|
Gnaeus Servilius Caepio (consul 203 BC)
Gnaeus Servilius Caepio (died 174 BC) was a Roman statesman who served as Roman consul in 203 BC. He was elected Pontiff in 213 BC, replacing C. Pupilius Maso; he became Aedile in 207, celebrating the Ludi Romani three times. In 205 he became Praetor. As consul, he was the last Roman general to fight against Hannibal in Bruttium, (South Italy); after the latter left Italy, Caepio crossed over into Sicily planning to go from there into Africa. The Roman Senate, fearing that Caepio would ignore their commands, created a dictator, Publius Sulpicius Galba Maximus, to recall him. Later on, in 194 BC, he was sent as a legate to Carthage, causing Hannibal's exile to Antiochus III the Great's court. Then in 192 BC, he was sent as a legate into Greece to rile up the Roman allies in a potential conflict with Antiochus the Great. Cnaeus Servilius died in 174 BC, during a great epidemic.Livy Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Ancient Rome, Roman historia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Sulpicius Galba Maximus
Publius Sulpicius Galba Maximus (fl. late 3rd to early 2nd century BC) was a Roman military officer and Senator who was elected Roman consul A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which politic ... twice, and appointed Roman dictator, dictator once. He fought in the Second Punic War and the First and Second Macedonian Wars. First consulship and the First Macedonian War A member of the Patrician (ancient Rome), Patrician ''Sulpicia (gens), gens Sulpicia'', Sulpicius Galba was the son of Servius Sulpicius Galba. Although he had held no previous Roman magistrate, curule magistracy, the crisis of the Second Punic War saw him elected Roman consul, consul in 211 BC, alongside Gnaeus Fulvius Centumalus Maximus. Entering his office on the Roman calendar, Ides of March, both consuls defended the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
174 BC Deaths
Year 174 (Roman numerals, CLXXIV) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Gallus and Flaccus (or, less frequently, year 927 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 174 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Empress Faustina the Younger accompanies her husband, Marcus Aurelius, on various military campaigns and enjoys the love of the Roman legionary, Roman soldiers. Aurelius gives her the title of ''Mater Castrorum'' ("Mother of the Camp"). * Marcus Aurelius officially confers the title ''Fulminata'' ("Thundering") to the Legio XII Fulminata. Asia * Reign in India of Yajnashri Satakarni, Satavahana king of the Andhra Pradesh, Andhra. He extends his empire from the center to the north of India. By topic Art and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Servilius Pulex Geminus
__NoToC__ Marcus Servilius Pulex Geminus was a Roman statesman during the Second Punic War, and the early decades of the second century BC. He was a renowned warrior, whose martial prowess was commemorated on coins issued by several of his descendants. Background Servilius was the younger son of Gaius Servilius Geminus, praetor about 220 BC, and grandson of Publius Servilius Geminus, consul in 252. The Servilii Gemini were a branch of an old and distinguished patrician family, but either Gaius or his sons went over to the plebeians, for reasons that are not entirely clear. Servilius' elder brother, Gaius, was tribune of the plebs in 211 BC, consul in 203, and dictator in 202. Servilius' additional surname, ''Pulex'', refers to a flea, but the circumstances of this cognomen are not mentioned in any source. Career Servilius was augur in 211 BC, curule aedile in 204, magister equitum in 203, and consul in 202. During his consulship, he was assigned to Etruria with two legions; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiberius Claudius Nero (consul 202 BC)
Tiberius Claudius Nero ( 204–202 BC) was a Roman senator. In 204 BC, as praetor, he was assigned to govern Sardinia, in which capacity he gathered and shipped supplies of grain and clothing for soldiers under the command of Scipio in Africa. Elected consul for 202 BC, he was assigned to Africa with ''imperium'' equal to that of Scipio, but storms and delays in his preparations prevented him from ever arriving. His consular colleague was M. Servilius Pulex Geminus. He was the last consul of the Claudii Nerones until his descendant (the future emperor) Tiberius was elected in 13 BC. It is possible that this Nero was the one who in 172 BC participated in diplomatic missions. The historical sources for which pose difficulties. Livy says he was sent on an embassy with a Marcus Decimius to Asia and islands in the Aegean, including Rhodes and Crete, and travelled as far as Syria and Egypt. His task was to renew friendships and alliances, and to gather information on the influence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Servilius Geminus (consul)
Gaius Servilius Geminus (died 180 BC) was a Roman statesman who served as Consul in 203 BC, Dictator in 202 BC (the last in 120 years), and '' Pontifex Maximus'' from 183 BC to 180 BC. Heritage Geminus was the son of Gaius Servilius Geminus, a Roman magistrate. He was a member of ''gens Servilia'', a patrician family. Early career In 212 BC Geminus was sent to Etruria to buy grain for the troops of the Roman garrison in Tarentum, then besieged by Hannibal. He successfully penetrated into the city and delivered supplies. In 210 BC he was elected Pontifex in place of Titus Otacilius Crassus and in 209 BC was chosen as Aedile. He was selected to serve as ''magister equitum'', while exercising his position as Aedile, under dictator Titus Manlius Torquatus. In 206 BC he became praetor and obtained Sicily as a province.Livy, 28.10 Consulship and later career Geminus was elected consul, alongside Gnaeus Servilius Caepio, in 203 BC, and obtained Etruria as a province. From there he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Roman Republican Consuls
This is a list of consuls known to have held office, from the beginning of the Roman Republic to the latest use of the title in Imperial times, together with those magistrates of the Republic who were appointed in place of consuls, or who superseded consular authority for a limited period. Background Republican consuls From the establishment of the Republic to the time of Augustus, the consuls were the chief magistrates of the Roman state, and normally there were two of them, so that the executive power of the state was not vested in a single individual, as it had been under the kings. As other ancient societies dated historical events according to the reigns of their kings, it became customary at Rome to date events by the names of the consuls in office when the events occurred, rather than (for instance) by counting the number of years since the foundation of the city, although that method could also be used. If a consul died during his year of office, another was elected to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Sempronius Tuditanus
Publius Sempronius C.f. Tuditanus (fl. 3rd century BC) was a Roman Republican consul and censor, best known for leading about 600 men to safety at Cannae in August, 216 BC and for the Treaty of Phoenice which ended the First Macedonian War, in 205 BC. Tuditanus at Cannae The consul L. Aemilius Paullus (who died at Cannae) had left a reserve camp of about 10,000 men on the other bank. These men who did not participate in the battle had three choices after the disastrous battle: surrender to Hannibal, attempt to break through the Carthaginian lines and escape, or stand their ground and die fighting. The smaller of the two camps was besieged by the Carthaginians. One of the few Roman officers who survived that fatal day, Publius Sempronius C.f. Tuditanus, along with his fellow tribune Gaius Octavius, advised that the men put on their shields, form a shield-wall, and break out through the lines of the exhausted Carthaginian army. Very few men agreed to go with him, the rest decidin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Cornelius Cethegus (consul 204 BC)
__NOTOC__ Marcus Cornelius Cethegus (c. 248 BC196 BC) was a Roman Republican consul and censor during the Second Punic War, best known as a political ally of his kinsman Scipio Africanus. Political career He was chosen as curule aedile in 213 BC, with his young kinsman Scipio Africanus as his colleague (although Scipio was under-age, being only 22 or 23 compared to the usual mid-thirties). He was appointed ''pontifex'' to replace the '' pontifex maximus'' Lucius Cornelius Lentulus Caudinus who had died. In 211 BC, as praetor, he was in charge of Apulia. In 209 BC, before he had been consul, he was elected censor with Publius Sempronius Tuditanus. During their censorship, Cethegus disagreed with his colleague about which senator should be elected Princeps Senatus. Tuditanus had the right of choice and chose Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, while Cethegus wanted the most senior censor Titus Manlius Torquatus to be the Princeps Senatus''.'' In 204 BC, he was elected consul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
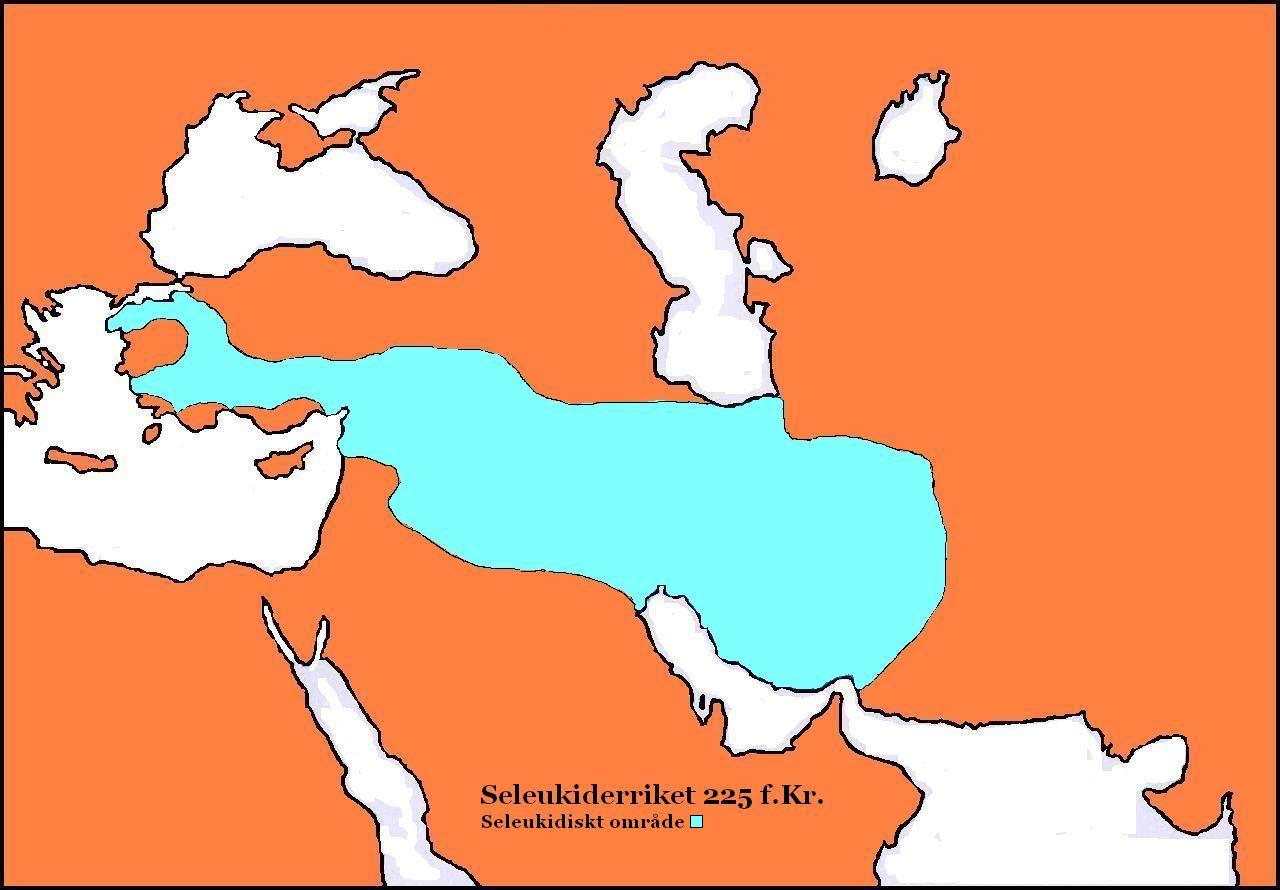
Antiochus III The Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legatus
A ''legatus'' (; anglicised as legate) was a high-ranking Roman military officer in the Roman Army, equivalent to a modern high-ranking general officer. Initially used to delegate power, the term became formalised under Augustus as the officer in command of a legion. From the times of the Roman Republic, legates received large shares of the military's rewards at the end of a successful campaign. This made the position a lucrative one, so it could often attract even distinguished consuls or other high-ranking political figures within Roman politics (e.g., the consul Lucius Julius Caesar volunteered late in the Gallic Wars as a legate under his first cousin, Gaius Julius Caesar). History Roman Republic The rank of legatus existed as early as the Samnite Wars, but it was not until 190 BC that it started to be standardized, meant to better manage the higher numbers of soldiers the Second Punic War had forced to recruit. The legatus of a Roman Republican army was essentially a sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |