|
Georgian Bay Formation
The Georgian Bay Formation is a geologic formation in Michigan and Ontario. It preserves fossils dating back to the Ordovician period. The type locality of the formation is on East Meaford Creek (previously called Workman Creek), south shore of Nottawasaga Bay, Georgian Bay. Description The formation consists of massive shale interbedded with siltstone/sandstone and limestone Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ..., with sub-horizontal bedding planes and widely-spaced jointing. Fossil content Ichnotaxa Vertebrates Invertebrates See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Michigan References * Ordovician Michigan Ordovician southern paleotemperate deposits Ordovician southern paleotropical deposits {{Michigan-geologic-formation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (stratigraphy)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness (geology), thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oulodus
''Oulodus'' is a genus of conodonts in the family Prioniodinidae. ''O. elegans'' is found in the Late Silurian to Early Devonian Keyser Formation, a mapped limestone bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia. References External links * Prioniodinida genera Paleozoic life of Ontario Paleozoic life of British Columbia Paleozoic life of the Northwest Territories Paleozoic life of Quebec Paleozoic life of Yukon {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagawong
Billings is a township in the Canadian province of Ontario, as well as the name of a community within that township. Located in the Manitoulin District, the township had a population of 603 in the Canada 2016 Census. Communities The primary community in the township is Kagawong. There are three smaller communities: Billings, Bowser's Corner, and Pleasant Valley. Kagawong Kagawong's harbour is located on Mudge Bay and is home to the Kagawong Lighthouse, which has been in continuous service since 1888. The name Kagawong means "where mists rise from falling waters" in the Ojibwe language, a reference to the nearby Bridal Veil Falls on the Kagawong River. Kagawong is home to numerous tourist attractions. The most popular being the famed Bridal Veil Falls. The legend is that those who swim under the falls are rewarded with good luck. The falls begin at the end of the upper Kagawong river, and flow past a series of small, cascading waterfalls down a winding trail towards Mudge Bay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorphognathus
''Amorphognathus'' is an extinct conodont genus in the family Balognathidae Balognathidae is an extinct conodont family. Genera Genera are: * †'' Amorphognathus'' * †'' Baltoniodus'' * †'' Birksfeldia'' * †'' Icriodella'' * †'' Notiodella'' * †'' Polyplacognathus'' * †'' Prioniodus'' * †''Promissum'' * � ... from the Ordovician.The Ordovician zone index conodont Amorphognathus ordovicicus Branson & Mehl, 1933 from its type locality and the evolution of the genus Amorphognathus Branson & Mehl, 1933. Stig M. Bergström and Stephen A. Leslie, April 2010, Journal of Micropalaeontology, 29, pages 73-80, References External links * Prioniodontida genera Ordovician conodonts Paleozoic life of Manitoba Paleozoic life of the Northwest Territories Paleozoic life of Nunavut {{conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
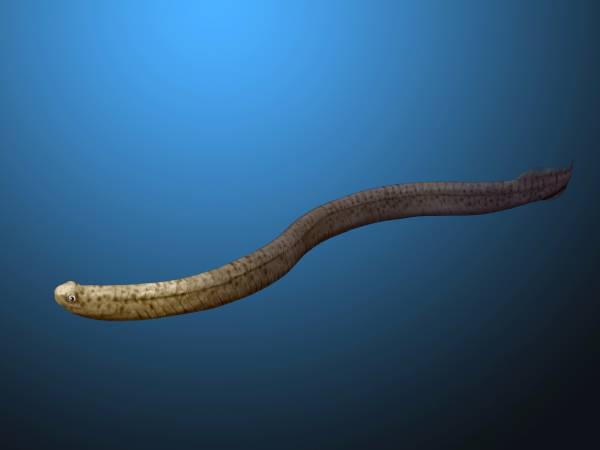
Conodont
Conodonts (Greek ''kōnos'', "cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil evidence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |