|
Glossary Of HVAC Terms
HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) is a major sub discipline of mechanical engineering. The goal of HVAC design is to balance indoor environmental comfort with other factors such as installation cost, ease of maintenance, and energy efficiency. The discipline of HVAC includes a large number of specialized terms and acronyms, many of which are summarized in this glossary. : The hourly ventilation rate divided by the volume of a space. For perfectly mixed air or laminar flow spaces, this is equal to the number of times per hour that the volume the space is exchanged by mechanical and natural ventilation. Also called air change rate or air exchange rate. Abbreviated ACH or ac/hr. : An appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. Usually this term is reserved for smaller self-contained units such as a residential system. : A central unit consisting of a blower, heating and cooling elements, filter racks or chamber, dampers, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HVAC
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers). HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes, apartment buildings, hotels, and senior living facilities; medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals; vehicles such as cars, trains, airplanes, ships and submarines; and in marine environments, where safe and Sick building syndrome, healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dropped Ceiling
A dropped ceiling is a secondary ceiling, hung below the main (structural) ceiling. It may also be referred to as a drop ceiling, T-bar ceiling, false ceiling, suspended ceiling, grid ceiling, drop in ceiling, drop out ceiling, or ceiling tiles and is a staple of modern construction and architecture in both residential and commercial applications. History Dropped ceilings and ceiling tiles were used in Japan for aesthetic reasons as early as the Muromachi Period (1337 to 1573).Interview with Matthew Welch, Curator of Japanese and Korean Art, Minneapolis Institute of Arts retrieved January 12, 2014 These could be made with simple planks, or |
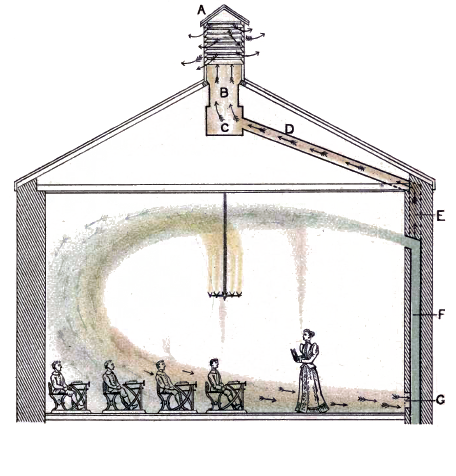
PLENUM
Plenum may refer to: * Plenum chamber, a chamber intended to contain air, gas, or liquid at positive pressure * Plenism, or ''Horror vacui'' (physics) the concept that "nature abhors a vacuum" * Plenum (meeting), a meeting of a deliberative assembly in which all members are present; contrast with quorum * Plenum space, enclosed spaces (in buildings) used for airflow * Plenum cable, electrical wire permitted in plenum spaces per building codes * Plenum Publishing Corporation, a publisher of scientific books and journals * Plenum (physics), a space completely filled with matter * Undergravel filters, in aquarium filtration, an open space under a layer of gravel or sand * Air-mixing plenum In building services engineering and HVAC, an air-mixing plenum (or mixing box) is used for mixing air from different ductwork systems. Usage The most common application for an air-mixing plenum is the mixing of ''return air'' (or ''extract ai ..., a place where ducts meet See also * Plenar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
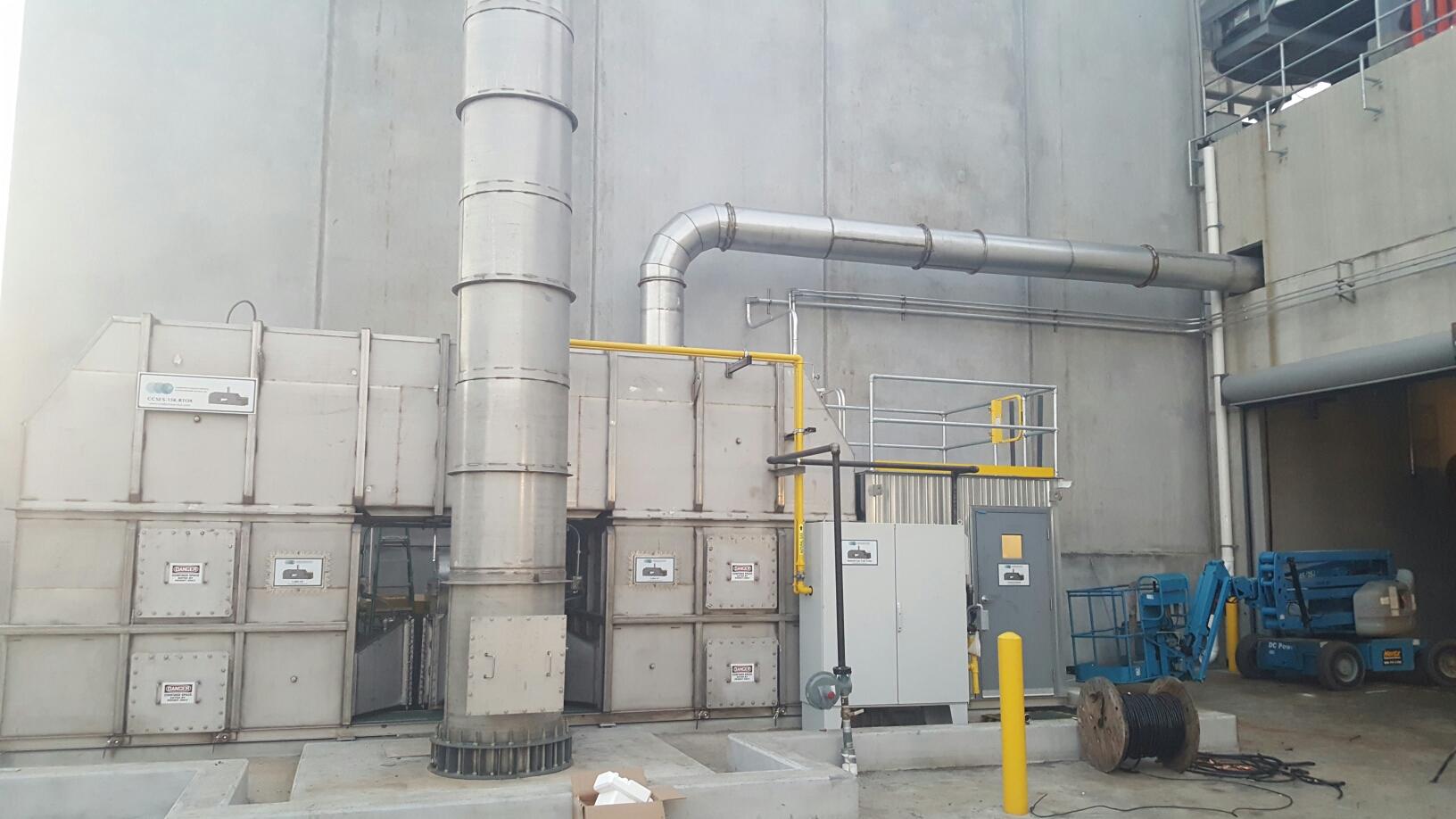
Air Handler
An air handler, or air handling unit (often abbreviated to AHU), is a device used to regulate and circulate air as part of a heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning (HVAC) system. An air handler is usually a large metal box containing a blower, heating or cooling elements, filter racks or chambers, sound attenuators, and dampers. Air handlers usually connect to a ductwork ventilation system that distributes the conditioned air through the building and returns it to the AHU. Sometimes AHUs discharge (''supply'') and admit (''return'') air directly to and from the space served without ductwork Small air handlers, for local use, are called terminal units, and may only include an air filter, coil, and blower; these simple terminal units are called blower coils or fan coil units. A larger air handler that conditions 100% outside air, and no recirculated air, is known as a makeup air unit (MAU) or fresh air handling unit (FAHU). An air handler designed for outdoor use, typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plenum Chamber
A plenum chamber is a pressurised housing containing a fluid (typically air) at positive pressure. One of its functions is to equalise pressure for more even distribution, compensating for irregular supply or demand. It is typically relatively large in volume and thus has relatively low velocity compared to the system's other components. In wind tunnels, rockets, and many flow applications, it is a chamber upstream on the fluid flow where the fluid initially resides (approximately at rest). It can also work as an acoustic silencer. Examples of plenum chambers include those used with: * Superchargers * Hovercraft * Corliss steam engines * Raised floors and false ceilings in equipment rooms * Some organs (to supplement the bellows) * A number of aerophones, such as the bag of bagpipes and the ''slow air chamber'' of the Native American flute * Plenum chamber anesthetic vaporizers * Rocket motor combustion chambers, which may have a section near the nozzle that is free of the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plenum Cable
__NOTOC__ Plenum cable is electrical cable that is laid in the plenum spaces of buildings. In the United States, plastics used in the construction of plenum cable are regulated under the National Fire Protection Association standard NFPA 90A: Standard for the Installation of Air Conditioning and Ventilating Systems. All materials intended for use on wire and cables to be placed in plenum spaces are designed to meet rigorous fire safety test standards in accordance with NFPA 262 and outlined in NFPA 90A. Plenum cable is jacketed with a fire-retardant plastic jacket of either a low-smoke polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or a fluorinated ethylene polymer ( FEP). Polyolefin formulations, specifically based on polyethylene compounding had been developed by at least two companies in the early to mid-1990s; however, these were never commercialized, and development efforts continue in these yet-untapped product potentials. Development efforts on a non-halogen plenum compound were announced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duct (HVAC)
Ducts are conduits or passages used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) to deliver and remove air. The needed airflows include, for example, ''supply air'', ''return air'', and ''exhaust air''. Ducts commonly also deliver '' ventilation air'' as part of the supply air. As such, air ducts are one method of ensuring acceptable indoor air quality as well as thermal comfort. A duct system is also called ''ductwork''. Planning (laying out), sizing, optimizing, detailing, and finding the pressure losses through a duct system is called ''duct design''. Materials Ducts can be made out of the following materials: Galvanized steel Galvanized mild steel is the standard and most common material used in fabricating ductwork because the zinc coating of this metal prevents rusting and avoids cost of painting. For insulation purposes, metal ducts are typically lined with faced fiberglass blankets (duct liner) or wrapped externally with fiberglass blankets (duct wrap). When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raised Floor
A raised floor (also raised flooring, access floor(ing), or raised-access computer floor) provides an elevated structural floor above a solid substrate (often a concrete slab) to create a hidden void for the passage of mechanical and electrical services. Raised floors are widely used in modern office buildings, and in specialized areas such as command centers, Information technology data centers and computer rooms, where there is a requirement to route mechanical services and cables, wiring, and electrical supply. Such flooring can be installed at varying heights from to heights above to suit services that may be accommodated beneath. Additional structural support and lighting are often provided when a floor is raised enough for a person to crawl or even walk beneath. In the U.S., underfloor air distribution is becoming a more common way to cool a building by using the void below the raised floor as a plenum chamber to distribute conditioned air, which has been done in Euro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rooftop Unit
An air handler, or air handling unit (often abbreviated to AHU), is a device used to regulate and circulate air as part of a heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning (HVAC) system. An air handler is usually a large metal box containing a blower, heating or cooling elements, filter racks or chambers, sound attenuators, and dampers. Air handlers usually connect to a ductwork ventilation system that distributes the conditioned air through the building and returns it to the AHU. Sometimes AHUs discharge (''supply'') and admit (''return'') air directly to and from the space served without ductwork Small air handlers, for local use, are called terminal units, and may only include an air filter, coil, and blower; these simple terminal units are called blower coils or fan coil units. A larger air handler that conditions 100% outside air, and no recirculated air, is known as a makeup air unit (MAU) or fresh air handling unit (FAHU). An air handler designed for outdoor use, typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches. Mechanical engineering requires an understanding of core areas including mechanics, dynamics, thermodynamics, materials science, structural analysis, and electricity. In addition to these core principles, mechanical engineers use tools such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and product lifecycle management to design and analyze manufacturing plants, industrial equipment and machinery, heating and cooling systems, transport systems, aircraft, watercraft, robotics, medical devices, weapons, and others. Mechanical engineering emerged as a field during the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 18th century; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Data
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is information represented as a string of discrete symbols each of which can take on one of only a finite number of values from some alphabet, such as letters or digits. An example is a text document, which consists of a string of alphanumeric characters . The most common form of digital data in modern information systems is ''binary data'', which is represented by a string of binary digits (bits) each of which can have one of two values, either 0 or 1. Digital data can be contrasted with ''analog data'', which is represented by a value from a continuous range of real numbers. Analog data is transmitted by an analog signal, which not only takes on continuous values, but can vary continuously with time, a continuous real-valued function of time. An example is the air pressure variation in a sound wave. The word ''digital'' comes from the same source as the words digit and ''digitus'' (the Latin word for ''finger'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |