|
Glaciers On Mars
Glaciers, loosely defined as patches of currently or recently flowing ice, are thought to be present across large but restricted areas of the modern Martian surface, and are inferred to have been more widely distributed at times in the past."The Surface of Mars" Series: Cambridge Planetary Science (No. 6) Michael H. Carr, United States Geological Survey, Menlo Park Lobate convex features on the surface known as viscous flow features and lobate debris aprons, which show the characteristics of non-Newtonian flow, are now almost unanimously regarded as true glaciers. However, a variety of other features on the surface have also been interpreted as directly linked to flowing ice, such as fretted terrain, lineated valley fill, concentric crater fill, and arcuate ridges. A variety of surface textures seen in imagery of the midlatitudes and polar regions are also thought to be linked to sublimation of glacial ice. Today, features interpreted as glaciers are largely restricted to la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide View Of Glacier Showing Image Field
{{Disambiguation, callsign ...
WIDE or Wide may refer to: *Wide (cricket) *Wide and narrow data, terms used to describe two different presentations for tabular data *WIDE Project, Widely Integrated Distributed Environment *Wide-angle Infinity Display Equipment *WIDE-LP, a radio station (99.1 FM) licensed to Madison, Wisconsin *Women in Development Europe; see * wide (tennis), meaning beyond the sidelines People with the name Wide *Ernst Wide (1888–1950), a Swedish Olympic long-distance runner *Edvin Wide (1896–1996), a Swedish Olympic long-distance runner *Samuel Wide (1861–1918), a Swedish archaeologist See also * * * *Widen *Width (other) Width is a measure of distance from side to side, measuring across an object at right angles to the length. Width may also refer to: Graph theory * Width of a partial order - the cardinality of a maximum antichain. * Width of a tree decomposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentric Crater Fill
A concentric crater fill (CCF) is a landform where the floor of a crater is mostly covered with many parallel ridges. It is common in the mid-latitudes of Mars, and is widely believed to be caused by glacial movement. Areas on Mars called Deuteronilus Mensae and Protonilus Mensae contain many examples of concentric crater fill. Description Concentric crater fill, like lobate debris aprons and lineated valley fill, is believed to be ice-rich. Sometimes boulders are found on concentric crater fill; it is believed they fell off the crater wall, then were transported away from the wall with the movement of the glacier. Erratics on Earth were carried by similar means. High resolution pictures taken with HiRISE reveal that some of the surfaces of concentric crater fill are covered with strange patterns called closed-cell and open-cell brain terrain. The terrain resembles a human brain. It is believed to be caused by cracks in the surface accumulating dust and other debris, togethe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaethontis Quadrangle
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Phaethontis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). The name comes from Phaethon, the son of Helios. The Phaethontis quadrangle lies between 30° and 65 ° south latitude and 120° and 180 ° west longitude on Mars. This latitude range is where numerous gullies have been discovered. An old feature in this area, called Terra Sirenum lies in this quadrangle; Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter discovered iron/magnesium smectites there. Part of this quadrangle contains what is called the Electris deposits, a deposit that is thick. It is light-toned and appears to be weak because of few boulders. Among a group of large craters is Mariner Crater, first observed by the Mariner IV spacecraft in the summer of 1965. It was named after that spacecraft. A low area in Terra Sirenum is believed to have once held a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
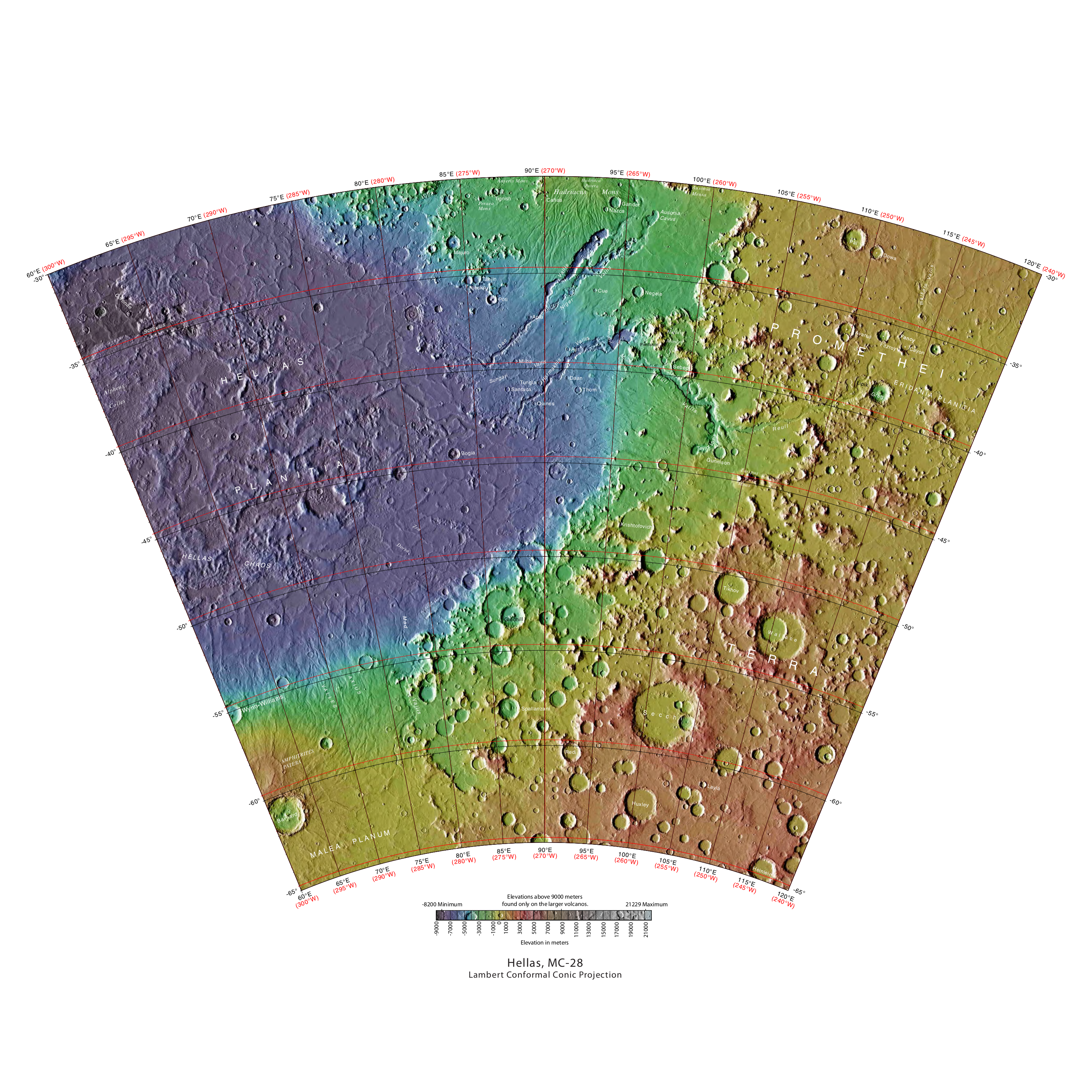
Hellas Quadrangle
The Hellas quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Hellas quadrangle is also referred to as MC-28 (Mars Chart-28). The Hellas quadrangle covers the area from 240° to 300° west longitude and 30° to 65° south latitude on the planet Mars. Within the Hellas quadrangle lies the classic features Hellas Planitia and Promethei Terra. Many interesting and mysterious features have been discovered in the Hellas quadrangle, including the giant river valleys Dao Vallis, Niger Vallis, Harmakhis, and Reull Vallis—all of which may have contributed water to a lake in the Hellas basin in the distant past. Many places in the Hellas quadrangle show signs of ice in the ground, especially places with glacier-like flow features. Hellas Basin The Hellas quadrangle contains part of the Hellas Basin, the largest known impact crater on the surface of Mars and the second largest in the solar sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coloe Fossae
Coloe Fossae is a set of troughs in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle of Mars. It is centered at 36.5 degrees north latitude and 302.9 west longitude. It is 576 km long and was named after a classical albedo feature. Image:Coloe Fossae.JPG, Coloe Fossae Dike (geology), Dikes and/or Fault (geology), faults, as seen by HiRISE. Dikes and faults may have produced mineral deposits. Image:Coloe Fossae Lineated Valley Fill.JPG, Coloe Fossae lineated valley fill, as seen by HiRISE. Scale bar is 500 meters long. Image:Cole Fossae Pits.JPG, Coloe Fossae pits, as seen by HiRISE. Pits are believed to result from escaping water. References See also * Fossa (geology) Ismenius Lacus quadrangle Valleys and canyons on Mars {{Mars-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casius Quadrangle
The Casius quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the north-central portion of Mars’ eastern hemisphere and covers 60° to 120° east longitude (240° to 300° west longitude) and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Casius quadrangle is also referred to as MC-6 (Mars Chart-6). Casius quadrangle contains part of Utopia Planitia and a small part of Terra Sabaea. The southern and northern borders of the Casius quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km and 1,500 km wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about 2,050 km (slightly less than the length of Greenland). The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars’ surface area. Origin of name Casius is the name of a telescopic albedo f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiWish Program
HiWish is a program created by NASA so that anyone can suggest a place for the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to photograph. It was started in January 2010. In the first few months of the program 3000 people signed up to use HiRISE. The first images were released in April 2010. Over 12,000 suggestions were made by the public; suggestions were made for targets in each of the 30 quadrangles of Mars. Selected images released were used for three talks at the 16th Annual International Mars Society Convention. Below are some of the over 4,224 images that have been released from the HiWish program as of March 2016. Glacial features Some landscapes look just like glaciers moving out of mountain valleys on Earth. Some have a hollowed-out appearance, looking like a glacier after almost all the ice has disappeared. What is left are the moraines—the dirt and debris carried by the glacier. The center is hollowed out because the ice is mostly gone. These supposed alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilosyrtis Mensae
Nilosyrtis Mensae is an area of Mars in the Casius quadrangle. It is centered on the coordinates of 36.87° N and 67.9° E. Its western and eastern longitudes are 51.1° E and 74.4° E. North and south latitudes are 36.87° N and 29.61° N. Nilosyrtis Mensae is just to the east of Protonilus Mensae and both lie along the Martian dichotomy boundary. Its name was adapted by the IAU in 1973. It was named after a classical albedo feature, and it is across. The surface of Nilosyrtis Mensae is classified as fretted terrain. This terrain contains cliffs, mesas, and wide flat valleys. Surface features are believed to have been caused by debris-covered glaciers. These glaciers are termed lobate debris aprons when surrounding mounds and mesas. When the glaciers are in the valleys they are called lineated valley fill. Climate change caused ice-rich features For decades many features on Mars, including ones in Nilosyrtis Mensae, were believed to contain large amounts of ice. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protonilus Mensae
Protonilus Mensae is an area of Mars in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. It is centered on the coordinates of 43.86° N and 49.4° E. Its western and eastern longitudes are 37° E and 59.7° E. North and south latitudes are 47.06° N and 39.87° N. Protonilus Mensae is between Deuteronilus Mensae and Nilosyrtis Mensae; all lie along the Martian dichotomy boundary. Its name was adapted by the IAU in 1973. Mapdeuteronilus.jpg, Map showing the relation of Protonilus and Deuteronilus Mensae to other nearby regions. Colors refer to altitudes. The surface is described as fretted terrain. This terrain contains cliffs, mesas, and wide flat valleys. Surface features are believed to have been caused by debris-covered glaciers. These glaciers are termed lobate debris aprons (LDA) when surrounding mounds and mesas. When glaciers are in valleys, they are called Lineated valley fill (LVF). Parts of the surface show flow patterns that start in numerous alcoves located within the walls of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuteronilus Mensae
Deuteronilus Mensae is a region on Mars 937 km across and centered at . It covers 344°–325° West and 40°–48° North. Deuteronilus region lies just to the north of Arabia Terra and is included in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. It is along the dichotomy boundary, that is between the old, heavily cratered southern highlands and the low plains of the northern hemisphere. The region contains flat-topped knobby terrain that may have been formed by glaciers at some time in the past. Deuteronilus Mensae is to the immediate west of Protonilus Mensae and Ismeniae Fossae. Glaciers persist in the region in modern times, with at least one glacier estimated to have formed as recently as 100,000 to 10,000 years ago. Recent evidence from the radar on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has shown that parts of Deuteronilus Mensae do indeed contain ice. Source of ice It is now widely believed that ice accumulated in many areas of Mars, including Deuteronilus Mensae, when the planet's orbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martian Dichotomy
The most conspicuous feature of Mars is a sharp contrast, known as the Martian dichotomy, between the Southern and the Northern hemispheres. The two hemispheres' geography differ in elevation by 1 to 3 km. The average thickness of the Martian crust is 45 km, with 32 km in the northern lowlands region, and 58 km in the southern highlands. The boundary between the two regions is quite complex in places. One distinctive type of topography is called fretted terrain. It contains mesas, knobs, and flat-floored valleys having walls about a mile high. Around many of the mesas and knobs are lobate debris aprons that have been shown to be rock glaciers. Many large valleys formed by the lava erupted from the volcanoes of Mars cut through the dichotomy. The Martian dichotomy boundary includes the regions called Deuteronilus Mensae, Protonilus Mensae, and Nilosyrtis Mensae. All three regions have been studied extensively because they contain landforms believed to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Terrain
Brain terrain, also called knobs-brain coral and brain coral terrain, is a feature of the Martian surface, consisting of complex ridges found on lobate debris aprons, lineated valley fill and concentric crater fill. It is so named because it suggests the ridges on the surface of the human brain. Wide ridges are called ''closed-cell'' brain terrain, and the less common narrow ridges are called ''open-cell'' brain terrain.Levy, J., J. Head, D. Marchant. 2009. Concentric crater fill in Utopia Planitia: History and interaction between glacial “brain terrain” and periglacial mantle processes. Icarus 202, 462–476. It is thought that the wide closed-cell terrain contains a core of ice, and when the ice disappears the center of the wide ridge collapses to produce the narrow ridges of the open-cell brain terrain. Shadow measurements from HiRISE indicate the ridges are 4-5 meters high. Brain terrain has been observed to form from what has been called an " Upper Plains Unit." The process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_with_poles_HiRes.jpg)