|
Gerov Pass
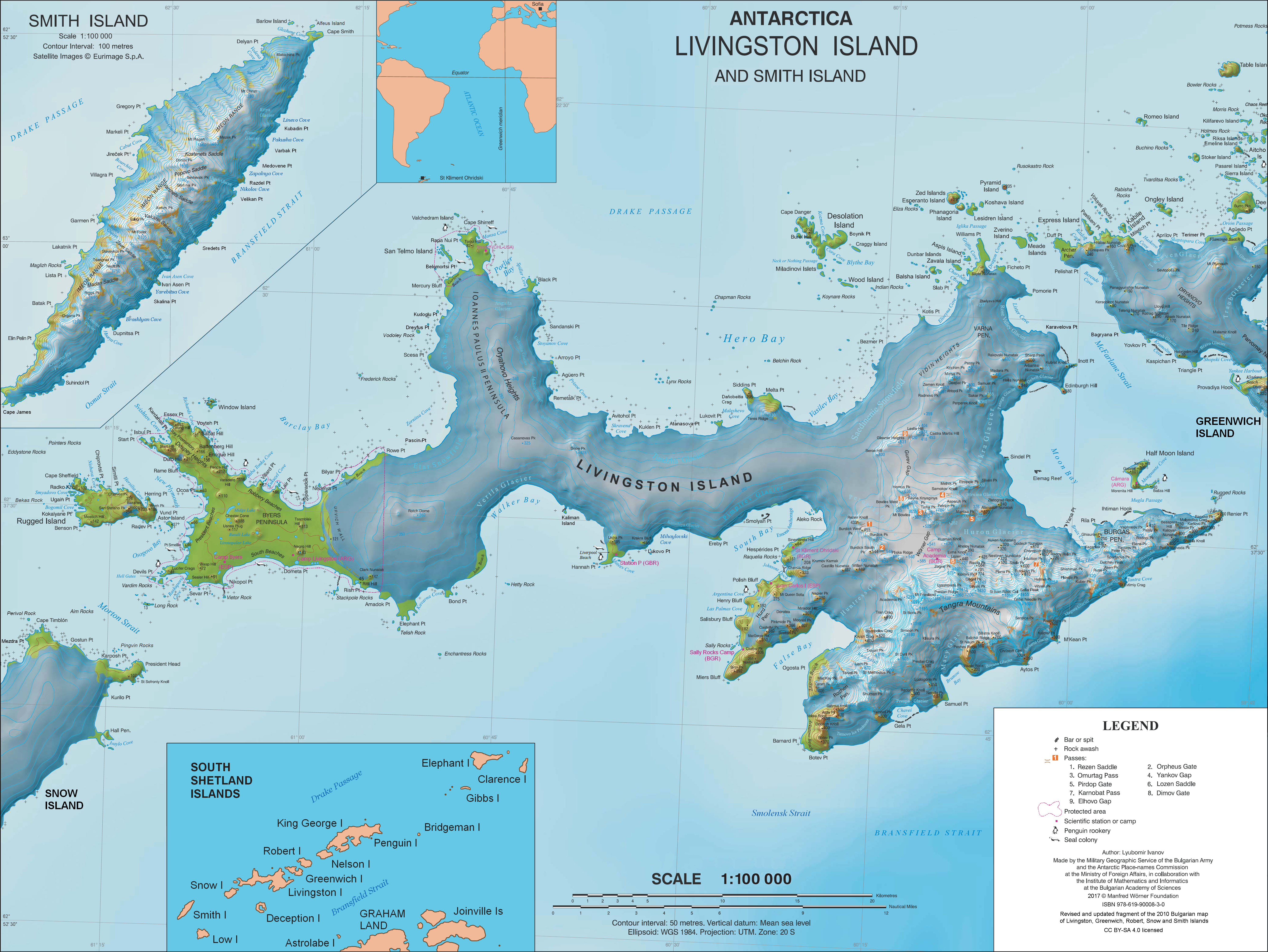
Gerov Pass ( bg, Геров проход, ‘Gerov Prohod’ \'ge-rov 'pro-hod\) is a pass of elevation 400 m in Friesland Ridge, Tangra Mountains on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Situated on Rozhen Peninsula, 1.6 km south-southeast of Pleven Saddle. Bounded by Shumen Peak to the east-northeast, and Gabrovo Knoll to the west-southwest. Providing overland access between Charity Glacier to the northwest and Tarnovo Ice Piedmont to the south. Bulgarian topographic survey Tangra 2004/05. Named after the Bulgarian linguist Nayden Gerov (1823–1900). Location Gerov Pass is located at . British mapping in 1968, Spanish in 1991 and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009. Map * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. References Gerov Pass.SCAR A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charity Glacier
Charity Glacier () is a glacier on Rozhen Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica draining the southwest slopes of St. Methodius Peak in Tangra Mountains, and flowing west-southwestwards into False Bay north of Barnard Point, between Zagore Beach and Arkutino Beach. The glacier was named by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee in 1958 after the brig ''Charity'' (Capt. Charles H. Barnard), one of a fleet of American sealers from New York which visited the South Shetland Islands in 1820–21, operating mainly from Yankee Harbor, Greenwich Island. The ''Charity'' also visited the islands the following season. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Map * L.L. Ivanov et al., Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands (from English Strait to Morton Strait, with illustrations and ice-cover distribution), 1:100000 scale topographic map, Antarctic Place-names Commission The Antarctic Place-nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Place-names Commission
The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria. The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in Antarctica, which are formally given by the President of the Republic according to the Bulgarian Constitution (Art. 98) and the established international practice. Bulgarian names in Antarctica Geographical names in Antarctica reflect the history and practice of Antarctic exploration. The nations involved in Antarctic research give new names to nameless geographical features for the purposes of orientation, logistics, and international scientific cooperation. As of 2021, there are some 20,091 named Antarctic geographical features, including 1,601 features with names given by Bulgaria.Bulgarian Antarctic Gazet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Gazetteer Of Antarctica
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Committee On Antarctic Research
The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is an interdisciplinary body of the International Science Council (ISC). SCAR coordinates international scientific research efforts in Antarctica, including the Southern Ocean. SCAR's scientific work is administered through several discipline-themed ''science groups''. The organisation has observer status at, and provides independent advice to Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings, and also provides information to other international bodies such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). History At the International Council of Scientific Unions (ICSU)’s Antarctic meeting held in Stockholm from 9–11 September 1957, it was agreed that a committee should be created to oversee scientific research in Antarctica. At the time there were 12 nations actively conducting Antarctic research and they were each invited to nominate one delegate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nayden Gerov
Nayden Gerov ( bg, Найден Геров), born Nayden Gerov Hadzhidobrevich ( bg, Найден Геров Хаджидобревич) February 23, 1823, Koprivshtitsa – October 9, 1900, Plovdiv) was a Bulgarian linguist, folklorist, writer and public figure during the Bulgarian National Revival. Gerov was the son of Gero Dobrevich, a teacher. He studied at his father's school, then at a Greek school in Plovdiv from 1834 to 1836, again in his hometown until 1839, and finally in Odessa, in the Russian Empire, where he graduated from the Richelieu Lyceum in 1845. Gerov became a Russian subject and came back to Koprivshtitsa, where he established his own school, named after Saints Cyril and Methodius. He became famous for his erudition and was invited to open a gymnasium in Plovdiv as well, an invitation which he accepted. As a publicist, he fought the "Graecisation" (assimilation to Greek culture) among the Bulgarians of the time, especially in Plovidiv. At the same time, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguist
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangra 2004/05
The Tangra 2004/05 Expedition was commissioned by the Antarctic Place-names Commission at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria, managed by the Manfred Wörner Foundation, and supported by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute, the Institute of Mathematics and Informatics at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Bulgarian Posts, Uruguayan Antarctic Institute, Peregrine Shipping (Australia), and Petrol Ltd, TNT, Mtel, Bulstrad, Polytours, B. Bekyarov and B. Chernev (Bulgaria). Expedition team Dr. Lyubomir Ivanov (team leader), senior research associate, Institute of Mathematics and Informatics at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences; chairman, Antarctic Place-names Commission; author of the 1995 Bulgarian Antarctic ''Toponymic Guidelines'' introducing in particular the present official system for the Romanization of Bulgarian; participant in four Bulgarian Antarctic campaigns, and author of the first Bulgarian Antarctic topographic maps. Doychin Vasilev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarnovo Ice Piedmont
Tarnovo Ice Piedmont ( bg, ледник Търново, lednik Tarnovo, ) is an ice piedmont on Rozhen Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica is situated southeast of Charity Glacier and west-southwest of Prespa Glacier. It extends 3.5 km in east-west direction and 2.5 km in north-south direction, is bounded to the west by Veleka Ridge, to the north by Arda Peak, Gerov Pass and Shumen Peak, and to the east by Yambol Peak, and flows southeastwards into Bransfield Strait east of Botev Point and west of Gela Point. The feature is named after the city of Tarnovo (Veliko Tarnovo) in northern Bulgaria, the capital of the medieval Second Bulgarian Empire. Location The midpoint is located at (UK Directorate of Overseas Surveys mapping in 1968, and Bulgarian mapping in 2005 and 2009). Maps South Shetland Islands.Scale 1:200000 topographic map. DOS 610 Sheet W 62 60. Tolworth, UK, 1968. * Islas Livingston y Decepción. Mapa topográfico a esca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabrovo Knoll
Gabrovo Knoll ( bg, връх Габрово, vrah Gabrovo, ) is a peak rising to 500m in the Friesland Ridge, Tangra Mountains, Livingston Island. The peak surmounts Charity Glacier to the north and Tarnovo Ice Piedmont to the southeast, and is separated from Shumen Peak to the east-northeast by Gerov Pass. The knoll is named after the Bulgarian town of Gabrovo. Location The peak is located at , which is 1.8 km south of MacKay Peak, 2.26 km west-southwest of Shumen Peak, 430 m north of Arda Peak and 1 km northeast of Veleka Peak (Bulgarian mapping in 2005 and 2009). Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. :commons:Image:Livingston-Greenwich-map.jpg, Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulgaria, 2005. * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. References Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |