|
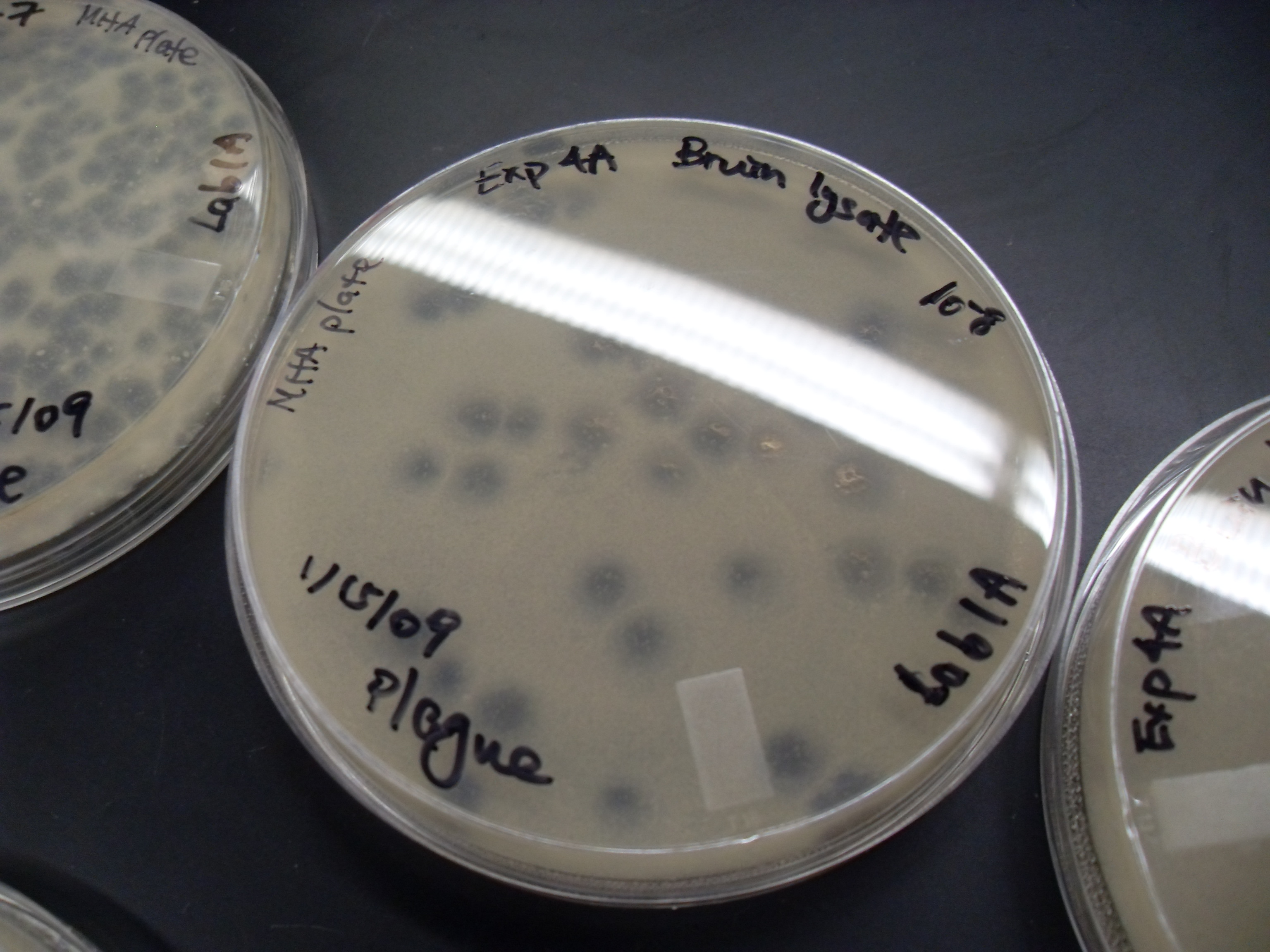
Giles (bacteriophage)
Giles is a bacteriophage that infects ''Mycobacterium smegmatis'' bacteria. The genome of this phage is very different from that of other mycobacteriophages and is highly mosaic A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop .... More than half of its predicted genes are novel and are not seen in other species. References External links Mycobacteriophage Database: GilesUniProt Taxonomy Mycobacteriophages Siphoviridae {{virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacterium Smegmatis
''Mycobacterium smegmatis'' is an acid-fast bacterial species in the phylum ''Actinomycetota'' and the genus ''Mycobacterium''. It is 3.0 to 5.0 µm long with a bacillus shape and can be stained by Ziehl–Neelsen method and the auramine-rhodamine fluorescent method. It was first reported in November 1884 by Lustgarten, who found a bacillus with the staining appearance of tubercle bacilli in syphilitic chancres. Subsequent to this, Alvarez and Tavel found organisms similar to that described by Lustgarten also in normal genital secretions (smegma). This organism was later named ''M. smegmatis''. Some species of the genus ''Mycobacterium'' have recently been renamed to ''Mycolicibacterium'', so that ''M. smegmatis'' is now ''Mycolicibacterium smegmatis''. Virulence ''M. smegmatis'' is generally considered a non-pathogenic microorganism; however, in some very rare cases, it may cause disease. Use in research ''M. smegmatis'' is useful for the research analysis of other ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle sequenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacteriophage
A mycobacteriophage is a member of a group of bacteriophages known to have mycobacteria as host bacterial species. While originally isolated from the bacterial species ''Mycobacterium smegmatis'' and ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', the causative agent of tuberculosis, more than 4,200 mycobacteriophage have since been isolated from various environmental and clinical sources. 2,042 have been completely sequenced. Mycobacteriophages have served as examples of viral Lysogenic cycle, lysogeny and of the divergent morphology and genetic arrangement characteristic of many phage types. All mycobacteriophages found thus far have had dsDNA, double-stranded DNA genomes and have been classified by their structure and appearance into siphoviridae or myoviridae. Discovery A bacteriophage found to infect ''Mycobacterium smegmatis'' in 1947 was the first documented example of a mycobacteriophage. It was found in cultures of the bacteria originally growing in moist compost. The first bacteriophag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaic (genetics)
Mosaicism or genetic mosaicism is a condition in multicellular organisms in which a single organism possesses more than one genetic line as the result of genetic mutation. This means that various genetic lines resulted from a single fertilized egg. Genetic mosaics may often be confused with chimerism, in which two or more genotypes arise in one individual similarly to mosaicism. In chimerism, though, the two genotypes arise from the fusion of more than one fertilized zygote in the early stages of embryonic development, rather than from a mutation or chromosome loss. Genetic mosaicism can result from many different mechanisms including chromosome nondisjunction, anaphase lag, and endoreplication. Anaphase lagging is the most common way by which mosaicism arises in the preimplantation embryo. Mosaicism can also result from a mutation in one cell during development, in which case the mutation will be passed on only to its daughter cells (and will be present only in certain adult ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacteriophages
A mycobacteriophage is a member of a group of bacteriophages known to have mycobacteria as host bacterial species. While originally isolated from the bacterial species ''Mycobacterium smegmatis'' and ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', the causative agent of tuberculosis, more than 4,200 mycobacteriophage have since been isolated from various environmental and clinical sources. 2,042 have been completely sequenced. Mycobacteriophages have served as examples of viral lysogeny and of the divergent morphology and genetic arrangement characteristic of many phage types. All mycobacteriophages found thus far have had double-stranded DNA genomes and have been classified by their structure and appearance into siphoviridae or myoviridae. Discovery A bacteriophage found to infect ''Mycobacterium smegmatis'' in 1947 was the first documented example of a mycobacteriophage. It was found in cultures of the bacteria originally growing in moist compost. The first bacteriophage that infects ''M. tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |