|
Ghost Nebula
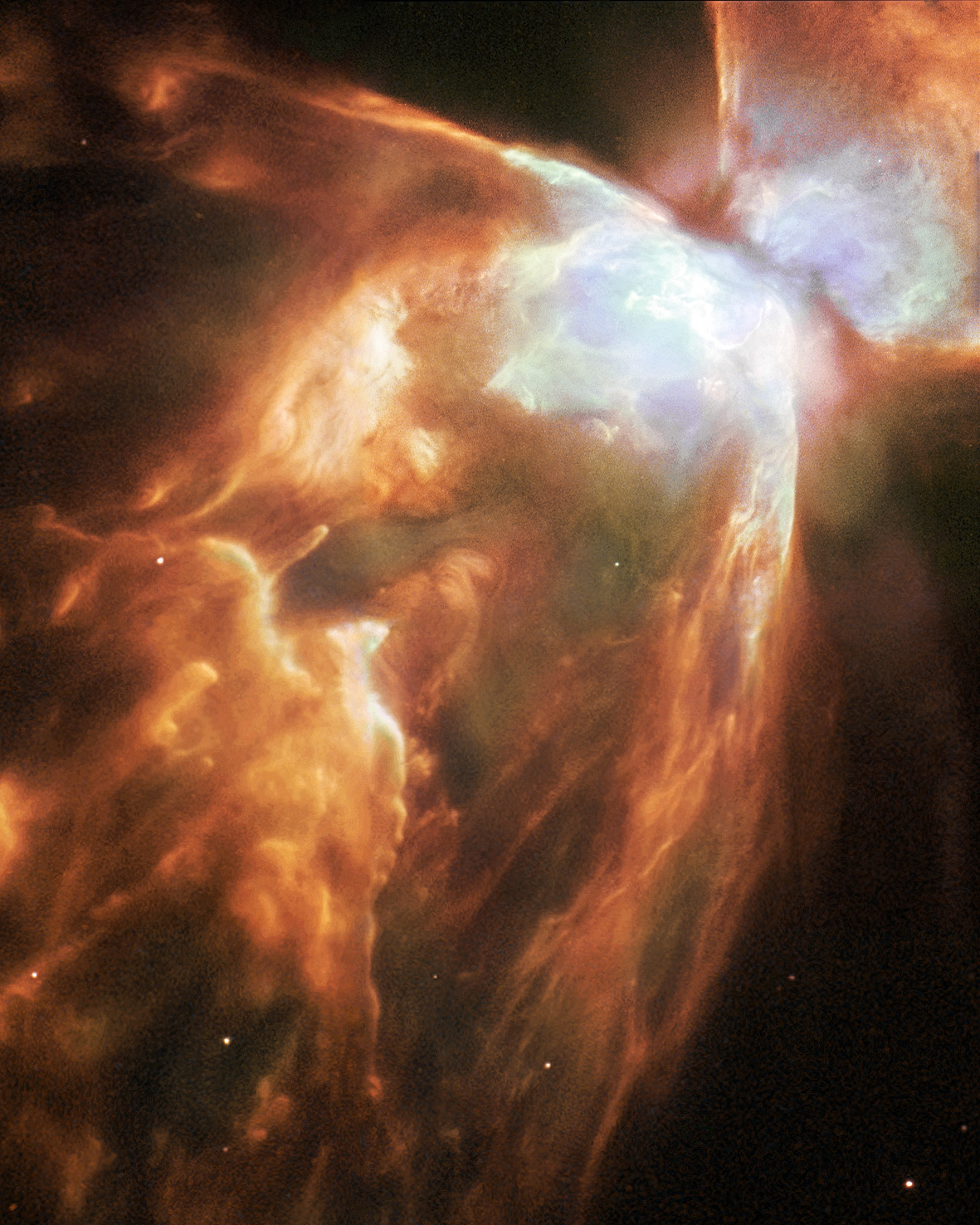
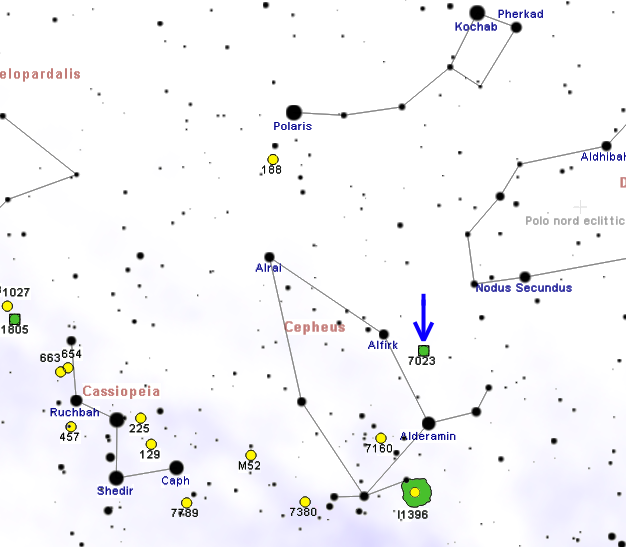
The Ghost Nebula (designated Sh2-136, VdB 141) is a reflection nebula located in the constellation Cepheus. It lies near the cluster may refer to: Science and technology Astronomy * Cluster (spacecraft), constellation of four European Space Agency spacecraft * Asteroid cluster, a small asteroid family * Cluster II (spacecraft), a European Space Agency mission to study t ... NGC 7023. Looking at the adjacent image, the nebula's name is easily understood. The Ghost Nebula is referred to as a globule (catalogued ''CB230'') and over 2 light-years across. There are several stars embedded, whose reflected light make the nebula appear a yellowish-brown colour. References External links Sky-Map.org - Sharpless Catalogue AAN Reflection nebulae Cepheus (constellation) {{nebula-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Lemmon Observatory
Mount Lemmon Observatory (MLO), also known as the Mount Lemmon Infrared Observatory, is an astronomical observatory located on Mount Lemmon in the Santa Catalina Mountains approximately northeast of Tucson, Arizona (US). The site in the Coronado National Forest is used with special permission from the U.S. Forest Service by the University of Arizona's Steward Observatory, and contains a number of independently managed telescopes. History The MLO site was first developed in 1954 as Mount Lemmon Air Force Station, a radar installation of the Air Defense Command. Upon transfer to the Steward Observatory 1970, the site was converted to an infrared observatory. Until 2003, a radar tower operated from Fort Huachuca was used to track launches from the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico and Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Telescopes Below are the 8 telescopes currently operating at the observatory. * The Steward Observatory Telescope is a Cassegrain reflector used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a instant, moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a Astronomical object, celestial body, as they are subject to Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or Perihelion and aphelion, aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cepheus (constellation)
Cepheus is a constellation in the far northern sky, named after Cepheus, a king of Aethiopia in Greek mythology. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the second century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 constellations in the modern times. The constellation's brightest star is Alpha Cephei, with an apparent magnitude of 2.5. Delta Cephei is the prototype of an important class of star known as a Cepheid variable. RW Cephei, an orange hypergiant, together with the red supergiants Mu Cephei, MY Cephei, SW Cephei, VV Cephei, and V354 Cephei are among the largest stars known. In addition, Cepheus also has the hyperluminous quasar S5 0014+81, which hosts an ultramassive black hole in its core, reported at 40 billion solar masses, about 10,000 times more massive than the central black hole of the Milky Way, making this among the most massive black holes currently known. This paper does acknowledge the possibility of an optical illusion that would cause an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidney Van Den Bergh
Sidney Van den Bergh, OC, FRS (born 20 May 1929 in Wassenaar) is a retired Dutch-Canadian astronomer. He showed an interest in science from an early age, learning to read with books on astronomy. In addition to being interested in astronomy. He also liked geology and archeology. His parents got him science books, a telescope, and a microscope, although they wished him to pursue a more practical career and only follow astronomy as a hobby. He went to Leiden University in the Netherlands from 1947 to 1948. He then attended Princeton University on scholarship where he received his A.B. in 1950. In December 1950, he was living in Columbus, Ohio and evidencing an interest in Astronomy. He obtained an MSc from Ohio State University (1952) and a Dr. rer. nat. from the University of Göttingen (1956). He took a faculty position at Ohio State University from 1956 to 1958 before moving to Toronto in 1958 where he spent the first part of his career at the David Dunlap Observatory (DDO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharpless Catalog
The Sharpless catalog is a list of 313 H II regions (emission nebulae) intended to be comprehensive north of declination −27°. (It does include some nebulae south of that declination as well.) The first edition was published in 1953 with 142 objects (Sh1), and the second and final version was published by US astronomer Stewart Sharpless in 1959 with 312 objects. Sharpless also includes some planetary nebulae and supernova remnants, in addition to H II regions. In 1953 Stewart Sharpless joined the staff of the United States Naval Observatory Flagstaff Station, where he surveyed and cataloged H II regions of the Milky Way using the images from the Palomar Sky Survey. From this work Sharpless published his catalog of H II regions in two editions: the first in 1953, with 142 nebula; and the second and final edition in 1959, with 312 nebulae.Stewart SharplessA Catalogue of H II Regions ''Astrophysical Journal'' Supplement, vol. 4, p.257, 1959 Sharpless coordinates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection Nebula
Reflection or reflexion may refer to: Science and technology * Reflection (physics), a common wave phenomenon ** Specular reflection, reflection from a smooth surface *** Mirror image, a reflection in a mirror or in water ** Signal reflection, in signal transmission * Elastic scattering, a process in nuclear and particle physics * Reflection nebula, a nebula that is extended and has no boundaries * Reflection seismology or seismic reflection, a method of exploration geophysics Mathematics * Reflection principle, in set theory * Point reflection, a reflection across a point * Reflection (mathematics), a transformation of a space * Reflection formula, a relation in a function * Reflective subcategory, in category theory Computing * Reflection (computer graphics), simulation of reflective surfaces * Reflection (computer programming), a program that accesses or modifies its own code * Reflection, terminal emulation software by Attachmate Arts and entertainment Film and television * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Cluster
Star clusters are large groups of stars. Two main types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of ten thousand to millions of old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters are more loosely clustered groups of stars, generally containing fewer than a few hundred members, and are often very young. Open clusters become disrupted over time by the gravitational influence of giant molecular clouds as they move through the galaxy, but cluster members will continue to move in broadly the same direction through space even though they are no longer gravitationally bound; they are then known as a stellar association, sometimes also referred to as a ''moving group''. Star clusters visible to the naked eye include the Pleiades, Hyades, and 47 Tucanae. Open cluster Open clusters are very different from globular clusters. Unlike the spherically distributed globulars, they are confined to the galactic plane, and are almost always found wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iris Nebula
The Iris Nebula (also known as NGC 7023 and Caldwell 4) is a bright reflection nebula in the constellation Cepheus. The designation NGC 7023 refers to the open cluster within the larger reflection nebula designated LBN 487. The nebula, which shines at magnitude +6.8, is illuminated by a magnitude +7.4 star designated SAO 19158. It is located near the Mira-type variable star T Cephei, and near the bright magnitude +3.23 variable star Beta Cephei Beta Cephei (β Cephei, abbreviated Beta Cep, β Cep) is a triple star system of the third magnitude in the constellation of Cepheus. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 690 light-y ... (Alfirk). It lies 1,300 light-years away and is six light-years across. Notes References * * External links * SEDS – NGC 7023VizieR – NGC 7023NED – NGC 7023Dark Atmospheres Photography – Iris Nebula NGC 7023See NGC 7023 in WorldWide Telescope {{DEFAULTSORT:Iris N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bok Globule
In astronomy, Bok globules are isolated and relatively small dark nebulae, containing dense cosmic dust and gas from which star formation may take place. Bok globules are found within H II regions, and typically have a mass of about 2 to 50 solar masses contained within a region about a light year or so across (about ). They contain molecular hydrogen (H2), carbon oxides and helium, and around 1% (by mass) silicate dust. Bok globules most commonly result in the formation of double- or multiple-star systems. History Bok globules were first observed by astronomer Bart Bok in the 1940s. In an article published in 1947, he and Edith Reilly hypothesized that these clouds were "similar to insect's cocoons" that were undergoing gravitational collapse to form new stars, from which stars and star clusters were born. This hypothesis was difficult to verify due to the observational difficulties of establishing what was happening inside a dense dark cloud that obscured all visible light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection Nebulae
Reflection or reflexion may refer to: Science and technology * Reflection (physics), a common wave phenomenon ** Specular reflection, reflection from a smooth surface *** Mirror image, a reflection in a mirror or in water ** Signal reflection, in signal transmission * Elastic scattering, a process in nuclear and particle physics * Reflection nebula, a nebula that is extended and has no boundaries * Reflection seismology or seismic reflection, a method of exploration geophysics Mathematics * Reflection principle, in set theory * Point reflection, a reflection across a point * Reflection (mathematics), a transformation of a space * Reflection formula, a relation in a function * Reflective subcategory, in category theory Computing * Reflection (computer graphics), simulation of reflective surfaces * Reflection (computer programming), a program that accesses or modifies its own code * Reflection, terminal emulation software by Attachmate Arts and entertainment Film and televisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |