|
German Imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and military power), but also soft power (cultural and diplomatic power). While related to the concepts of colonialism and empire, imperialism is a distinct concept that can apply to other forms of expansion and many forms of government. Etymology and usage The word ''imperialism'' originated from the Latin word ''imperium'', which means supreme power, "sovereignty", or simply "rule". It first became common in the current sense in Great Britain during the 1870s, when it was used with a negative connotation. Hannah Arendt and Joseph Schumpeter defined imperialism as expansion for the sake of expansion. Previously, the term had been used to describe what was perceived as Napoleon III's attempts at obtaining political support through foreig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punch Rhodes Colossus
Punch commonly refers to: * Punch (combat), a strike made using the hand closed into a fist * Punch (drink), a wide assortment of drinks, non-alcoholic or alcoholic, generally containing fruit or fruit juice Punch may also refer to: Places * Punch, U.S. Virgin Islands * Poonch (other), often spelt as Punch, several places in India and Pakistan People * Punch (surname), a list of people with the name * Punch (nickname), a list of people with the nickname * Punch Masenamela (born 1986), South African footballer * Punch (rapper), 21st century American rapper Terrence Louis Henderson Jr. * Punch (singer), South Korean singer Bae Jin-young (born 1993) Arts, entertainment and media Fictional entities * Mr. Punch (also known as Pulcinella or Pulcinello), the principal puppet character in the traditional ''Punch and Judy'' puppet show * Mr. Punch, the masthead image and nominal editor of ''Punch'', largely borrowed from the puppet show * Mr. Punch, a fictional character in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periphery Countries
In world systems theory, the periphery countries (sometimes referred to as just the periphery) are those that are less developed than the semi-periphery countries, semi-periphery and core countries. These countries usually receive International inequality, a disproportionately small share of global wealth. They have weak state institutions and are dependent on – according to some, exploited by – more developed countries. These countries are usually behind because of obstacles such as lack of technology, unstable government, and poor education and health systems. In some instances, the exploitation of periphery countries' agriculture, cheap labor, and natural resources aid core countries in remaining dominant. This is best described by dependency theory,Thomas Shannon. An Introduction to the World-System Perspective. 1996. which is one theory on how globalization can affect the world and the countries in it. It is, however, possible for periphery countries to rise out of their st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
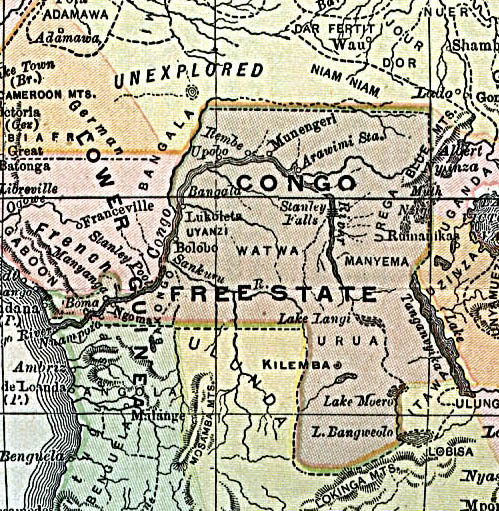
Atrocities In The Congo Free State
In the period from 1885 to 1908, many well-documented atrocities were perpetrated in the Congo Free State (today the Democratic Republic of the Congo) which, at the time, was a State (polity), state under the absolute rule of Leopold II of Belgium, King Leopold II of the Belgians. These atrocities were particularly associated with the labour policies used to collect natural rubber for export. Together with epidemic disease, famine, and a falling birth rate caused by these disruptions, the atrocities contributed to a sharp decline in the Congolese population. The magnitude of the population fall over the period is disputed, with modern estimates ranging from 1.5 million to 13 million. At the Berlin Conference of 1884–1885, the European powers allocated most of the Congo Basin region to a supposedly philanthropic organisation run by Leopold II, who had long held ambitions for colonial expansion. The territory under Leopold's control exceeded ; amid financial problems, it was dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utsa Patnaik
Utsa Patnaik is an Indian Marxian economist. She taught at the Centre for Economic Studies and Planning in the School of Social Sciences at Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) in New Delhi, from 1973 until her retirement in 2010. Her husband is the Marxian economist Prabhat Patnaik. Biography Patnaik obtained her doctorate in economics from the Somerville College, Oxford, before returning to India to join JNU. Her main areas of research interest are the problems of transition from agriculture and peasant predominant societies to industrial society, both in a historical context and at present in relation to India; and questions relating to food security and poverty. Selected works These issues have been discussed in more than 110 papers published as chapters in books and in journal A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to: *Bullet journal, a method of personal organization *Diary, a record of what happened over the course of a day or other peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Bengal
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Bengal) encompassing much of the Bengal region, which includes modern Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, Indian state of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odissa between the 16th and 18th centuries. The state was established following the dissolution of the Bengal Sultanate, a major trading nation in the world, when the region was absorbed into one of the gunpowder empires. Bengal was the wealthiest region in the Indian subcontinent, due to their thriving merchants, Seth's, Bankers and traders and its proto-industrial economy showed signs of driving an Industrial revolution. Bengal Subah has been variously described the "Paradise of Nations" and the "Golden Age of Bengal", due to its inhabitants' living standards and real wages, which were am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald Robinson
Ronald "Robbie" Edward Robinson, FBA (3 September 1920 – 19 June 1999) was a distinguished historian of the British Empire who between 1971 and 1987 held the Beit Professorship of Commonwealth History at the University of Oxford. After schooling at Battersea Grammar School, he proceeded to St. John's College, Cambridge, as a History Scholar in 1938 and with the outbreak of the Second World War he joined the Royal Air Force, eventually spending most of his armed service in Africa. After the end of the war, between 1947 and 1949, Robinson worked on the subject of "trusteeship" for his doctorate at Cambridge. He was subsequently elected a Fellow of St. John's College, Cambridge, in 1949. Robinson's extraordinarily influential work, '' Africa and the Victorians: The Official Mind of Imperialism'', was co-authored with John Gallagher (with the help of his wife Alice Denny) and first published in 1961. The latter work had been preceded by a widely read article – also co-author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Andrew Gallagher
John Andrew Gallagher (1 April 1919 – 5 March 1980), known as Jack Gallagher, was an historian of the British Empire who between 1963 and 1970 held the Beit Professorship of Commonwealth History at the University of Oxford and from 1971 until his death was the Vere Harmsworth Professor of Imperial and Naval History at the University of Cambridge. Early life and career Gallagher was born on 1 April 1919. After schooling at the Birkenhead Institute, he proceeded to Trinity College, Cambridge, as a history scholar and with the outbreak of the Second World War he joined the Royal Tank Regiment, eventually serving in Italy, Greece, and North Africa. After the end of the war, Gallagher returned to Cambridge to complete his studies and was elected a Fellow of Trinity College in 1948. Scholarship Gallagher's influential work "The Imperialism of Free Trade" and '' Africa and the Victorians: The Official Mind of Imperialism'', was co-authored with Ronald Robinson (with the help of Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonial Africa 1913 Map
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to: * Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology) Architecture * American colonial architecture * French Colonial * Spanish Colonial architecture Automobiles * Colonial (1920 automobile), the first American automobile with four-wheel brakes * Colonial (Shaw automobile), a rebranded Shaw sold from 1921 until 1922 * Colonial (1921 automobile), a car from Boston which was sold from 1921 until 1922 Places * The Colonial (Indianapolis, Indiana) * The Colonial (Mansfield, Ohio), a National Register of Historic Places listing in Richland County, Ohio * Ciudad Colonial (Santo Domingo), a historic central neighborhood of Santo Domingo * Colonial Country Club (Memphis), a golf course in Tennessee * Colonial Country Club (Fort Worth), a golf course in Texas ** Fort Worth Invitational or The Colonial, a PGA golf tournament Trains * ''Colonial'' (PRR train), a Pennsylvania Railroad run between Washington, DC and New York C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scramble For Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonisation of Africa, colonization of most of Africa by seven Western Europe, Western European powers during a short period known as New Imperialism (between 1881 and 1914). The 10 percent of Africa that was under formal European control in 1870 increased to almost 90 percent by 1914, with only Liberia and Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopia remaining independent. The Berlin Conference of 1884, which regulated European colonization and trade in Africa, is usually accepted as the beginning. In the last quarter of the 19th century, there were considerable political rivalries within the empires of the European continent, leading to the African continent being partitioned without wars between European nations. The later years of the 19th century saw a transition from "Informal empire, informal imperialism" – military influence and economic dominance – to di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1924 and of the Soviet Union from 1922 to 1924. Under his administration, Russia, and later the Soviet Union, became a one-party socialist state governed by the Communist Party. Ideologically a Marxist, his developments to the ideology are called Leninism. Born to an upper-middle-class family in Simbirsk, Lenin embraced revolutionary socialist politics following his brother's 1887 execution. Expelled from Kazan Imperial University for participating in protests against the Russian Empire's Tsarist government, he devoted the following years to a law degree. He moved to Saint Petersburg in 1893 and became a senior Marxist activist. In 1897, he was arrested for sedition and exiled to Shushenskoye in Siberia for three years, where he married ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roubaud (died 1014 or 1015), Count and Margrave of Provence
{{surname ...
Roubaud may refer to: * Émile Roubaud (1882–1962), a French biologist, pathologist and entomologist * Franz Roubaud (1856-1928), a Russian painter who created some of the largest panoramic paintings * Jacques Roubaud (born 1932), a French poet and mathematician * Jean-Marc Roubaud (born 1951), a member of the National Assembly of France See also * Rotbold I of Provence (died 1008) Count and Margrave of Provence * Rotbold II of Provence Rotbold II (also ''Rothbold'', ''Rotbald'', ''Rodbald'', ''Roubaud'', or ''Rotbaud'') (died 1014 or 1015) was the Count and Margrave of Provence from 1008 to his death. He was the only son of Rotbold I and Emilde, daughter of Stephen, Viscount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert J
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |