explorer. Exploration Early in his career, Monod was made professor at the ''Muséum national d'histoire naturelle'' and founded the '' Institut fondamental d’Afrique noire'' in Senegal. He became a member of the '' Académie des sciences d'outre-mer'' in 1949, member of the ''Académie de marine'' in 1957 and member of the ''Académie des sciences'' in 1963. In 1960, he became one of the founders of the ''World Academy of Art and Science''. He began his career in Africa with the study of monk seals on Mauritania's Cap Blanc peninsula. However, he soon turned his attention to the Sahara desert, which he would survey for more than sixty years in search of meteorites. Though he failed to find the meteorite he sought, he discovered numerous plant species as well as several important Neolithic sites. Perhaps his most important find (together with Wladimir Besnard) was the Assel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By William Elford Leach
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

