|
Gipsy Six
The de Havilland Gipsy Six is a British six-cylinder, air-cooled, inverted inline piston engine developed by the de Havilland Engine Company for aircraft use in the 1930s. It was based on the cylinders of the four-cylinder Gipsy Major and went on to spawn a whole series of similar aero engines that were still in common use until the 1980s. The engines were of particular note for their exceptionally low cross-sectional area, a drag-reducing feature which made them ideal for the many racing aircraft of that period. In 1934, the basic bronze-headed Gipsy Six, rated at 185 horsepower (138 kW) at 2,100 rpm was modified for use in the DH.88 Comet air racer as the Gipsy Six "R" which produced 223 horsepower (166 kW) at 2,400 rpm for takeoff. Many Gipsy Six engines remain in service powering vintage aircraft types today. Design and development The De Havilland Engine Company company had hoped to produce a version of the basic engine capable of utilising a hydraulicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocating Engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.''Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach'' by Yunus A. Cengal and Michael A. Boles Common features in all types There may be one or more pistons. Each piston is inside a cylinder, into which a gas is intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
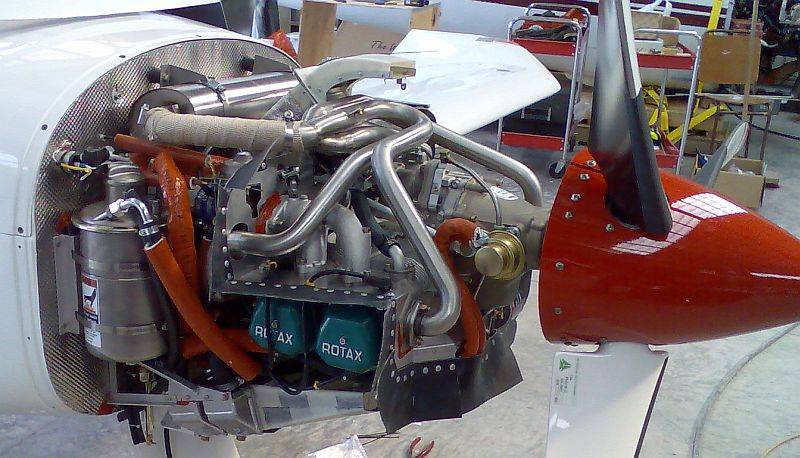
Ratier
Ratier-Figeac is an aircraft components manufacturer in Figeac, France. From 1926 until 1930 it also built a car with a 746 cc overhead camshaft engine. From 1959 until 1962 Ratier made motorcycles, having taken over the motorcycle business of the Centre d'Études de Moteurs à Explosion et à Combustion ( CEMEC). The engines were flat-twins derived from Second World War BMW designs. History Ratier was originally a joinery firm at the beginning of the century. By the outbreak of the first world-war, the company specialized in propeller blades for the aircraft of the French Air Force. Afterwards it produced for the French mail service Aéropostale all the way through its heyday of the 1930s when the service broke many flight-records. The factory was originally in Malakoff and then transferred to Montrouge. Much of its workload consisted of the contract work it received from Citroën to produce the Citroenette, a child's pedal-car. Paulin Ratier fabricated a prototype propeller- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudel-Hobson
Claudel-Hobson was a series of British carburettors manufactured by H. M. Hobson Ltd. Introduced in 1908, they were widely used on British car and aircraft engines in the early 20th century. Applications included Sunbeam automobiles as well as Armstrong Siddeley, Bristol, de Havilland The de Havilland Aircraft Company Limited () was a British aviation manufacturer established in late 1920 by Geoffrey de Havilland at Stag Lane Aerodrome Edgware on the outskirts of north London. Operations were later moved to Hatfield in H ..., and Napier aircraft engines. (retrieved 1 August 2018) References External links [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometric
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis to help find surface troughs, pressure systems and frontal boundaries. Barometers and pressure altimeters (the most basic and common type of altimeter) are essentially the same instrument, but used for different purposes. An altimeter is intended to be used at different levels matching the corresponding atmospheric pressure to the altitude, while a barometer is kept at the same level and measures subtle pressure changes caused by weather and elements of weather. The average atmospheric pressure on the earth's surface varies between 940 and 1040 hPa (mbar). The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1013 hPa (mbar). Etymology The word ''barometer'' is derived from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "weight", and (), meaning "measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant Speed Unit
In aeronautics, a variable-pitch propeller is a type of propeller (airscrew) with blades that can be rotated around their long axis to change the blade pitch. A controllable-pitch propeller is one where the pitch is controlled manually by the pilot. Alternatively, a constant-speed propeller is one where the pilot sets the desired engine speed (RPM), and the blade pitch is controlled automatically without the pilot's intervention so that the rotational speed remains constant. The device which controls the propeller pitch and thus speed is called a propeller governor or constant speed unit. Reversible propellers are those where the pitch can be set to negative values. This creates reverse thrust for braking or going backwards without the need to change the direction of shaft revolution. Some aircraft have ground-adjustable propellers, however these are not considered variable-pitch. These are typically found only on light aircraft and microlights. Purpose When an aircraft is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankcase
In a piston engine, the crankcase is the housing that surrounds the crankshaft. In most modern engines, the crankcase is integrated into the engine block. Two-stroke engines typically use a crankcase-compression design, resulting in the fuel/air mixture passing through the crankcase before entering the cylinder(s). This design of the engine does not include an oil sump in the crankcase. Four-stroke engines typically have an oil sump at the bottom of the crankcase and the majority of the engine's oil is held within the crankcase. The fuel/air mixture does not pass through the crankcase in a four-stroke engine, however a small amount of exhaust gasses often enter as "blow-by" from the combustion chamber. The crankcase often forms the lower half of the main bearing journals (with the bearing caps forming the other half), although in some engines the crankcase completely surrounds the main bearing journals. An ''open-crank'' engine has no crankcase. This design was used in early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubrication
Lubrication is the process or technique of using a lubricant to reduce friction and wear and tear in a contact between two surfaces. The study of lubrication is a discipline in the field of tribology. Lubrication mechanisms such as fluid-lubricated systems are designed so that the applied load is partially or completely carried by hydrodynamic or hydrostatic pressure, which reduces solid body interactions (and consequently friction and wear). Depending on the degree of surface separation, different lubrication regimes can be distinguished. Adequate lubrication allows smooth, continuous operation of machine elements, reduces the rate of wear, and prevents excessive stresses or seizures at bearings. When lubrication breaks down, components can rub destructively against each other, causing heat, local welding, destructive damage and failure. Lubrication mechanisms Fluid-lubricated systems As the load increases on the contacting surfaces, distinct situations can be observed wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Sump
A dry-sump system is a method to manage the lubricating motor oil in four-stroke and large two-stroke piston driven internal combustion engines. The dry-sump system uses two or more oil pumps and a separate oil reservoir, as opposed to a conventional wet-sump system, which uses only the main sump (U.S.: oil pan) below the engine and a single pump. A dry-sump engine requires a pressure relief valve to regulate negative pressure inside the engine, so internal seals are not inverted. Dry-sumps are common on larger diesel engines such as those used in ships, as well as gasoline engines used in racing cars, aerobatic aircraft, high-performance personal watercraft and motorcycles. Dry sump lubrication may be chosen for these applications due to increased reliability, oil capacity, reduction of oil starvation under high g-loads and/or other technical or performance reasons. Dry sump systems may not be suitable for all applications due to increased cost, complexity, and/or bulk, am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting rods. The crankpins are also called ''rod bearing journals'', and they rotate within the "big end" of the connecting rods. Most modern crankshafts are located in the engine block. They are made from steel or cast iron, using either a forging, casting or machining process. Design The crankshaft located within the engine block, held in place via main bearings which allow the crankshaft to rotate within the block. The up-down motion of each piston is transferred to the crankshaft via connecting rods. A flywheel is often attached to one end of the crankshaft, in order to smoothen the power delivery and reduce vibration. A crankshaft is subjected to enormous stresses, in some cases more than per cylinder. Crankshafts for single-cylin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamilton Standard
Hamilton Standard was an American aircraft propeller parts supplier. It was formed in 1929 when United Aircraft and Transport Corporation consolidated Hamilton Aero Manufacturing and Standard Steel Propeller into the Hamilton Standard Propeller Corporation. Other members of United Aircraft included Boeing, United Airlines, Sikorsky and Pratt & Whitney. At the time, Hamilton was the largest manufacturer of aircraft propellers in the world. History Standard Steel Propeller had been formed in 1918 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and Hamilton Aero Manufacturing had been formed in 1920 in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, by Thomas F. Hamilton. Charles Lindbergh's ''Spirit of St. Louis'' used a propeller made by Standard Steel Propeller Company in his historic solo crossing of the Atlantic Ocean. The two companies were merged in 1929 by the United Aircraft and Transport Corporation. In the early 1930s, Frank W. Caldwell of Hamilton Standard led a team that developed a variable-pitch prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poppet Valve
A poppet valve (also called mushroom valve) is a valve typically used to control the timing and quantity of gas or vapor flow into an engine. It consists of a hole or open-ended chamber, usually round or oval in cross-section, and a plug, usually a disk shape on the end of a shaft known as a valve stem. The working end of this plug, the valve face, is typically ground at a 45° bevel to seal against a corresponding valve seat ground into the rim of the chamber being sealed. The shaft travels through a valve guide to maintain its alignment. A pressure differential on either side of the valve can assist or impair its performance. In exhaust applications higher pressure against the valve helps to seal it, and in intake applications lower pressure helps open it. The poppet valve was invented in 1833 by American E.A.G. Young of the New Castle and Frenchtown Turnpike and Railroad Company, Newcastle and Frenchtown Railroad. Young had patented his idea, but the 1836 U.S. Patent Offic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering ports in the cylinder. __TOC__ Piston engines Internal combustion engines An internal combustion engine is acted upon by the pressure of the expanding combustion gases in the combustion chamber space at the top of the cylinder. This force then acts downwards through the connecting rod and onto the crankshaft. The connecting rod is att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)



