|
Gillot Saint-Evre
Gillot Saint-Evre (1791 in Boult-sur-Suippe – 1858 in Paris) was a French painter and engraver. He created scenes on historical and literary subjects, as well as genre scenes and portraits. Life and work His creative career began in the 1820s and first attracted attention at the Paris Salon in 1822, where he displayed two paintings depicting scenes from '' The Tempest'' by Shakespeare. A young journalist named Adolphe Thiers (who would later become the President of France) wrote a positive review of the exhibit and called him a painter of great promise. This inspired him to create more works on literary themes. Among these works are lithographs showing Louis XI with Countess Isabelle de Croye, from ''Quentin Durward'' by Sir Walter Scott, and scenes from ''Henry III and His Court'', an early play by Alexandre Dumas. The failure of a series of works on '' Don Quixote'' forced him to do a critical reevaluation of his work. He decided to abandon literature in favor of history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
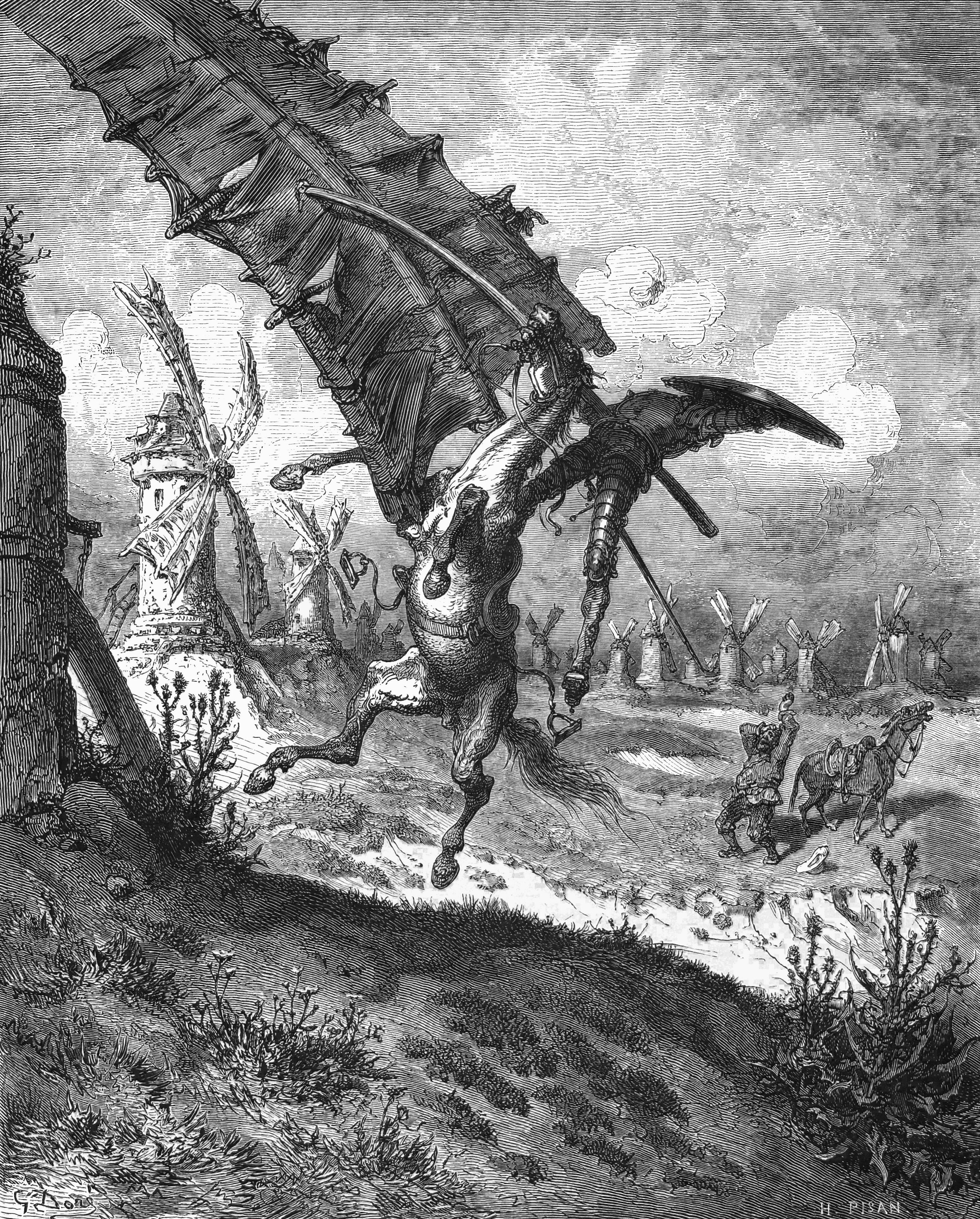
Don Quixote
is a Spanish epic novel by Miguel de Cervantes. Originally published in two parts, in 1605 and 1615, its full title is ''The Ingenious Gentleman Don Quixote of La Mancha'' or, in Spanish, (changing in Part 2 to ). A founding work of Western literature, it is often labelled as the first modern novel and one of the greatest works ever written. ''Don Quixote'' is also one of the most-translated books in the world. The plot revolves around the adventures of a member of the lowest nobility, an hidalgo from La Mancha named Alonso Quijano, who reads so many chivalric romances that he either loses or pretends to have lost his mind in order to become a knight-errant () to revive chivalry and serve his nation, under the name . He recruits a simple farmer, Sancho Panza, as his squire, who often employs a unique, earthy wit in dealing with Don Quixote's rhetorical monologues on knighthood, already considered old-fashioned at the time, and representing the most droll realism in contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century French Painters
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the large S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1858 Deaths
Events January–March * January – **Benito Juárez (1806–1872) becomes Liberal President of Mexico. At the same time, conservatives install Félix María Zuloaga (1813–1898) as president. **William I of Prussia becomes regent for his brother, Frederick William IV, who had suffered a stroke. * January 9 ** British forces finally defeat Rajab Ali Khan of Chittagong ** Anson Jones, the last president of the Republic of Texas, commits suicide. * January 14 – Orsini affair: Felice Orsini and his accomplices fail to assassinate Napoleon III in Paris, but their bombs kill eight and wound 142 people. Because of the involvement of French émigrés living in Britain, there is a brief anti-British feeling in France, but the emperor refuses to support it. * January 25 – The ''Wedding March'' by Felix Mendelssohn becomes a popular wedding recessional, after it is played on this day at the marriage of Queen Victoria's daughter Victoria, Princess Royal, to Princ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1791 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – Austrian composer Joseph Haydn arrives in England, to perform a series of concerts. * January 2 – Northwest Indian War: Big Bottom Massacre – The war begins in the Ohio Country, with this massacre. * January 12 – Holy Roman troops reenter Liège, heralding the end of the Liège Revolution, and the restoration of its Prince-Bishops. * January 25 – The British Parliament passes the Constitutional Act 1791, splitting the old province of Quebec into Upper and Lower Canada. * February 8 – The Bank of the United States, based in Philadelphia, is incorporated by the federal government with a 20-year charter and started with $10,000,000 capital.''Harper's Encyclopaedia of United States History from 458 A. D. to 1909'', ed. by Benson John Lossing and, Woodrow Wilson (Harper & Brothers, 1910) p169 * February 21 – The United States opens diplomatic relations with Portugal. * March 2 – Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joconde
Joconde is the central database created in 1975 and now available online, maintained by the French Ministry of Culture, for objects in the collections of the main French public and private museums listed as ''Musées de France'', according to article L. 441-1 of the ''Code du patrimoine'' amounting to more than 1,200 institutions. "La Joconde" is the French name of the ''Mona Lisa'', which like about half of the collections of the Louvre, is included in the database, as one of 295 items by, after, or connected with Leonardo da Vinci; of these, only 42 works are by Leonardo da Vinci, including 6 paintings. By November 2012, Joconde contained over 475,000 object online and over 290,000 with images, from 366 collections in France, including 209,350 drawings, 63,547 paintings, 34,561 prints, 34,102 sculptures or 16,631 costumes and their accessories and is still expanding. By June 2022 it counted 636,405 objects. The database is not only dedicated to the information of the publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée De La Vie Romantique
The Musée de la Vie romantique (Museum of Romantic Life, or ''Museum of the Romantics'') stands at the foot of Montmartre hill in the 9th arrondissement of Paris, 16 rue Chaptal, Paris, France in an 1830 ''hôtel particulier'' facing two twin-studios, a greenhouse, a small garden, and a paved courtyard. The museum is open daily except Monday. Permanent collections are free. An admission fee is charged for temporary exhibitions. The nearest métro stations are Pigalle, Blanche, Saint-Georges, and Liège. The Musée de la Vie romantique is one of the 14 City of Paris Museums that have been incorporated since January 1, 2013 in the public institution Paris Musées. Property The main pavilion, built in 1830, was the Paris base of the Dutch-born painter Ary Scheffer (1795–1858), one of the prominent artists of the time, close to King Louis-Philippe and his family. For decades, Scheffer and his daughter hosted Friday-evening salons, among the most famous in ''La Nouvelle Athèn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph-Jacques Ramée
Joseph-Jacques Ramée (April 26, 1764 in Charlemont, France — May 18, 1842 at the Chateau de Beaurains, Noyon) was a French architect, interior designer, and landscape architect working within the neoclassicist idiom. He was a student of the architect and landscape architect François-Joseph Bélanger. In his lifetime, he worked in France, Denmark, Germany, Belgium, and the United States. He also published books on landscaping with his own numerous garden designs as examples. Ramée is known for his work at Union College, in Schenectady, New York, where in 1812 he designed the first comprehensively planned college campus in America Work at Union College By the early 1800s he had already established a reputation as a skilled designer of landscapes combined with houses and other kinds of buildings. New York State land speculator David Parish, for whose father Ramée had designed an estate in Hamburg, Germany, persuaded Ramée to visit America in search of projects.Tunnard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, under the direction of the Ministry of Culture (France), French Ministry of Culture, by the Public Establishment of the Palace, Museum and National Estate of Versailles. Some 15,000,000 people visit the palace, park, or gardens of Versailles every year, making it one of the most popular tourist attractions in the world. Louis XIII built a simple hunting lodge on the site of the Palace of Versailles in 1623 and replaced it with a small château in 1631–34. Louis XIV expanded the château into a palace in several phases from 1661 to 1715. It was a favorite residence for both kings, and in 1682, Louis XIV moved the seat of his court and government to Versailles, making the palace the ''de facto'' capital of France. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles VII Of France
Charles VII (22 February 1403 – 22 July 1461), called the Victorious (french: le Victorieux) or the Well-Served (), was King of France from 1422 to his death in 1461. In the midst of the Hundred Years' War, Charles VII inherited the throne of France under desperate circumstances. Forces of the Kingdom of England and the duke of Burgundy occupied Guyenne and northern France, including Paris, the most populous city, and Reims, the city in which French kings were traditionally crowned. In addition, his father, Charles VI, had disinherited him in 1420 and recognized Henry V of England and his heirs as the legitimate successors to the French crown. At the same time, a civil war raged in France between the Armagnacs (supporters of the House of Valois) and the Burgundian party (supporters of the House of Valois-Burgundy, which was allied to the English). With his court removed to Bourges, south of the Loire River, Charles was disparagingly called the "King of Bourges", because the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joan Of Arc
Joan of Arc (french: link=yes, Jeanne d'Arc, translit= �an daʁk} ; 1412 – 30 May 1431) is a patron saint of France, honored as a defender of the French nation for her role in the siege of Orléans and her insistence on the coronation of Charles VII of France during the Hundred Years' War. Stating that she was acting under divine guidance, she became a military leader who transcended gender roles and gained recognition as a savior of France. Joan was born to a propertied peasant family at Domrémy in northeast France. In 1428, she requested to be taken to Charles, later testifying that she was guided by visions from the archangel Michael, Saint Margaret, and Saint Catherine to help him save France from English domination. Convinced of her devotion and purity, Charles sent Joan, who was about seventeen years old, to the siege of Orléans as part of a relief army. She arrived at the city in April 1429, wielding her banner and bringing hope to the demoralized Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentimentalist
Sentimentality originally indicated the reliance on feelings as a guide to truth, but in current usage the term commonly connotes a reliance on shallow, uncomplicated emotions at the expense of reason. Moral sense theory, Sentimentalism in philosophy is a view in meta-ethics according to which morality is somehow grounded in moral sentiments or emotions. Sentimentalism (literature), Sentimentalism in literature refers to techniques a writer employs to induce a tender emotional response disproportionate to the situation at hand (and thus to substitute heightened and generally uncritical feeling for normal ethical and intellectual judgments). The term may also characterize the tendency of some readers to invest strong emotions in trite or conventional fictional situations. "A sentimentalist", Oscar Wilde wrote, "is one who desires to have the luxury of an emotion without paying for it." In James Joyce's ''Ulysses (novel), Ulysses'', Stephen Dedalus sends Buck Mulligan a telegram t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |