|
Ghost Cell Glaucoma
Ghost cell glaucoma (GCG) is a type of secondary glaucoma occurs due to long standing vitreous hemorrhage. The rigid and less pliable degenerated red blood cells (ghost cells) block the trabecular meshwork and increase the pressure inside eyes. Pathophysiology The ghost cells develop within the vitreous cavity, 1–3 weeks after vitreous hemorrhage. They obstruct the trabecular meshwork and eventually the pressure inside eye (intraocular pressure) increases and leads to glaucoma. A variety of ocular conditions may cause GCG. Main causes include ocular trauma, diabetes, sickle cell disease, uveitis, UGH syndrome, many eye surgeries etc. Signs and symptoms Myriad small cells may be seen in the aqueous humor during slit lamp examination. Intraocular pressure rises up to 30 to 70 mm Hg. The increased intraocular pressure may cause blurring of vision, headache, brow ache, nausea and/or vomiting. The angle of anterior chamber is seen open with gonioscopy. Complications If the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many include research as part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UGH Syndrome
Ugh or UGH may refer to: *''Ugh!'', a computer game * "UGH!" (song), by The 1975 * "Ugh" (''SpongeBob SquarePants''), a 2004 TV episode *"Ugh! Your Ugly Houses!," a 1995 single by British alternative music band Chumbawamba *"Ugh Ugh Ugh", a song by rapper Juicy J from his 2009 album ''Hustle Till I Die ''Hustle Till I Die'' is the second studio album by Three 6 Mafia member Juicy J, released June 16, 2009. The LP was released on Hypnotize Minds, with manufacturing and distribution from Select-O-Hits. The album debuted at number 106 on the ''Bi ...'' See also * UG (other) * UGG (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Chamber
The anterior chamber ( AC) is the aqueous humor-filled space inside the eye between the iris and the cornea's innermost surface, the endothelium. Hyphema, anterior uveitis and glaucoma are three main pathologies in this area. In hyphema, blood fills the anterior chamber as a result of a hemorrhage, most commonly after a blunt eye injury. Anterior uveitis is an inflammatory process affecting the iris and ciliary body, with resulting inflammatory signs in the anterior chamber. In glaucoma, blockage of the trabecular meshwork prevents the normal outflow of aqueous humour, resulting in increased intraocular pressure, progressive damage to the optic nerve head, and eventually blindness. The depth of the anterior chamber of the eye varies between 1.5 and 4.0 mm, averaging 3.0 mm. It tends to become shallower at older age and in eyes with hypermetropia (far sightedness). As depth decreases below 2.5 mm, the risk for angle closure glaucoma increases. Clinical significance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres. The cornea can be reshaped by surgical procedures such as LASIK. While the cornea contributes most of the eye's focusing power, its focus is fixed. Accommodation (the refocusing of light to better view near objects) is accomplished by changing the geometry of the lens. Medical terms related to the cornea often start with the prefix "'' kerat-''" from the Greek word κέρας, ''horn''. Structure The cornea has unmyelinated nerve endings sensitive to touch, temperature and chemicals; a touch of the cornea causes an involuntary reflex to close the eyelid. Because transparency is of prime importance, the healthy cornea does not have or need blood vessels with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Impairment
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment– visual impairment may cause the individual difficulties with normal daily tasks including reading and walking. Low vision is a functional definition of visual impairment that is chronic, uncorrectable with treatment or correctable lenses, and impacts daily living. As such low vision can be used as a disability metric and varies based on an individual's experience, environmental demands, accommodations, and access to services. The American Academy of Ophthalmology defines visual impairment as the best-corrected visual acuity of less than 20/40 in the better eye, and the World Health Organization defines it as a presenting acuity of less than 6/12 in the better eye. The term blindness is used for complete or nearly complete vision loss. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived from optic stalks during the seventh week of development and is composed of retinal ganglion cell axons and glial cells; it extends from the optic disc to the optic chiasma and continues as the optic tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus, Pretectal area, pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus. Structure The optic nerve has been classified as the second of twelve paired cranial nerves, but it is technically part of the central nervous system, rather than the peripheral nervous system because it is derived from an out-pouching of the diencephalon (optic stalks) during embryonic development. As a consequence, the fibers of the optic nerve are covered with myelin produced by oligodendrocytes, rather than Schwann cells of the per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the Human nose, nose. Vomiting can be the result of ailments like Food-poisoning, food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pregnancy, motion sickness, or hangover; or it can be an after effect of diseases such as brain tumors, elevated intracranial pressure, or overexposure to ionizing radiation. The feeling that one is about to vomit is called nausea; it often precedes, but does not always lead to vomiting. Impairment due to Alcoholic drink, alcohol or anesthesia can cause inhalation of vomit, leading to suffocation. In severe cases, where dehydration develops, intravenous fluid may be required. Antiemetics are sometimes necessary to suppress nausea and vomiting. Self-induced vomiting can be a component of an eating disorder such as bulimia nervosa, bulimia, and is itself now classified as an eating disorder on its own, purging di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat. Over 30 definitions of nausea were proposed in a 2011 book on the topic. Nausea is a non-specific symptom, which means that it has many possible causes. Some common causes of nausea are gastroenteritis and other gastrointestinal disorders, food poisoning, motion sickness, dizziness, migraine, fainting, low blood sugar, anxiety, and lack of sleep. Nausea is a side effect of many medications including chemotherapy, or morning sickness in early pregnancy. Nausea may also be caused by disgust and depression. Medications taken to prevent and treat nausea and vomiting are called antiemetics. The most commonly prescribed antiemetics in the US are promethazine, metoclopramide, and the newer ondansetron. The word nausea is from Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headache
Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches. Headaches can occur as a result of many conditions. There are a number of different classification systems for headaches. The most well-recognized is that of the International Headache Society, which classifies it into more than 150 types of primary and secondary headaches. Causes of headaches may include dehydration; fatigue; sleep deprivation; stress; the effects of medications (overuse) and recreational drugs, including withdrawal; viral infections; loud noises; head injury; rapid ingestion of a very cold food or beverage; and dental or sinus issues (such as sinusitis). Treatment of a headache depends on the underlying cause, but commonly involves pain medication (especially in case of migraine or cluster headache). A headache is one of the most commonly experienced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slit Lamp
A slit lamp is an instrument consisting of a high-intensity light source that can be focused to shine a thin sheet of light into the eye. It is used in conjunction with a biomicroscope. The lamp facilitates an examination of the anterior segment and posterior segment of the human eye, which includes the eyelid, sclera, conjunctiva, iris, natural crystalline lens, and cornea. The binocular slit-lamp examination provides a stereoscopic magnified view of the eye structures in detail, enabling anatomical diagnoses to be made for a variety of eye conditions. A second, hand-held lens is used to examine the retina. History Two conflicting trends emerged in the development of the slit lamp. One trend originated from clinical research and aimed to apply the increasingly complex and advanced technology of the time. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous Humor
The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball. It fills both the anterior and the posterior chambers of the eye, and is not to be confused with the vitreous humour, which is located in the space between the lens and the retina, also known as the posterior cavity or vitreous chamber. Blood cannot normally enter the eyeball. Structure Composition *Amino acids: transported by ciliary muscles *98% water *Electrolytes ( pH = 7.4 -one source gives 7.1) **Sodium = 142.09 **Potassium = 2.2 - 4.0 **Calcium = 1.8 **Magnesium = 1.1 **Chloride = 131.6 **HCO3- = 20.15 **Phosphate = 0.62 ** Osm = 304 *Ascorbic acid *Glutathione *Immunoglobulins Function *Maintains the intraocular pressure and inflates the globe of the eye. It is this hydrostatic pressure that keeps the eyeball in a roughly spherical shape and keeps the walls of the eyeball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
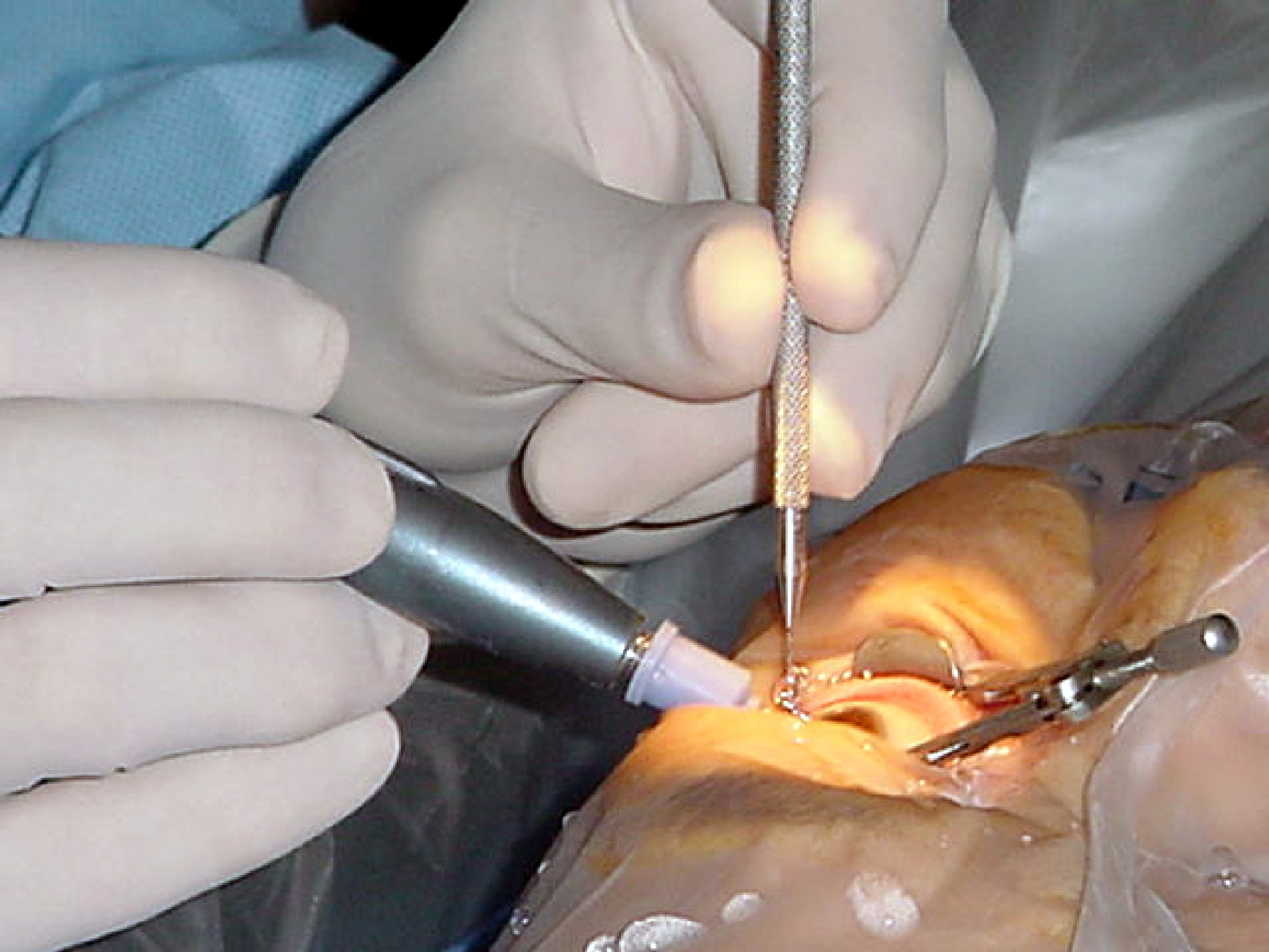
Eye Surgery
Eye surgery, also known as ophthalmic or ocular surgery, is surgery performed on the eye or its adnexa, by an ophthalmologist or sometimes, an optometrist. Eye surgery is synonymous with ophthalmology. The eye is a very fragile organ, and requires extreme care before, during, and after a surgical procedure to minimize or prevent further damage. An expert eye surgeon is responsible for selecting the appropriate surgical procedure for the patient, and for taking the necessary safety precautions. Mentions of eye surgery can be found in several ancient texts dating back as early as 1800 BC, with cataract treatment starting in the fifth century BC. Today it continues to be a widely practiced type of surgery, with various techniques having been developed for treating eye problems. Preparation and precautions Since the eye is heavily supplied by nerves, anesthesia is essential. Local anesthesia is most commonly used. Topical anesthesia using lidocaine topical gel is often used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |