|
Giant Magnetoimpedance
In materials science Giant Magnetoimpedance (GMI) is the effect that occurs in some materials where an external magnetic field causes a large variation in the electrical impedance of the material. It should not be confused with the separate physical phenomenon of Giant Magnetoresistance. The phenomenology of the GMI GMI is caused by the penetration length that is a measure of how deep an ac electrical current can flow inside an electrical conductor. The penetration length (also known as the skin-depth effect) increases with the square root of the electrical resistivity of the material and is inversely proportional to the square root of the product of the magnetic permeability and the frequency of the ac electrical current. Thus, in materials with very high values of magnetic permeability, such as soft-ferromagnetic materials, the penetration-length can be much less than the thickness of the conductor even for moderate values of frequencies driving the current near the surface of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the hole in the center of the coil. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet. The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field. Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, electromechanical solen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomagnetism
Biomagnetism is the phenomenon of magnetic fields ''produced'' by living organisms; it is a subset of bioelectromagnetism. In contrast, organisms' use of magnetism in navigation is magnetoception and the study of the magnetic fields' ''effects'' on organisms is ''magnetobiology''. (The word biomagnetism has also been used loosely to include magnetobiology, further encompassing almost any combination of the words magnetism, cosmology, and biology, such as "magnetoastrobiology".) The origin of the word biomagnetism is unclear, but seems to have appeared several hundred years ago, linked to the expression "animal magnetism". The present scientific definition took form in the 1970s, when an increasing number of researchers began to measure the magnetic fields produced by the human body. The first valid measurement was actually made in 1963, but the field of research began to expand only after a low-noise technique was developed in 1970.{{cite journal , last1=Cohen , first1=David , la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
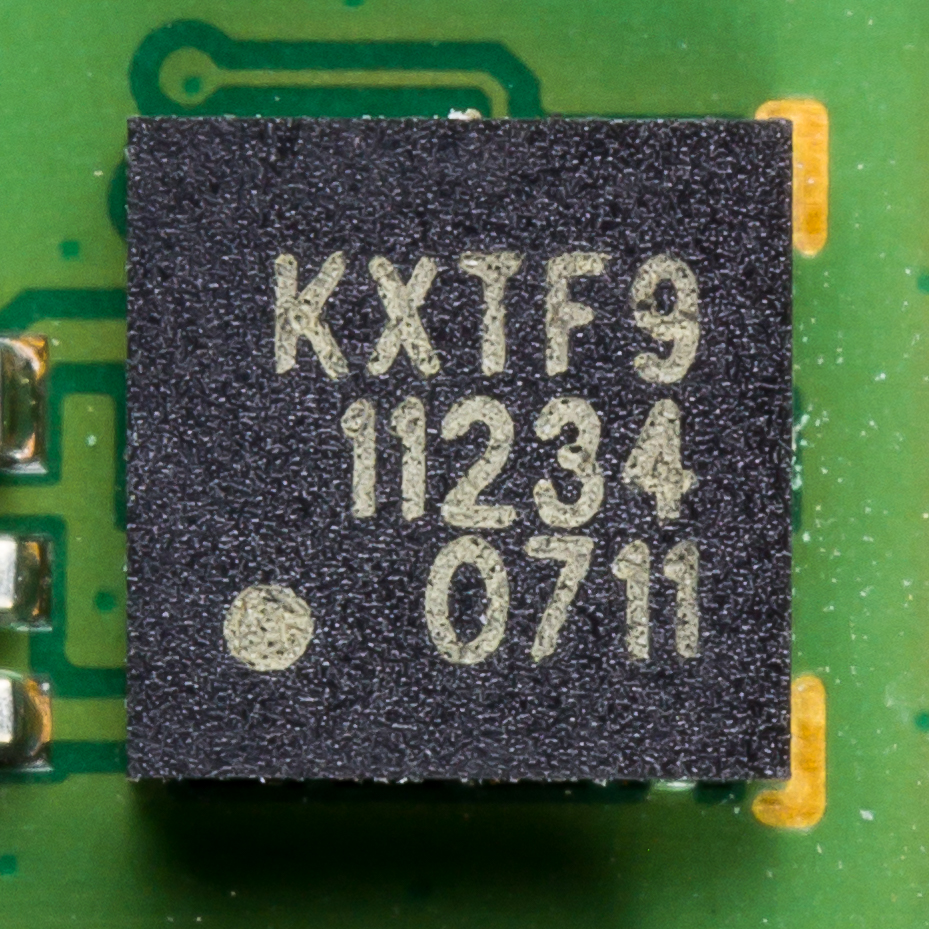
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with magnetic north. Other methods may be used, including gyroscopes, magnetometers, and GPS receivers. Compasses often show angles in degrees: north corresponds to 0°, and the angles increase clockwise, so east is 90°, south is 180°, and west is 270°. These numbers allow the compass to show azimuths or bearings which are commonly stated in degrees. If local variation between magnetic north and true north is known, then direction of magnetic north also gives direction of true north. Among the Four Great Inventions, the magnetic compass was first invented as a device for divination as early as the Chinese Han Dynasty (since c. 206 BC),Li Shu-hua, p. 176 and later adopted for navigation by the Song Dynasty Chinese during the 11th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oven
upA double oven A ceramic oven An oven is a tool which is used to expose materials to a hot environment. Ovens contain a hollow chamber and provide a means of heating the chamber in a controlled way. In use since antiquity, they have been used to accomplish a wide variety of tasks requiring controlled heating. Because they are used for a variety of purposes, there are many different types of ovens. These types differ depending on their intended purpose and based upon how they generate heat. Ovens are often used for cooking, where they can be used to heat food to a desired temperature. Ovens are also used in the manufacturing of ceramics and pottery; these ovens are sometimes referred to as kilns. Metallurgical furnaces are ovens used in the manufacturing of metals, while glass furnaces are ovens used to produce glass. There are many methods by which different types of ovens produce heat. Some ovens heat materials using the combustion of a fuel, such as wood, coal, or na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryostat
A cryostat (from ''cryo'' meaning cold and ''stat'' meaning stable) is a device used to maintain low cryogenic temperatures of samples or devices mounted within the cryostat. Low temperatures may be maintained within a cryostat by using various refrigeration methods, most commonly using cryogenic fluid bath such as liquid helium. Hence it is usually assembled into a vessel, similar in construction to a vacuum flask or Dewar. Cryostats have numerous applications within science, engineering, and medicine. Types Closed-cycle cryostats Closed-cycle cryostats consist of a chamber through which cold helium vapour is pumped. An external mechanical refrigerator extracts the warmer helium exhaust vapour, which is cooled and recycled. Closed-cycle cryostats consume a relatively large amount of electrical power, but need not be refilled with helium and can run continuously for an indefinite period. Objects may be cooled by attaching them to a metallic coldplate inside a vacuum ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferromagnetic Resonance
Ferromagnetic resonance, or FMR, is coupling between an electromagnetic wave and the magnetization of a medium through which it passes. This coupling induces a significant loss of power of the wave. The power is absorbed by the precessing magnetization (Larmor precession) of the material and lost as heat. For this coupling to occur, the frequency of the incident wave must be equal to the precession frequency of the magnetization (Larmor frequency) and the polarization of the wave must match the orientation of the magnetization. This effect can be used for various applications such as spectroscopic techniques or conception of microwave devices. The FMR spectroscopic technique is used to probe the magnetization of ferromagnetic materials. It is a standard tool for probing spin waves and spin dynamics. FMR is very broadly similar to electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), and also somewhat similar to nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), except that FMR probes the sample magnetization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in multilayers composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR. The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on spin orientation. The main application of GMR is in magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain Wall (magnetism)
A domain wall is a term used in physics which can have similar meanings in magnetism, optics, or string theory. These phenomena can all be generically described as topological solitons which occur whenever a discrete symmetry is spontaneously broken. Magnetism In magnetism, a domain wall is an interface separating magnetic domains. It is a transition between different magnetic moments and usually undergoes an angular displacement of 90° or 180°. A domain wall is a gradual reorientation of individual moments across a finite distance. The domain wall thickness depends on the anisotropy of the material, but on average spans across around 100–150 atoms. The energy of a domain wall is simply the difference between the magnetic moments before and after the domain wall was created. This value is usually expressed as energy per unit wall area. The width of the domain wall varies due to the two opposing energies that create it: the magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy and the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Magnetic Field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo. The magnitude of Earth's magnetic field at its surface ranges from . As an approximation, it is represented by a field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11° with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were an enormous bar magnet placed at that angle through the center of Earth. The North geomagnetic pole actually represents the South pole of Earth's magnetic field, and conversely the South geomagnetic pole corresponds to the north pole of Earth's magnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |