|
Glympeis
Glyppia or Glympia ( grc, Γλυππία) was a village of ancient Laconia in Mount Parnon, situated near the frontiers of Argolis and Cynuria. Glyppia is the name in Pausanias, who simply describes it as situated in the interior above Marius. It appears to be the same place as the fortress called Glympeis (Γλυμπεῖς) by Polybius, who places it near the borders of the Argolis and Laconia, and who relates that the Messenians were defeated here in 218 BCE by the Spartans, when they were endeavouring, by a round-about march from Tegea, to penetrate into the southern valley of the Eurotas In Greek mythology, Eurotas (; Ancient Greek: Εὐρώτας) was a king of Laconia. Family Eurotas was the son of King Myles of Laconia and grandson of Lelex, eponymous ancestor of the Leleges. The '' Bibliotheca'' gave a slight variant of the .... It is also mentioned on another occasion by Polybius (4.36). Its site is located near the modern Agios Vasileios. References Pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynuria
Cynuria ( – ''Kynouria'' or – ''Kynouriake'') is an ancient district on the eastern coast of the Peloponnese, between the Argolis and Laconia, so called from the Cynurians, one of the most ancient tribes in the peninsula. It was believed to have taken its name from the mythical Cynurus. Location and history Herodotus regarded the Cynurians as autochthones, but at the same time called them Ionians. There can be little doubt, however, that they were Pelasgians; but in consequence of their maritime position, they were regarded as a different race from the Arcadian Pelasgians, and came to be looked upon as Ionians, which was the case with the Pelasgians dwelling upon the coast of the Gulf of Corinth, in the district afterwards called Achaia. They were a semi-barbarous and predatory tribe, dwelling chiefly in the eastern slopes of Mount Parnon; but their exact boundaries cannot be defined, as they were only a tribe, and never formed a political body. At a later time they were alm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
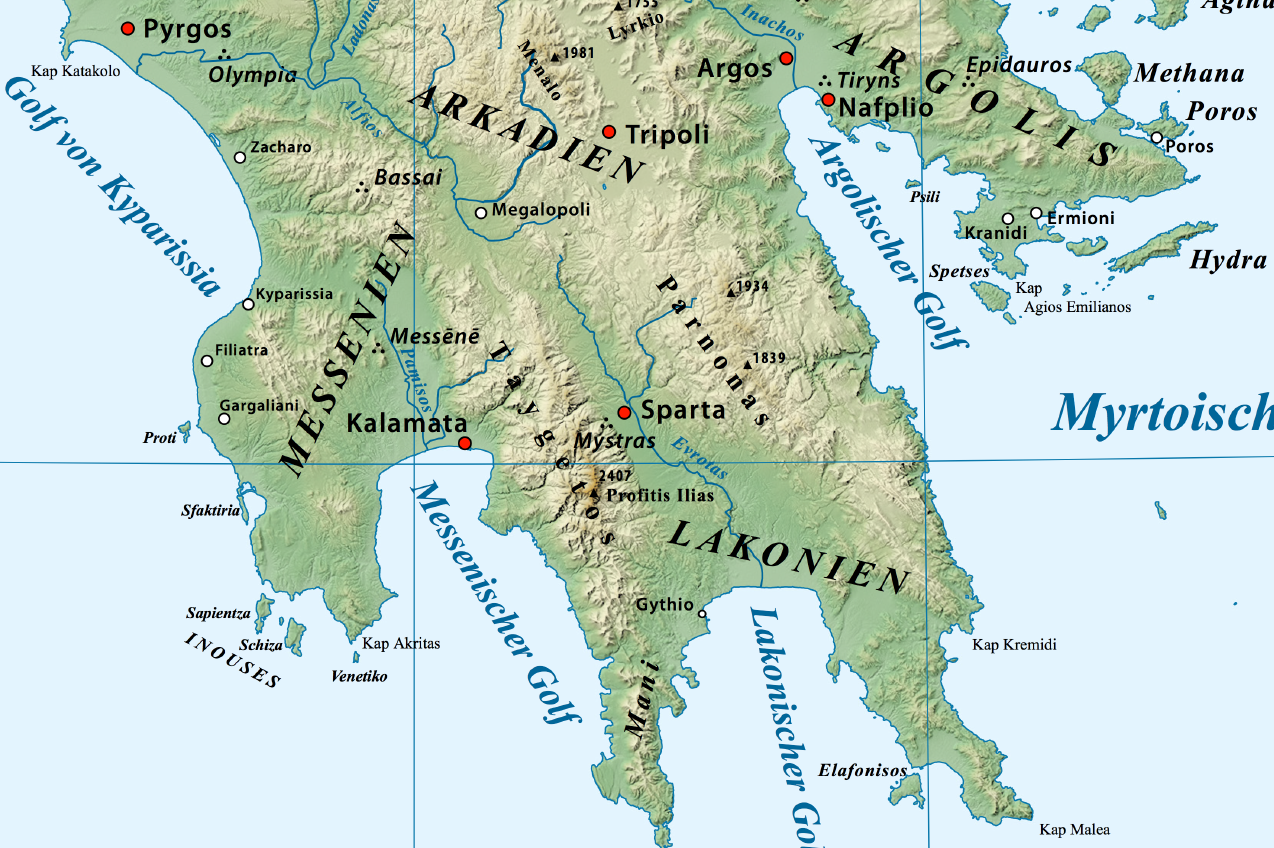
Ancient Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia ( el, Λακωνία, , ) is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word ''laconic''—to speak in a blunt, concise way—is derived from the name of this region, a reference to the ancient Spartans who were renowned for their verbal austerity and blunt, often pithy remarks. Geography Laconia is bordered by Messenia to the west and Arcadia to the north and is surrounded by the Myrtoan Sea to the east and by the Laconian Gulf and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. It encompasses Cape Malea and Cape Tainaron and a large part of the Mani Peninsula. The Mani Peninsula is in the west region of Laconia. The islands of Kythira and Antikythera lie to the south, but they administratively belong to the Attica regional unit of islands. The island, Elafonisos, situated between the Laconian mainland and Kythira, is part of Laconia. The Eurotas is the longe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Parnon
Parnon or Parnonas ( el, Πάρνων/Πάρνωνας) or Malevos (Μαλεβός) is a mountain range, or massif, on the east of the Laconian plain and the Evrotas valley. It is visible from Athens above the top of the Argive mountains. The western part is in the Laconia prefecture and the northeastern part is in the Arcadia prefecture. The Parnon range separates Laconia from Arcadia. Its summit offers panoramic views of southeastern Arcadia and South Kynouria and much of Laconia that includes the northern and the central portions and reaches as far as the Taygetos mountains. It also views a part of the central Arcadia and the southern Argolis prefectures. It views the Myrtoan and the Laconian Gulfs. Geography Physical The Parnon Massif is divided into three parts.Unless otherwise cited this section relies heavily on The northernmost, which is the highest, runs from just north of Ano Doliana in North Kynouria, eastern Arcadia, southeast to Platanaki Pass. Platanaki, ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias ( /pɔːˈseɪniəs/; grc-gre, Παυσανίας; c. 110 – c. 180) was a Greek traveler and geographer of the second century AD. He is famous for his ''Description of Greece'' (, ), a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from his firsthand observations. ''Description of Greece'' provides crucial information for making links between classical literature and modern archaeology. Biography Not much is known about Pausanias apart from what historians can piece together from his own writing. However, it is mostly certain that he was born c. 110 AD into a Greek family and was probably a native of Lydia in Asia Minor. From c. 150 until his death in 180, Pausanias travelled through the mainland of Greece, writing about various monuments, sacred spaces, and significant geographical sites along the way. In writing ''Description of Greece'', Pausanias sought to put together a lasting written account of "all things Greek", or ''panta ta hellenika''. Living in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marius (Laconia)
Marius or Marios ( grc, Μαρίος) was a town of ancient Laconia, belonging in the time of Pausanias (2nd century) to the Eleuthero-Lacones; it was situated 100 stadia east of Geronthrae. It contained a sanctuary of all the gods and, one of Artemis, and in each there were copious springs of water. It is represented by Mari, which stands on the road from Geraki (Geronthrae) over the mountains to Kremasti Kremasti ( el, Κρεμαστή) is a town on the Greek island of Rhodes (', ''Ródhos''). Located on the west coast of the island, Kremasti is 12 kilometers from the capital of Rhodes, on the road to the airport. It has a population of 5,363 .... There are ruins of the ancient town about a mile and a half (2.5 km) to the south of the modern village, and the place is still characterised by its abundant fountains., 3.22.8. References Populated places in ancient Laconia Former populated places in Greece {{AncientLaconia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail. Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed constitution or the separation of powers in government, his in-depth discussion of checks and balances to limit power, and his introduction of "the people", which influenced Montesquieu's ''The Spirit of the Laws'', John Locke's ''Two Treatises of Government'', and the framers of the United States Constitution. The leading expert on Polybius for nearly a century was F. W. Walbank (1909–2008), who published studies related to him for 50 years, including a long commentary of his ''Histories'' and a biography. Early life Polybius was born around 200 BC in Megalopolis, Greece, Megalopolis, Arcadia (region), Arcadia, when it was an active member of the Achaean League. The town was revived, along with other Achaean states, a century before he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Messenia
Messenia or Messinia ( el, Μεσσηνία) was an ancient district of the southwestern Peloponnese, more or less overlapping the modern Messenia region of Greece. To the north it had a border with Elis along the Neda river. From there the border with Arcadia ran along the tops of Mount Elaeum and Mount Nomia and then through foothills of Taygetus. The eastern border with Laconia went along the Taygetus ridge up to the Koskaraka river, and then along that river to the sea, near the city of Abia. Ancient Messenia descended continuously without change of name and with little change of territory to the modern Regional Unit of Greece of the same name. History Bronze age The earliest inhabitants of Messenia were thought by the Greeks of the Classical period to have been 'Pelasgians', as in other regions of Greece. Supposedly, the Hellenic tribes had then arrived in Greece, and Messenia was settled by Aeolian Greeks. The Mycenaean city of Pylos has been identified with the modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tegea
Tegea (; el, Τεγέα) was a settlement in ancient Arcadia, and it is also a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the Tripoli municipality, of which it is a municipal unit with an area of 118.350 km2. It is near the modern villages of Alea and Episkopi. The legendary founder of Tegea was Tegeates, a son of Lycaon. History Tegea ( grc, Τεγέα; grc-x-ionic, Τεγέη) was one of the most ancient and powerful towns of ancient Arcadia, situated in the southeast of the country. Its territory, called Tegeatis (Τεγεᾶτις), was bounded by Cynuria and Argolis on the east, from which it was separated by Mount Parthenium, by Laconia on the south, by the Arcadian district of Maenalia on the west, and by the territory of Mantineia on the north. The Tegeatae are said to have derived their name from Tegeates, a son of Lycaon, and to have dwelt originally in eight, afterwards nine, demoi or townships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurotas (river)
The Eurotas ( grc, Εὐρώτας) or Evrotas (modern Greek: ) is the main river of Laconia and one of the major rivers of the Peloponnese, in Greece. The river's springs are located just northwest of the border between Laconia and Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia, at Skortsinos. The river is also fed by underwater springs at Pellana and by tributaries coursing down from Taygetos, Mt. Taygetos and Parnon, Mt. Parnon, which flank the Eurotas valley to the west and east, respectively. The river is long, flowing in a north-south direction and emptying into the Laconian Gulf. Its drainage basin is . Etymology The classical Eurotas was changed to Iri in the Middle Ages and only changed back to Eurotas in recent times. Eurotas, however, is not the most ancient name of the river. It does not appear in the works of Homer, which purport to recount the stories and geography of Mycenaean Greece. In that legendary time, the Dorians are not known to have been present in the Eurotas Valley. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |