|
George Forrester And Company
George Forrester and Company was a British marine engine and locomotive manufacturer at Vauxhall Foundry in Liverpool, established by Scottish engineer George Forrester (b. 1780/81). The company opened in 1827 as iron founders and commenced building steam locomotives in 1834. History The company was noted in Liverpool directories from 1827 as "Iron founders", the works established in the former "Union Mill" cotton factory, known locally as the "Welsh Factory", built by Messrs. Kirkman & Co. on the east side of Vauxhall Road in the late eighteenth century, but closed after a few years, remaining empty for some time thereafter. The factory was later enlarged and the original building demolished. A significant product for the company in its early days was the production of machinery involved in sugar processing for the West Indies, before branching into marine engines. A few Railway locomotives were produced from 1834 to 1847. The Crimean War saw the factory stretched to its maximu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Partnership
A general partnership, the basic form of partnership under common law, is in most countries an association of persons or an unincorporated company with the following major features: *Must be created by agreement, proof of existence and estoppel. *Formed by two or more persons *The owners are jointly and severally liable for any legal actions and debts the company may face, unless otherwise provided by law or in the agreement. It is a partnership in which partners share equally in both responsibility and liability. Characteristics Partnerships have certain default characteristics relating to both (a) the relationship between the individual partners and (b) the relationship between the partnership and the outside world. The former can generally be overridden by express agreement between the partners. Whilst the latter is in general hardly varied, a careful draft would oust certain kinds of third party liability. A clause can contain that only the negligent partners can be sued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
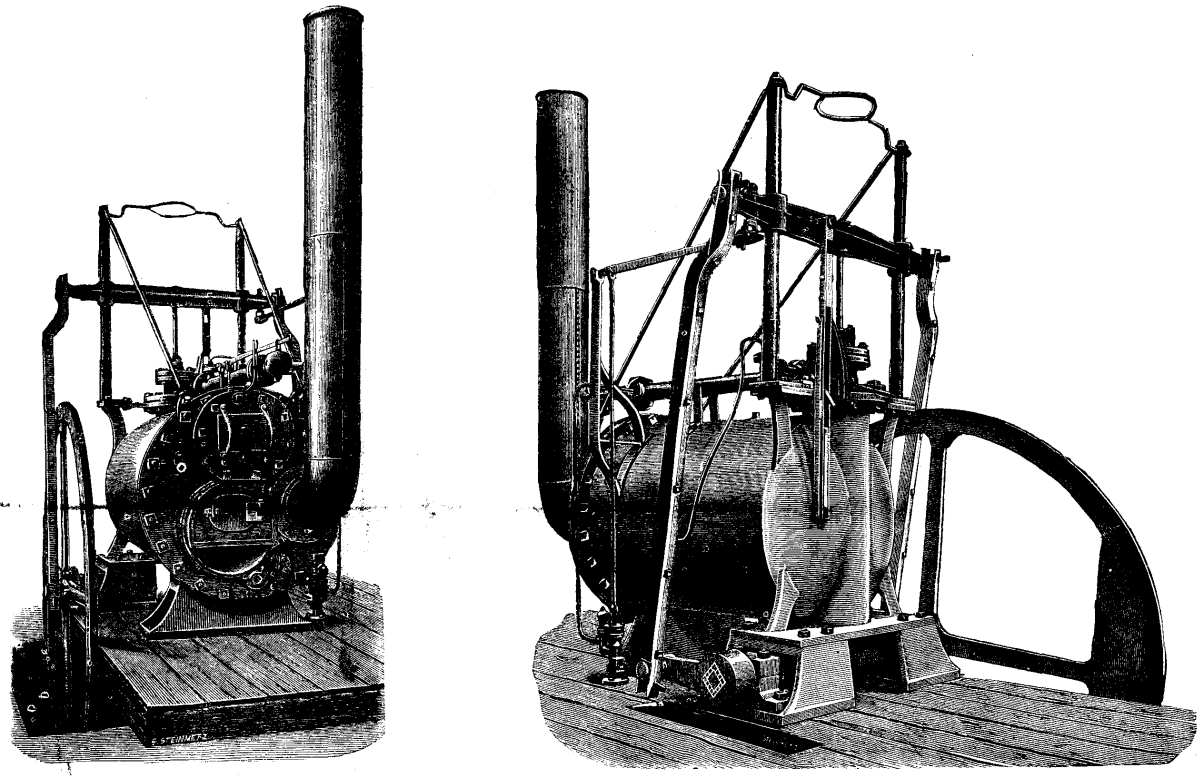
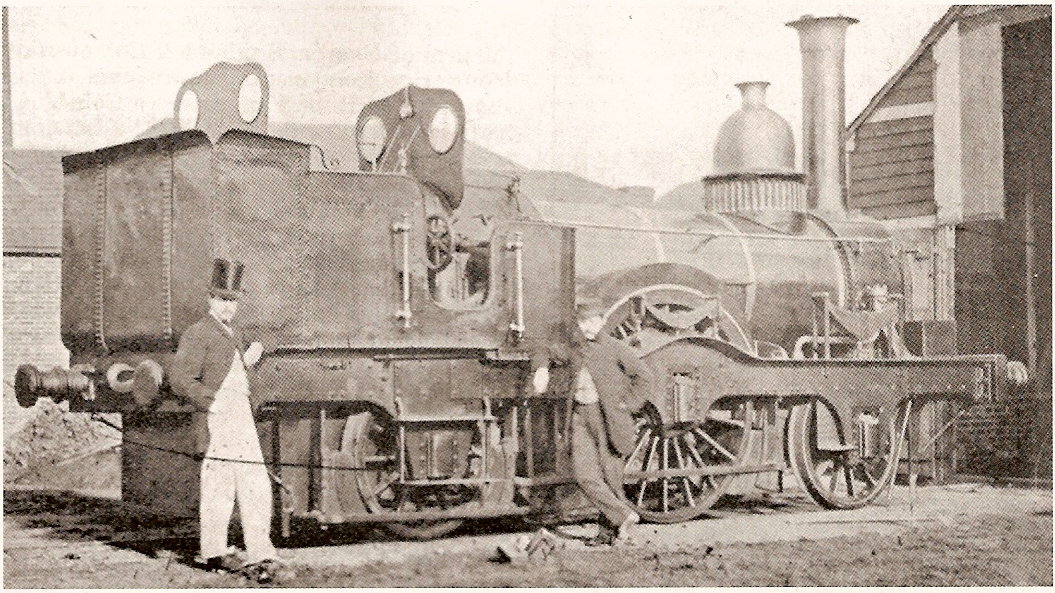
Forrester Single (locomotive)
Swiftsure was first of eight or more similar locomotives with a single pair of driving wheels built by George Forrester and Company (Forresters) from 1834. The tank variant was the first passenger tank engine to enter service in the world. They have been claimed to be the first locomotives to use outside horizontal cylinders and also the first to use 4 eccentric cranks. The use of outside cylinders on a short wheelbases with no wheel balances resulted in an oscillating movement at speed, resulting in a nickname of "Boxers" and most being rebuilt from to incorporate trailing axle becoming configured as . Locomotives were supplied to the Liverpool and Manchester Railway (L&MR), Dublin and Kingstown (D&KR), London and Greenwich (L&GR), Birmingham and Gloucester (B&GR), and a few other minor railways. History George Forrester's Vauxhall Foundry had been established in Liverpool by 1827, taking over a disused cotton mill. The location was about from the L&MR's Edge Hill Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Canal Street Railway Works
Grand Canal Street railway works, also known as ''The Factory'', served the Dublin and Kingstown Railway (D&KR), its successors the Dublin, Wicklow and Wexford Railway (DW&WR) and the Dublin and South Eastern Railway (DSER). It was preceded by a small "engine hospital" maintenance depot at Serpentine Avenue. History The D&KR had initially set up an "Engine Hospital" for the servicing of locomotives at Serpentine Avenue, about south west of past the River Dodder where railway cottages were subsequently built. The Serpentine depot had two sections, one for the three engines from Sharp, Stewart and Company, Robert Sharps, initially supported by their engineer Francis Wrigley, and the three from George Forrester and Company, Forresters supported by their man Alexander Allan (locomotive engineer), Alexander Allan. The works was bought in 1840, engine and carriage repair having previously been carried out since 1834 at Serpentine Avenue. The workshop was the former two-story Dock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Boiler Locomotive
The Long Boiler locomotive was the object of a patent by Robert Stephenson and the name became synonymous with the pattern. Its defining feature is that the firebox is placed ''behind'' the rearmost driving axle. This gives a long boiler barrel, with long fire-tubes. There is thus a generous heating surface area, giving a boiler that is both powerful and efficient. It is generally perceived that it arose out of attempts to match the power of broad gauge locomotives within the limitations of the standard gauge of Stephenson railways. However, the patent originally arose from a problem which became apparent as trains travelled longer distances, specifically on the North Midland Railway in England around 1841, where fire tubes and smokeboxes were becoming destroyed by the heat. Experiments Experiments at the North Midland's Derby Works showed temperatures as high as , determined by placing a small cup of zinc within the smokebox beneath the chimney. Stephenson extended the boiler, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Eastern Railway (UK)
The South Eastern Railway (SER) was a railway company in south-eastern England from 1836 until 1922. The company was formed to construct a route from London to Dover. Branch lines were later opened to Tunbridge Wells, Hastings, Canterbury and other places in Kent. The SER absorbed or leased other railways, some older than itself, including the London and Greenwich Railway and the Canterbury and Whitstable Railway. Most of the company's routes were in Kent, eastern Sussex and the London suburbs, with a long cross-country route from in Surrey to Reading, Berkshire. Much of the company's early history saw attempts at expansion and feuding with its neighbours; the London Brighton and South Coast Railway (LBSCR) in the west and the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR) to the north-east. However, in 1899 the SER agreed with the LCDR to share operation of the two railways, work them as a single system (marketed as the South Eastern and Chatham Railway) and pool receipts: but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Urpeth Rastrick
John Urpeth Rastrick (26 January 1780 – 1 November 1856) was one of the first English steam locomotive builders. In partnership with James Foster, he formed Foster, Rastrick and Company, the locomotive construction company that built the ''Stourbridge Lion'' in 1829 for export to the Delaware and Hudson Railroad in America. From the 1830s he concentrated on civil engineering with his major project from 1838 being the construction of the London and Brighton Railway. Early years Rastrick was born in Morpeth, Northumberland, to John Rastrick and Mary (Urpeth). He attended local public schools; at age 15, in 1795 he was apprenticed in his father's engineering practice. In 1802 he was hired by the Ketley Ironworks in Shropshire. Hazeldine & Rastrick After five years at Ketley, Rastrick partnered with John Hazledine, in Bridgnorth, Shropshire. While at Bridgnorth, Rastrick helped Richard Trevithick develop his ideas for the high pressure steam engine and locomotive, and he l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London & Brighton Railway
The London and Brighton Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in England which was incorporated in 1837 and survived until 1846. Its railway ran from a junction with the London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) at Norwood – which gives it access from London Bridge, just south of the River Thames in central London. It ran from Norwood to the South Coast at Brighton, together with a branch to Shoreham-by-Sea. Background During the English Regency, and particularly after the Napoleonic Wars, Brighton rapidly became a fashionable social resort, with more than 100,000 passengers being carried there each year by coach. Early schemes A proposal by William James in 1823 to connect London "with the ports of Shoreham (Brighton), Rochester (Chatham) and Portsmouth by a line of Engine Railroad" was largely ignored. However, about 1825 a company called The Surrey, Sussex, Hants, Wilts & Somerset Railway employed John Rennie to survey a route to Brighton, but again the proposal came to nothing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Early Locomotives Of The London Brighton And South Coast Railway
The following table gives details of locomotives owned by the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway from its creation in July 1846 until the end of 1849. The locomotives acquired by the London Brighton and South Coast Railway at its creation in July 1846 came from the division of those owned previously operated by the Joint Committee of the South Eastern, London and Croydon and London and Brighton Railways. The division took place in 1845 but only took effect at the dissolution of the Committee in January 1846. The creation of the LB&SCR (which was an amalgamation of the London and Croydon and London and Brighton Railways), seven months later meant that the new company acquired those locomotives allocated to both companies. The majority of the locomotives acquired had formerly been owned or ordered by one of the three constituent railways, but some had been ordered by the Joint Committee. After the dissolution of the Joint Committee, there some locomotives on ordered by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-4-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles and no trailing wheels. The notation 2-4-0T indicates a tank locomotive of this wheel arrangement, on which its water and fuel is carried on board the engine itself, rather than in an attached tender. Overview The 2-4-0 configuration was developed in the United Kingdom in the late 1830s or early 1840s as an enlargement of the 2-2-0 and 2-2-2 types, with the additional pair of coupled wheels giving better adhesion. The type was initially designed for freight haulage. One of the earliest examples was the broad-gauge GWR Leo Class, designed by Daniel Gooch and built during 1841 and 1842 by R. & W. Hawthorn, Leslie and Company; Fenton, Murray and Jackson; and Rothwell, Hick and Rothwell. Because of its popularity for a period with English railways, noted railway author C. Hamilton Ellis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trailing Wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle ( wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing truck. On some large locomotives, a booster engine was mounted on the trailing truck to provide extra tractive effort when starting a heavy train and at low speeds on gradients. Trailing wheels were used in some early locomotives but fell out of favor for a time during the latter 19th century. As demand for more powerful locomotives increased, trailing wheels began to be used to support the crew cab and rear firebox area. Trailing wheels first appeared on American locomotives between 1890 and 1895, but their axle worked in rigid pedestals. It enabled boilers to be lowered, since the top of the main frames was dropped down behind the driving wheels and under the firebox. The firebox could also be longer and wider, increasing the heating surface area and steam generation c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
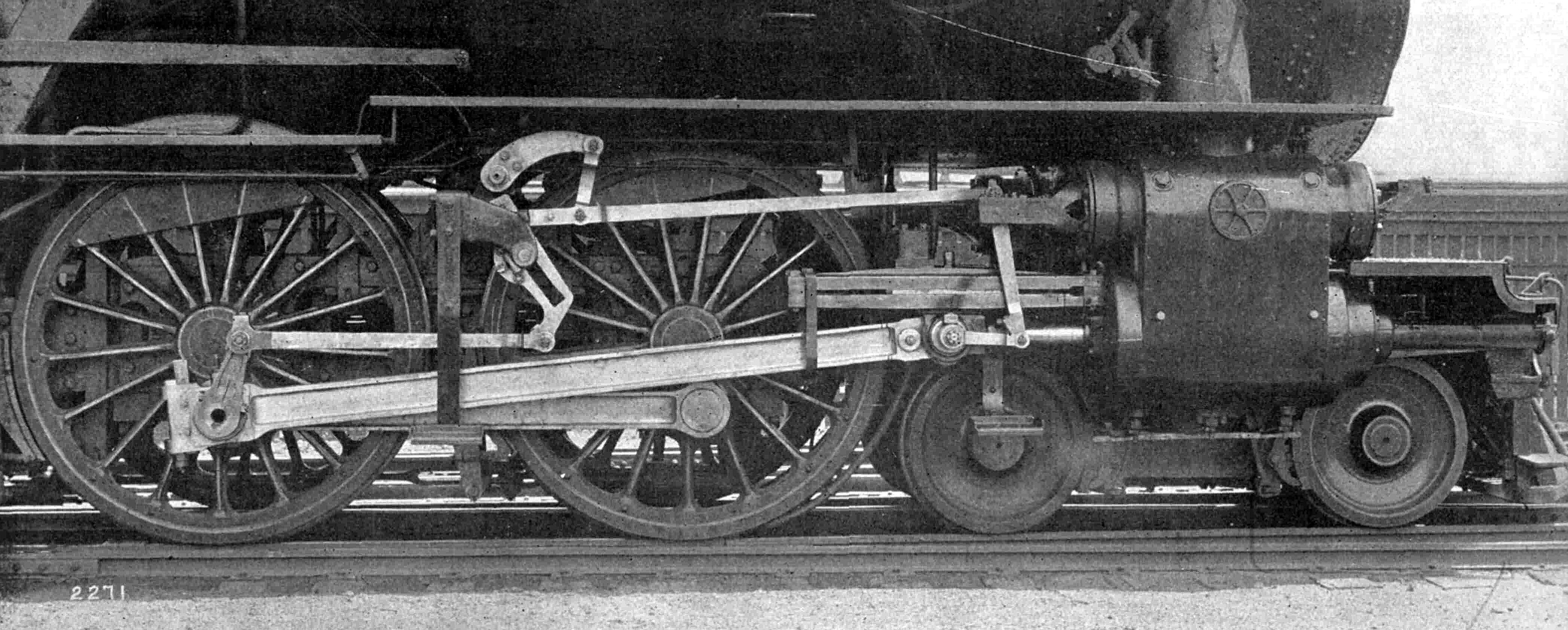
Valve Gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion". Purpose In the simple case, this can be a relatively simple task as in the internal combustion engine in which the valves always open and close at the same points. This is not the ideal arrangement for a steam engine, though, because greatest power is achieved by keeping the inlet valve open throughout the power stroke (thus having full boiler pressure, minus transmission losses, against the piston throughout the stroke) while peak efficiency is achieved by only having the inlet valve open for a short time and then letting the steam expand in the cylinder (expansive working). The point at which steam stops being admitted to the cylinder is known as the '' cutoff'', and the optimal positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccentric (mechanism)
In mechanical engineering, an eccentric is a circular disk (''eccentric sheave'') solidly fixed to a rotating axle with its centre offset from that of the axle (hence the word "eccentric", out of the center). It is used most often in steam engines, and used to convert rotary motion into linear reciprocating motion to drive a sliding valve or pump ram. To do so, an eccentric usually has a groove at its circumference closely fitted a circular collar (''eccentric strap''). An attached ''eccentric rod'' is suspended in such a way that its other end can impart the required reciprocating motion. A return crank fulfills the same function except that it can only work at the end of an axle or on the outside of a wheel whereas an eccentric can also be fitted to the body of the axle between the wheels. Unlike a cam, which also converts rotary into linear motion at almost any rate of acceleration and deceleration, an eccentric or return crank can only impart an approximation of simple harmoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |