|
Glowmatography
Glowmatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of dyes present in solutions contained in glow sticks. The chemical components of such solutions can be chromatography, chromatographically separated into Chemical polarity, polar and nonpolar components. Developed as a laboratory class experiment, it can be used to demonstrate chemistry concepts of polarity, chemical kinetics, and chemiluminescence. Description In the chromatography of a glow stick solution, a piece of Sidewalk chalk, chalk, a highly polarity (chemistry), polar substance, is used as the stationary phase (chemistry), stationary phase while comparatively less-polar solvents like acetone and 91% isopropyl alcohol can be used as the mobile phase. Chalk is made up of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) or calcium sulfate (CaSO4), and therefore contains ions. This allows it to attract other ions and polar molecules, but not nonpolar molecules. As a result, ionic and more-polar dyes would be attracted to the stationar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glowmatography
Glowmatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of dyes present in solutions contained in glow sticks. The chemical components of such solutions can be chromatography, chromatographically separated into Chemical polarity, polar and nonpolar components. Developed as a laboratory class experiment, it can be used to demonstrate chemistry concepts of polarity, chemical kinetics, and chemiluminescence. Description In the chromatography of a glow stick solution, a piece of Sidewalk chalk, chalk, a highly polarity (chemistry), polar substance, is used as the stationary phase (chemistry), stationary phase while comparatively less-polar solvents like acetone and 91% isopropyl alcohol can be used as the mobile phase. Chalk is made up of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) or calcium sulfate (CaSO4), and therefore contains ions. This allows it to attract other ions and polar molecules, but not nonpolar molecules. As a result, ionic and more-polar dyes would be attracted to the stationar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glow Sticks
A glow stick, also known as a light stick, chem light, light wand, light rod, and rave light, is a self-contained, short-term light-source. It consists of a translucent plastic tube containing isolated substances that, when combined, make light through chemiluminescence. The light cannot be turned off and can be used only once. The used tube is then thrown away. Glow sticks are often used for recreation, such as for events, camping, outdoor exploration, and concerts. Glow sticks are also used for light in military and emergency services applications. Industrial uses include marine, transportation, and mining. History Bis(2,4,5-trichlorophenyl-6-carbopentoxyphenyl)oxalate, trademarked "Cyalume", was invented in 1971 by Michael M. Rauhut, of American Cyanamid, based on work by Edwin A. Chandross of Bell Labs. Other early work on chemiluminescence was carried out at the same time, by researchers under Herbert Richter at China Lake Naval Weapons Center. Several US patents for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be preparative or analytical. The purpose of preparativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stationary Phase (chemistry)
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be preparative or analytical. The purpose of preparativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatogram
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be preparative or analytical. The purpose of preparativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glow Stick Solution And Chalks
Glow or GLOW may refer to: In science and technology In computing and telecommunications * Glow (JavaScript library), an open-source JavaScript library created by the BBC * Glow (Scottish Schools National Intranet), a telecommunications project in Scotland In physics * Incandescence, the emission of electromagnetic radiation from a hot object * Luminescence, any form of light emission ''not'' resulting from heat * List of light sources Other uses in science and technology * Glow or Bloom (shader effect), computer graphics effect * GLOW (gross lift-off weight), see maximum takeoff weight In arts and entertainment In film and television * ''The Glow'' (film), a 2002 TV film starring Portia de Rossi * ''Glow'' (2000 film), a film starring Frankie Ingrassia * ''Glow'' (2011 film), a film starring Tony Lo Bianco * ''The Glow'' (TV series), a 2000s television series starring Dean Cain * GLOW TV, a syndicated televised version of the Gorgeous Ladies of Wrestling events from 1986 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonpolar Molecules
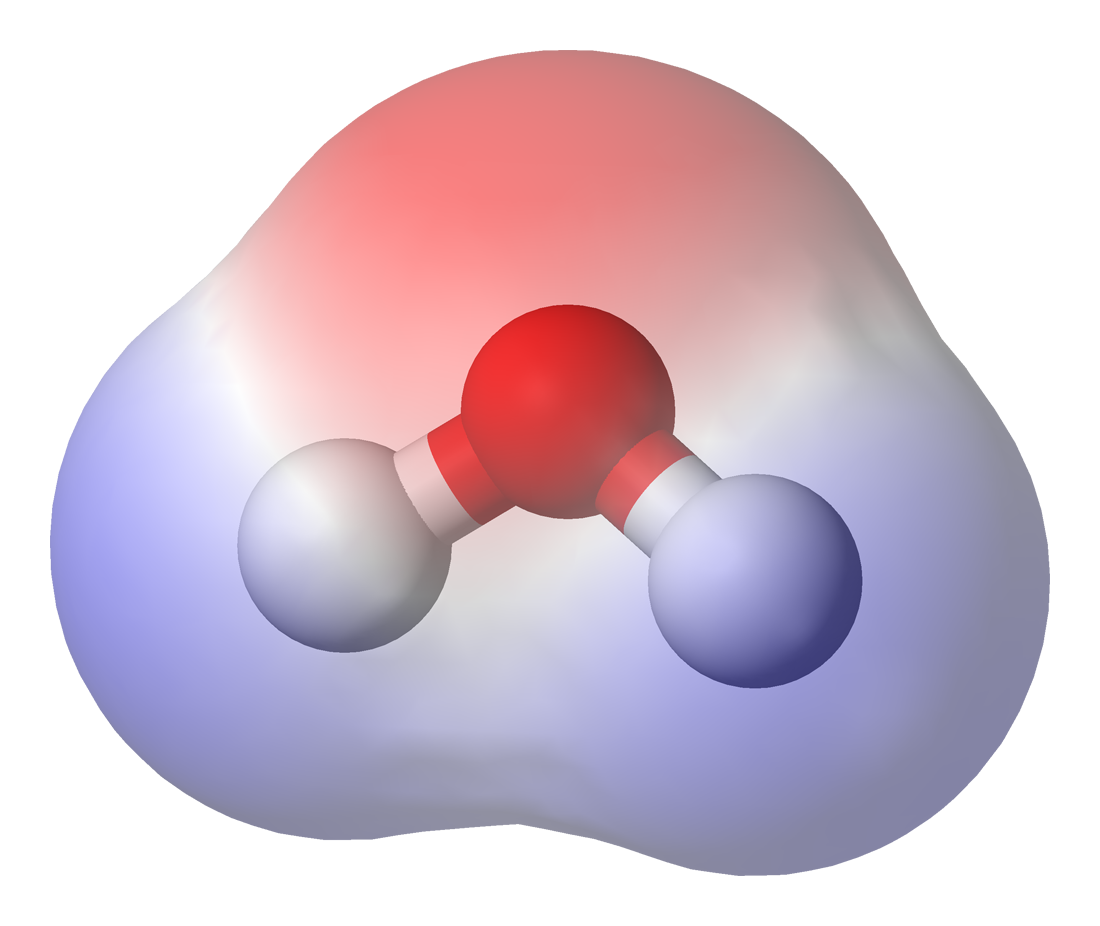
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retardation Factor
In chromatography, the retardation factor (''R'') is the fraction of an analyte in the mobile phase of a chromatographic system. In planar chromatography in particular, the retardation factor ''R''F is defined as the ratio of the distance traveled by the center of a spot to the distance traveled by the solvent front. Ideally, the values for ''RF'' are equivalent to the R values used in column chromatography. Although the term retention factor is sometimes used synonymously with retardation factor in regard to planar chromatography the term is not defined in this context. However, in column chromatography, the retention factor or capacity factor (''k'') is defined as the ratio of time an analyte is retained in the stationary phase to the time it is retained in the mobile phase, which is inversely proportional to the retardation factor. General definition In chromatography, the retardation factor, ''R'', is the fraction of the sample in the mobile phase at equilibrium, defined as: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Solvent
Green chemistry, also called sustainable chemistry, is an area of chemistry and chemical engineering focused on the design of products and processes that minimize or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. While environmental chemistry focuses on the effects of polluting chemicals on nature, green chemistry focuses on the environmental impact of chemistry, including lowering consumption of nonrenewable resources and technological approaches for preventing pollution. The overarching goals of green chemistry—namely, more resource-efficient and inherently safer design of molecules, materials, products, and processes—can be pursued in a wide range of contexts. History Green chemistry emerged from a variety of existing ideas and research efforts (such as atom economy and catalysis) in the period leading up to the 1990s, in the context of increasing attention to problems of chemical pollution and resource depletion. The development of green chemistry in Europe a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Carbon Dioxide
Liquid carbon dioxide is the liquid state of carbon dioxide (), which cannot occur under atmospheric pressure. It can only exist at a pressure above , under (temperature of critical point) and above (temperature of triple point). Low-temperature carbon dioxide is commercially used in its solid form, commonly known as "dry ice". Solid sublimes at at Earth atmospheric pressure — that is, it transitions directly from solid to gas without an intermediate liquid stage. The uses and applications of liquid carbon dioxide include decaffeinating coffee, extracting virgin olive oil from olive paste, in fire extinguishers, and as a coolant. Properties Liquid carbon dioxide is a type of liquid which is formed from highly compressed and cooled gaseous carbon dioxide. It does not form under atmospheric conditions. It only exists when the pressure is above 5.1 atm and the temperature is under (temperature of critical point) and above (temperature of triple point). The chemical symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silanol
A silanol is a functional group in silicon chemistry with the connectivity Si–O–H. It is related to the hydroxy functional group (C–O–H) found in all alcohols. Silanols are often invoked as intermediates in organosilicon chemistry and silicate mineralogy. If a silanol contains one or more organic residue, it is an organosilanol. Preparation From alkoxysilanes The first isolated example of a silanol was , reported in 1871 by Albert Ladenburg. He prepared the “silicol” by hydrolysis of (Et = ). From silyl halides and related compounds Silanols are generally synthesized by hydrolysis of halosilanes, alkoxysilanes, or aminosilanes. Chlorosilanes are the most common reactants: :R3Si–Cl + H2O → R3Si–OH + HCl The hydrolysis of fluorosilanes requires more forcing reagents, i.e. alkali. The alkoxysilanes (silyl ethers) of the type are slow to hydrolyze. Compared to the silyl ethers, silyl acetates are faster to hydrolyze, with the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexanes
Hexane () is an organic compound, a straight-chain alkane with six carbon atoms and has the molecular formula C6H14. It is a colorless liquid, odorless when pure, and with boiling points approximately . It is widely used as a cheap, relatively safe, largely unreactive, and easily evaporated non-polar solvent, and modern gasoline blends contain about 3% hexane. The term ''hexanes'' refers to a mixture, composed largely (>60%) of hexane, with varying amounts of the isomeric compounds 2-methylpentane and 3-methylpentane, and, possibly, smaller amounts of nonisomeric C5, C6, and C7 (cyclo)alkanes. These ''hexanes'' are cheaper than pure hexane and are often used in large-scale operations not requiring a single isomer (e.g., as cleaning solvent or for chromatography). Isomers Uses In industry, hexanes are used in the formulation of adhesive, glues for shoes, leather products, and roofing. They are also used to extract cooking oils (such as canola oil or soy oil) from seeds, for c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |