|
George Van Driem
George "Sjors" van Driem (born 1957) is a Dutch linguist associated with the University of Bern, where he is the chair of Historical Linguistics and directs the Linguistics Institute. Education * Leiden University, 1983–1987 (PhD, ''A Grammar of Limbu'') * Leiden University, 1981–1983 (MA Slavic, BA English, MA General Linguistics) * Leiden University, 1979–1981 (BA Slavic) * University of Virginia at Charlottesville, 1975–1979 (BA Biology) * Katholieke Universiteit Nijmegen, 1978–1979 * Watling Island Marine Biological Station on San Salvador Island in the Bahamas, 1977 * Duke University at Durham, North Carolina, 1976 Research George van Driem has conducted field research in the Himalayas since 1983. He was commissioned by the Royal Government of Bhutan to codify a grammar of Dzongkha, the national language, design a phonological romanisation for the language known as Roman Dzongkha, and complete a survey of the language communities of the kingdom. He and native Dzo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
) , anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau") , image_map = , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands , established_title = Before independence , established_date = Spanish Netherlands , established_title2 = Act of Abjuration , established_date2 = 26 July 1581 , established_title3 = Peace of Münster , established_date3 = 30 January 1648 , established_title4 = Kingdom established , established_date4 = 16 March 1815 , established_title5 = Liberation Day (Netherlands), Liberation Day , established_date5 = 5 May 1945 , established_title6 = Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Kingdom Charter , established_date6 = 15 December 1954 , established_title7 = Dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, Caribbean reorganisation , established_date7 = 10 October 2010 , official_languages = Dutch language, Dutch , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = , languages2_type = Reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayan Languages Project
The Himalayan Languages Project, launched in 1993, is a research collective based at Leiden University and comprising much of the world's authoritative research on the lesser-known and endangered languages of the Himalayas, in Nepal, China, Bhutan, and India. Its members regularly spend months or years at a time doing field research with native speakers. The Director of the Himalayan Languages Project is George van Driem; other top authorities include Mark Turin and Jeroen Wiedenhof. It recruits grad students to collect new field research on little-known languages as the topics for their Ph.D. dissertations. The Himalayan Languages Project was officially commissioned by the government of Bhutan to devise a standard romanization of Dzongkha. Since George van Driem's move to the University of Bern, many members of the Himalayan Languages Project are now based out of Switzerland. Languages studied Many of the languages studied by the Project are believed to be doomed to extinction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzongkha Language
Dzongkha (; ) is a Sino-Tibetan language that is the official and national language of Bhutan. It is written using the Tibetan script. The word means "the language of the fortress", from ' "fortress" and ' "language". , Dzongkha had 171,080 native speakers and about 640,000 total speakers. Dzongkha is considered a South Tibetic language. It is closely related to and partially intelligible with Sikkimese, and to some other Bhutanese languages such as Chocha Ngacha, Brokpa, Brokkat and Lakha. It has a more distant relationship to Standard Tibetan. Spoken Dzongkha and Tibetan are around 50 to 80 percent mutually intelligible. Usage Dzongkha and its dialects are the native tongue of eight western districts of Bhutan (''viz.'' Wangdue Phodrang, , Thimphu, Gasa, Paro, Ha, Dagana and Chukha). There are also some native speakers near the Indian town of Kalimpong, once part of Bhutan but now in North Bengal and in Sikkim. Dzongkha was declared the national language of Bhutan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden University Faculty
Leiden (; in English and archaic Dutch also Leyden) is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland, Netherlands. The municipality of Leiden has a population of 119,713, but the city forms one densely connected agglomeration with its suburbs Oegstgeest, Leiderdorp, Voorschoten and Zoeterwoude with 206,647 inhabitants. The Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) further includes Katwijk in the agglomeration which makes the total population of the Leiden urban agglomeration 270,879, and in the larger Leiden urban area also Teylingen, Noordwijk, and Noordwijkerhout are included with in total 348,868 inhabitants. Leiden is located on the Oude Rijn, at a distance of some from The Hague to its south and some from Amsterdam to its north. The recreational area of the Kaag Lakes (Kagerplassen) lies just to the northeast of Leiden. A university city since 1575, Leiden has been one of Europe's most prominent scientific centres for more than four centuries. Leiden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden University Alumni
Leiden (; in English and archaic Dutch also Leyden) is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland, Netherlands. The municipality of Leiden has a population of 119,713, but the city forms one densely connected agglomeration with its suburbs Oegstgeest, Leiderdorp, Voorschoten and Zoeterwoude with 206,647 inhabitants. The Statistics Netherlands, Netherlands Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS) further includes Katwijk in the agglomeration which makes the total population of the Leiden urban agglomeration 270,879, and in the larger Leiden urban area also Teylingen, Noordwijk, and Noordwijkerhout are included with in total 348,868 inhabitants. Leiden is located on the Oude Rijn (Utrecht and South Holland), Oude Rijn, at a distance of some from The Hague to its south and some from Amsterdam to its north. The recreational area of the Kaag Lakes (Kagerplassen) lies just to the northeast of Leiden. A University town, university city since 1575, Leiden has been one of Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguists Of Southeast Asian Languages
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguists Of Himalayan Languages
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social contex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguists From The Netherlands
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social contex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
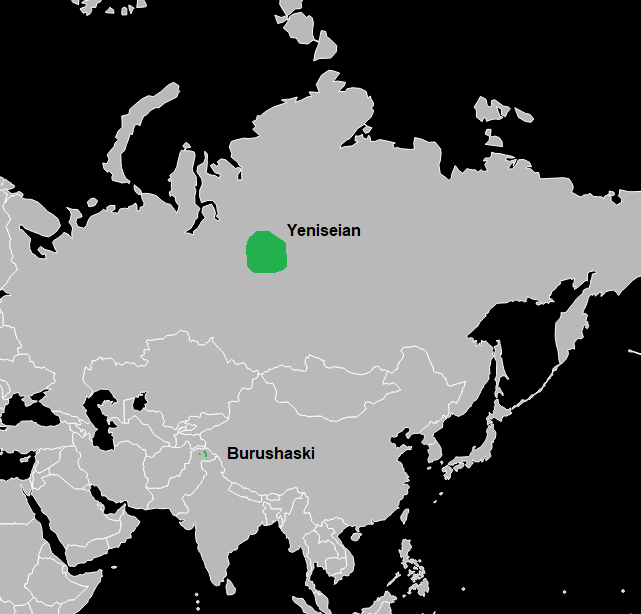
Karasuk Languages
Karasuk is a hypothetical language family that links the Yeniseian languages of central Siberia with the Burushaski language of northern Pakistan. History of proposals Hyde Clarke (1870) first noted a possible connection between the Yeniseian and Burushaski languages. The name ''Karasuk'' was proposed by George van Driem of the University of Leiden The family is named after the Karasuk culture, which existed in Central Asia during the Bronze Age in second millennium BCE. Van Driem postulates the Burusho people took part in the Indo-Aryan migration out of Central Asia and into the northern part of the Indian sub-continent, while other Karasuk peoples migrated northwards to become the Yeniseians. These claims have been picked up by anthropologist and linguist Roger Blench (1999). Václav Blažek (2019) places the linguistic homeland of Proto-Yeniseian close to where Burushaski is now spoken today. He argues that based on hydronomic evidence, Yeniseian languages were originally spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahakiranti Languages
The Mahakiranti or Maha-Kiranti ('Greater Kiranti') languages are a proposed intermediate level of classification of the Sino-Tibetan languages, consisting of the Kiranti languages and neighbouring languages thought to be closely related to them. Researchers disagree on which languages belong in Mahakiranti, or even whether Mahakiranti is a valid group. The group was originally proposed by George van Driem, who retracted his proposal in 2004 after a field study in Bhutan. Conceptions of Mahakiranti van Driem (2001) posits that the Mahakiranti languages besides Kiranti proper are Newar, Baram, and Thangmi. Baram and Thangmi are clearly related, but it is not yet clear if the similarities they share with Newar demonstrate a 'Para-Kiranti' family, as van Driem suggests, or if they are borrowings. He sees Lepcha, Lhokpu, and the Magaric languages (in the narrow sense, whether or not Chepangic proves to be Magar) as the Bodic languages closest to Mahakiranti. ;van Driem's concepti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathmandu
, pushpin_map = Nepal Bagmati Province#Nepal#Asia , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Province , subdivision_name1 = Bagmati Province , subdivision_type2 = District , subdivision_name2 = Kathmandu , established_title = , founder = Manjushri , parts_type = No. of Wards , parts = 32 , seat_type = , seat = , government_footnotes = , government_type = Mayor–council government , governing_body = Kathmandu Metropolitan Government, , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Balendra Shah ( Ind.) , leader_title1 = Deputy mayor , leader_name1 = Sunita Dangol (UML) , leader_title2 = Executive Officer , leader_name2 = Basanta Adhikari , unit_pref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirat Yakthung Chumlung
Kirat Yakthung Chumlung ( Nepali: किरात याक्थुङ चुम्लुङ) (1989) is a social organization of the Limbu indigenous ethnic group of Nepal. See also * Kirat The Kirati people, also spelled as Kirant or Kiranti, are a Sino-Tibetan ethnic group. They are peoples of the Himalayas, mostly the Eastern Himalaya extending eastward from Nepal to North East India (predominantly in the Indian state of Sikkim ... References External links Official web site of Kirat Yakthung Chumlung Central Committee NepalOfficial web site of Kirat Yakthung Chumlung in UK Indigenous organisations in Nepal 1989 establishments in Nepal {{Nepal-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |