|
George Lincoln Goodale
George Lincoln Goodale (August 3, 1839 – April 12, 1923) was an American botanist and the first director of Harvard’s Botanical Museum (now part of the Harvard Museum of Natural History). It was he who commissioned the making of the University's legendary Glass Flowers collection. Early life Goodale was born in Saco, Maine. He graduated from Amherst College in 1860 and from Harvard Medical School in 1863, after which he practiced in Portland, Maine, until 1867. Career Goodale became professor of natural science and applied chemistry at Bowdoin. In 1872, he was appointed instructor in botany and University lecturer on vegetable physiology at Harvard, and advanced to assistant professor of the latter subject a year later. In 1878, he became a professor of botany and the Fisher professor of natural science, a chair formerly held by Asa Gray. Glass Flowers At some point during his career as a Harvard/Radcliffe Professor, Goodale taught avid Botany student Mary L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saco, Maine
Saco is a city in York County, Maine, York County, Maine, United States. The population was 20,381 at the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census. It is home to Ferry Beach State Park, Funtown Splashtown USA, Thornton Academy, as well as General Dynamics Armament Systems (also known by its former name, Saco Defense), a subsidiary of the defense contractor General Dynamics. Saco sees much tourism during summer months due to its amusement parks, Ferry Beach State Park, and proximity to Old Orchard Beach. Saco is part of the Portland, Maine, Portland–South Portland, Maine, South Portland–Biddeford, Maine, Biddeford, Maine Portland-South Portland-Biddeford metropolitan area, metropolitan statistical area. Saco's twin-city is Biddeford. History This was territory of the Abenaki tribe whose fortified village was located up the Sokokis Trail at Pequawket (now Fryeburg, Maine, Fryeburg). There was a settlement at the mouth of the Saco river, with homes and permanent cultiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecturer
Lecturer is an List of academic ranks, academic rank within many universities, though the meaning of the term varies somewhat from country to country. It generally denotes an academic expert who is hired to teach on a full- or part-time basis. They may also conduct research. Comparison The table presents a broad overview of the traditional main systems, but there are universities which use a combination of those systems or other titles. Note that some universities in Commonwealth countries have adopted the American system in place of the Commonwealth system. Uses around the world Australia In Australia, the term lecturer may be used informally to refer to anyone who conducts lectures at a university or elsewhere, but formally refers to a specific academic rank. The academic ranks in Australia are similar to those in the UK, with the rank of associate professor roughly equivalent to reader in UK universities. The academic levels in Australia are (in ascending academic level) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark (currency)
The mark was a currency or unit of account in many states. It is named for the mark unit of weight. The word ''mark'' comes from a merging of three Teutonic/ Germanic words, Latinised in 9th-century post-classical Latin as ', ', ' or '. It was a measure of weight mainly for gold and silver, commonly used throughout Europe and often equivalent to . Considerable variations, however, occurred throughout the Middle Ages. As of 2022, the only circulating currency named "mark" is the Bosnia and Herzegovina convertible mark. List of currencies named "mark" or similar "Mark" can refer * to one of the following historical German currencies: ** Since the 11th century: the , used in the Electorate of Cologne; ** 1319: the , minted and used by the North German Hanseatic city of Stralsund and various towns in Pomerania; ** 1502: the , a uniform coinage for the ''Wends'' () Hanseatic cities of Lübeck, Hamburg, Wismar, Lüneburg, Rostock, Stralsund, Anklam, among others, who joined th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopold And Rudolf Blaschka
Leopold Blaschka (27 May 1822 – 3 July 1895) and his son Rudolf Blaschka (17 June 1857 – 1 May 1939) were glass artists from Dresden, Germany, native to the Bohemian (Czech)–German borderland, and known for the production of biological models such as the glass sea creatures and Harvard University's Glass Flowers. Family background The Blaschka family traces its roots to Josefův Důl (Josefsthal) in the Jizera Mountains, Bohemia, a region known for processing glass, metals, and gems. Members of the Blacschka family had worked in Venice, Bohemia, and Germany. Leopold referred to this history in an 1889 letter to Mary Lee Ware: Born in Český Dub, Bohemia, and one of Joseph Blaschke's three sons, Leopold was apprenticed to a goldsmith and gemcutter in Turnov, a town in the Liberec Region of today's Czech Republic. He then joined the family business, which produced glass ornaments and glass eyes. It was there that Leopold developed a technique which he termed "glass-spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
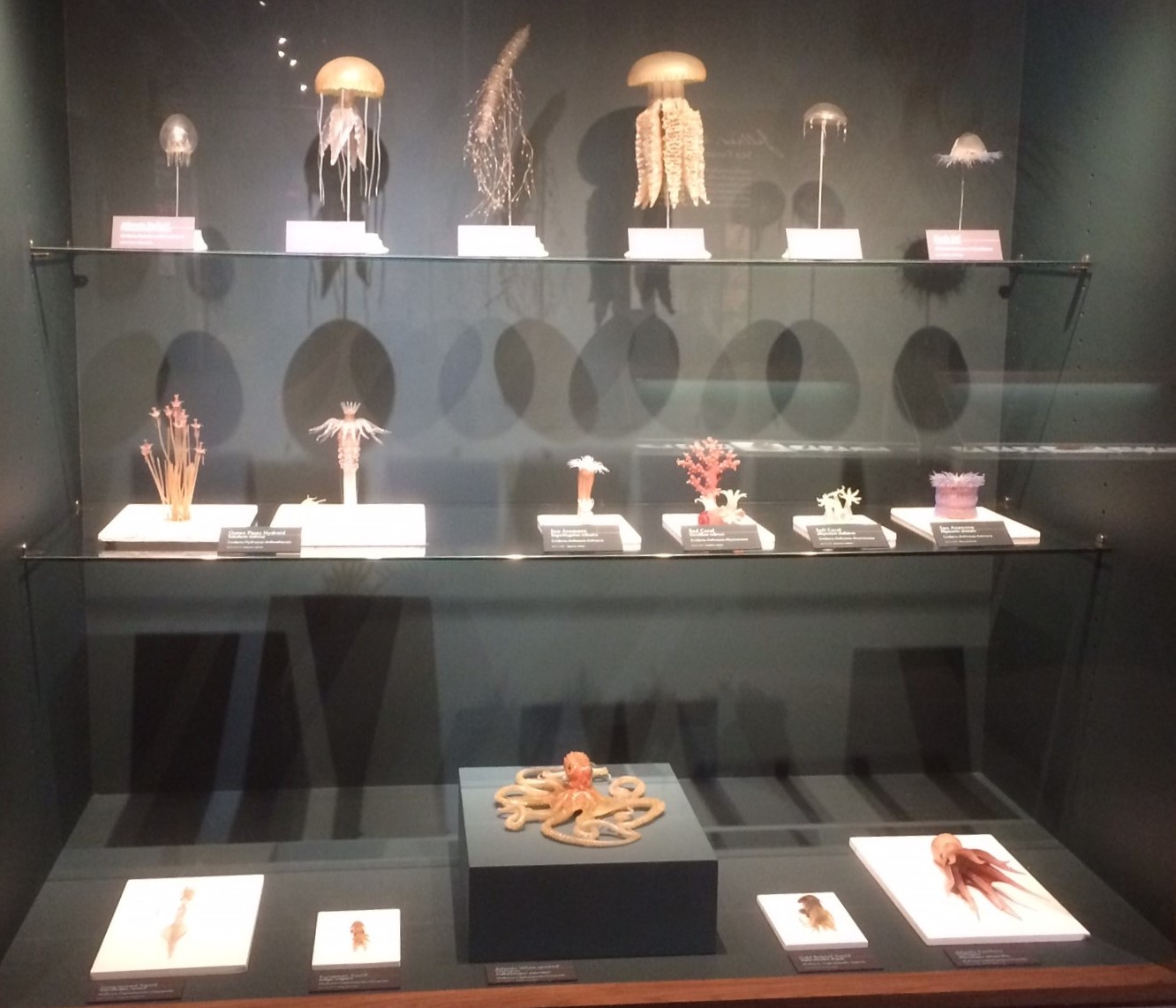
Glass Sea Creatures
The glass sea creatures (alternately called the Blaschka sea creatures, glass marine invertebrates, Blaschka invertebrate models, and Blaschka glass invertebrates) are works of glass artists Leopold and Rudolf Blaschka. The artistic predecessors of the Glass Flowers, the sea creatures were the output of the Blaschkas' successful mail-order business of supplying museums and private collectors around the world with sets of glass models of marine invertebrates. Between 1863 and 1880, the Blaschkas – working in Dresden – executed at least 10,000 of these highly detailed glass models, representing some 700 different species. A number of large collections of the models are held by museums and other academic institutions. Harvard's Museum of Natural History exhibits many of the Blaschka's glass creations, and its Museum of Comparative Zoology hold 430 items in the Blaschka Glass Invertebrate Collection and display about 60 at any given time. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Museum
The Harvard University Herbaria and Botanical Museum are institutions located on the grounds of Harvard University at 22 Divinity Avenue, Cambridge, Massachusetts. The Botanical Museum is one of three which comprise the Harvard Museum of Natural History. The Herbaria, founded in 1842 by Asa Gray, are one of the 10 largest in the world with over 5 million specimens, and including the Botany Libraries, form the world's largest university owned herbarium. The Gray Herbarium is named after him. HUH hosts the Gray Herbarium Index (GCI) as well as an extensive specimen, botanist, and publications database. HUH was the center for botanical research in the United States of America by the time of its founder's retirement in the 1870s. The materials deposited there are one of the three major sources for the International Plant Names Index. The Botanical museum was founded in 1858. It was originally called the ''Museum of Vegetable Products'' and was predominantly focused on an interdisc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curator
A curator (from la, cura, meaning "to take care") is a manager or overseer. When working with cultural organizations, a curator is typically a "collections curator" or an "exhibitions curator", and has multifaceted tasks dependent on the particular institution and its mission. In recent years the role of curator has evolved alongside the changing role of museums, and the term "curator" may designate the head of any given division. More recently, new kinds of curators have started to emerge: "community curators", "literary curators", " digital curators" and " biocurators". Collections curator A "collections curator", a "museum curator" or a "keeper" of a cultural heritage institution (e.g., gallery, museum, library or archive) is a content specialist charged with an institution's collections and involved with the interpretation of heritage material including historical artifacts. A collections curator's concern necessarily involves tangible objects of some sort—artwork, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Eliot Ware
Charles Eliot Ware (May 7, 1814 September 3, 1887) was a prominent Boston physician and the husband of Elizabeth Cabot Lee, their daughter being Mary Lee Ware. It is to him that the Harvard Museum of Natural History's famous Glass Flowers exhibit is dedicated to as a memorial, his wife and daughter being the sponsors of the project. Dr. Ware was also a close friend of John Holmes, the younger brother of Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr. Family life Son of Henry Ware (17641845), Dr. Charles Eliot Ware married the wealthy Elizabeth Cabot Lee (from then on Elizabeth C. Ware) on November 20, 1854; and, in 1858, their daughter Mary was born in the town of Rindge, New Hampshire (Dr. Charles Eliot Ware's brother, Thornton, named his eldest son after Charles, with the suffix Jr., causing confusion of lineage.) While not a botanist himself, Dr. Ware and his wife raised Mary to love botany with a passion and live according to the precept "It is more blessed to give than to receive,"Hale, Emil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabot Family
The Cabot family was part of the Boston Brahmin, also known as the "first families of Boston". History Family origin The Boston Brahmin Cabot family descended from John Cabot (born 1680 in Jersey, a British Crown Dependencies and one of the Channel Islands), who emigrated from his birthplace to Salem, Massachusetts in 1700. The Cabot family emigrated from Jersey, where the family name can be traced back to at least 1274. In Latin, ''caput'' means "head", and the Rev. George Balleine writes that in Jersey the "cabot" is a small fish that seems all head. In French, the basis of the Jèrriais language, "cabot" means a dog, or a military corporal, "caboter" is to navigate along the coast, and "cabotin" means "theatrical". Rise to prominence John Cabot (born 1680 Isle of Jersey) and his son, Joseph Cabot (born 1720 in Salem), became highly successful merchants, operating a fleet of privateers carrying opium, rum, and slaves. Shipping during the eighteenth century was the life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Lee Ware
Mary Lee Ware, (Jan. 7, 1858 – Jan. 9, 1937) daughter of Elizabeth Cabot (Lee) Ware and Charles Eliot Ware, was born to a wealthy Bostonian family and, with her mother, was the principal sponsor of the Harvard Museum of Natural History's famous Glass Flowers (formally ''The Ware Collection of Blaschka Glass Models of Plants''). She was an avid student of botany, particularly of the work of George Lincoln Goodale; a close friend and sponsor of Leopold and Rudolf Blaschka, creators of the Glass Flowers; and a leading philanthropist and farmer of Rindge, New Hampshire and Boston, Massachusetts. Early life Born into a respected family in the New Hampshire town of Rindge, specifically to naturalist and Harvard Medical School professor Dr. Charles Eliot Ware ("a leading physician in Boston") and his wife Elizabeth in 1858, Mary Lee Ware was an avid nature-lover and lived according to the precept "It is more blessed to give than to receive."Hale, Emily. Mary Lee Ware. Boston, 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asa Gray
Asa Gray (November 18, 1810 – January 30, 1888) is considered the most important American botanist of the 19th century. His ''Darwiniana'' was considered an important explanation of how religion and science were not necessarily mutually exclusive. Gray was adamant that a genetic connection must exist between all members of a species. He was also strongly opposed to the ideas of hybridization within one generation and special creation in the sense of its not allowing for evolution. He was a strong supporter of Darwin, although Gray's theistic evolution was guided by a Creator. As a professor of botany at Harvard University for several decades, Gray regularly visited, and corresponded with, many of the leading natural scientists of the era, including Charles Darwin, who held great regard for him. Gray made several trips to Europe to collaborate with leading European scientists of the era, as well as trips to the southern and western United States. He also built an extensive ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)



.jpg)