|
Glaucophyte
The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of species in the group varies from about 14 to 26. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants (Viridiplantae or Chloroplastida), they form the Archaeplastida. However, the relationships among the red algae, green algae and glaucophytes are unclear, in large part due to limited study of the glaucophytes. The glaucophytes are of interest to biologists studying the development of chloroplasts because some studies suggest they may be similar to the original algal type that led to green plants and red algae in that glaucophytes may be basal Archaeplastida. Unlike red and green algae, glaucophytes only have asexual reproduction. Characteristics The plastids of glaucophytes are known as 'muroplasts', 'cyanoplast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like '' Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeplastida
The Archaeplastida (or kingdom Plantae '' sensu lato'' "in a broad sense"; pronounced /ɑːrkɪ'plastɪdə/) are a major group of eukaryotes, comprising the photoautotrophic red algae (Rhodophyta), green algae, land plants, and the minor group glaucophytes. It also includes the non-photosynthetic lineage Rhodelphidia, a predatorial (eukaryotrophic) flagellate that is sister to the Rhodophyta, and probably the microscopic picozoans. The Archaeplastida have chloroplasts that are surrounded by two membranes, suggesting that they were acquired directly through a single endosymbiosis event by feeding on a cyanobacterium. All other groups which have chloroplasts, besides the amoeboid genus '' Paulinella'', have chloroplasts surrounded by three or four membranes, suggesting they were acquired secondarily from red or green algae. Unlike red and green algae, glaucophytes have never been involved in secondary endosymbiosis events. The cells of the Archaeplastida typically lack centri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as '' Chlorella'', '' Prototheca'' and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to in length. Most are aquatic and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the '' Charophyta'', a division of green algae which includes, for example, '' Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. Algae that are carried by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton. Algae constitute a polyphyletic group since they do not include a common ancestor, and although their plastids seem to have a single ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastid
The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded – plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. Examples include chloroplasts (used for photosynthesis), chromoplasts (used for pigment synthesis and storage), and leucoplasts (non-pigmented plastids that can sometimes differentiate). The event which led to permanent endosymbiosis in the Archaeplastida clade (of land plants, red algae, and green algae) probably occurred with a cyanobiont (a symbiotic cyanobacteria) related to the genus '' Gloeomargarita'', around 1.5 billion years ago. A later primary endosymbiosis event occurred in photosynthetic ''Paulinella'' amoeboids about 90–140 million years ago. This plastid belongs to the "PS-clade" (of the cyanobacteria genera ''Prochlorococcus'' and ''Synechococcus''). Secondary and tertiary endosymbiosis has also occurred, in a wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Plant
The Embryophyta (), or land plants, are the most familiar group of green plants that comprise vegetation on Earth. Embryophytes () have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of green algae as sister of the Zygnematophyceae. The Embryophyta consist of the bryophytes plus the polysporangiophytes. Living embryophytes therefore include hornworts, liverworts, mosses, lycophytes, ferns, gymnosperms and flowering plants. The land plants have diplobiontic life cycles and it is accepted now that they emerged from freshwater, multi-celled algae. The embryophytes are informally called land plants because they live primarily in terrestrial habitats (with exceptional members who evolved to live once again in aquatic habitats), while the related green algae are primarily aquatic. Embryophytes are complex multicellular eukaryotes with specialized reproductive organs. The name derives from their innovative characteristic of nurturing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Fixation
Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon (particularly in the form of carbon dioxide) is converted to organic compounds by living organisms. The compounds are then used to store energy and as structure for other biomolecules. Carbon is primarily fixed through photosynthesis, but some organisms use a process called chemosynthesis in the absence of sunlight. Organisms that grow by fixing carbon are called autotrophs, which include photoautotrophs (which use sunlight), and lithoautotrophs (which use inorganic oxidation). Heterotrophs are not themselves capable of carbon fixation but are able to grow by consuming the carbon fixed by autotrophs or other heterotrophs. "Fixed carbon", "reduced carbon", and "organic carbon" may all be used interchangeably to refer to various organic compounds. Chemosynthesis is carbon fixation driven by chemical energy, rather than from sunlight. Sulfur- and hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria often use the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
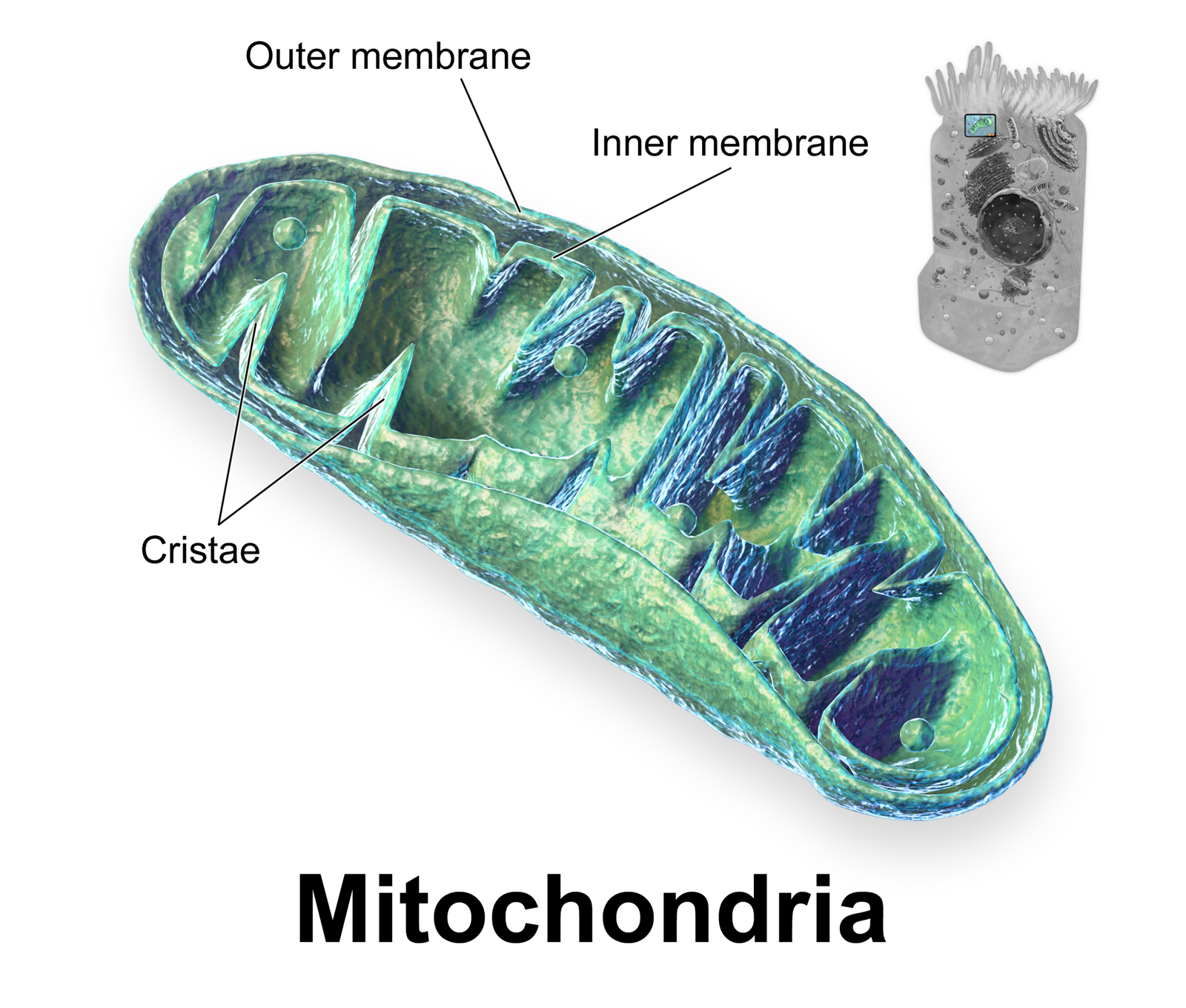
Mitochondrion
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, '' Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cristae
A crista (; plural cristae) is a fold in the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. The name is from the Latin for ''crest'' or ''plume'', and it gives the inner membrane its characteristic wrinkled shape, providing a large amount of surface area for chemical reactions to occur on. This aids aerobic cellular respiration, because the mitochondrion requires oxygen. Cristae are studded with proteins, including ATP synthase and a variety of cytochromes. Background With the discovery of the dual-membrane nature of mitochondria, the pioneers of mitochondrial ultrastructural research proposed different models for the organization of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Three models proposed were: *Baffle model – According to Palade (1953), the mitochondrial inner membrane is convoluted in a baffle-like manner with broad openings towards the intra-cristal space. This model entered most textbooks and was widely believed for a long time. *Septa model – Sjöstrand (1953) suggested that sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
In cell biology, mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Therefore, mitosis is also known as equational division. In general, mitosis is preceded by S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis; which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycobilisome
Phycobilisomes are light harvesting antennae of photosystem II in cyanobacteria, red algae and glaucophytes. It was lost in the plastids of green algae / plants (chloroplasts). General structure Phycobilisomes are protein complexes (up to 600 polypeptides) anchored to thylakoid membranes. They are made of stacks of chromophorylated proteins, the phycobiliproteins, and their associated linker polypeptides. Each phycobilisome consists of a core made of allophycocyanin, from which several outwardly oriented rods made of stacked disks of phycocyanin and (if present) phycoerythrin(s) or phycoerythrocyanin. The spectral property of phycobiliproteins are mainly dictated by their prosthetic groups, which are linear tetrapyrroles known as phycobilins including phycocyanobilin, phycoerythrobilin, phycourobilin and phycobiliviolin. The spectral properties of a given phycobilin is influenced by its protein environment. Function Each phycobiliprotein has a specific absorptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centriole
In cell biology a centriole is a cylindrical organelle composed mainly of a protein called tubulin. Centrioles are found in most eukaryotic cells, but are not present in conifers ( Pinophyta), flowering plants ( angiosperms) and most fungi, and are only present in the male gametes of charophytes, bryophytes, seedless vascular plants, cycads, and '' Ginkgo''. A bound pair of centrioles, surrounded by a highly ordered mass of dense material, called the pericentriolar material (PCM), makes up a structure called a centrosome. Centrioles are typically made up of nine sets of short microtubule triplets, arranged in a cylinder. Deviations from this structure include crabs and '' Drosophila melanogaster'' embryos, with nine doublets, and ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' sperm cells and early embryos, with nine singlets. Additional proteins include centrin, cenexin and tektin. The main function of centrioles is to produce cilia during interphase and the aster and the spindle du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |