|
George Chaworth Musters
George Chaworth Musters (1841–1879) was a British Royal Navy commander and traveller, known as the "King of Patagonia". Life He was born in Naples while his parents were travelling, 13 February 1841, the son of John George Musters of Wiverton Hall, Nottinghamshire, formerly of the 10th Royal Hussars, and his wife Emily, daughter of Philip Hamond of Westacre, Norfolk. His paternal grandparents were John Musters of Colwick Hall, Nottinghamshire, "the king of gentlemen huntsmen", who had married in 1805 Mary Anne Chaworth, heiress of Chaworth of Annesley Hall, Nottinghamshire, the "Mary" of Lord Byron's poem, '' The Dream''. Musters was one of three children. His father dying in 1842, and his mother in 1845, Musters was brought up mainly by his mother's brothers, one of whom, Robert Hamond, had sailed with Admiral Robert Fitzroy in HMS ''Beagle''. He went to school at Saxby's in the Isle of Wight, and Green's at Sandgate, Kent, and then to Burney's academy at Gosport, to prepare f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musters
{{surname ...
Musters is a surname. People with the surname include: * George Chaworth Musters (1841–1879), British Royal Navy commander and traveller * Marcel Musters (born 1959), Dutch actor * Pauline Musters (1878–1895), the shortest woman ever recorded * William Musters (1810–1870), English cricketer See also * Muster (other) Muster may refer to: Military terminology * Muster (military), a process or event for the accounting for members in a military unit * Muster list, list of the functions for team members * A mustering, in military terminology, is a specialised for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper, and Don. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea covers (not including the Sea of Azov), has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end of the Balkan Mountains; and the Dobruja Plateau considerably farth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Río Negro (Argentina)
Río Negro (; ''Black River'') is the main river of Patagonia in terms of the size of its drainage basin, its associated agricultural produce and population living at its shores. In eastern Patagonia it is also the largest by flow rate. The river flows through the Argentine province of Río Negro which is named after it. Its name comes from the literal translation of the Mapuche term ''Curu Leuvu'', although the water is more green than black. Formerly, it was also known as "river of the willows" because of the big number of weeping willows that grow along the bank. It is 635 km in length. It originates from the junction of the Limay River and Neuquén River at the border with the Neuquén Province, and flows southeast incised through steppes to the Atlantic Ocean at , near El Cóndor beach resort some downstream from Viedma, Río Negro province's capital. The river allows the Río Negro province to produce 70% of the pears and 72% the apples of Argentina. The main area o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magellan Straits
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and Tierra del Fuego to the south. The strait is considered the most important natural passage between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. It was discovered and first traversed by the Spanish expedition of Ferdinand Magellan in 1520, after whom it is named. Prior to this, the strait had been navigated by canoe-faring indigenous peoples including the Kawésqar. Magellan's original name for the strait was ''Estrecho de Todos los Santos'' ("Strait of All Saints"). The King of Spain, Emperor Charles V, who sponsored the Magellan-Elcano expedition, changed the name to the Strait of Magellan in honor of Magellan. The route is difficult to navigate due to frequent narrows and unpredictable winds and currents. Maritime piloting is now compulsory. The strait is shorter and more sheltered than the Drake Passage, the often stormy open sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
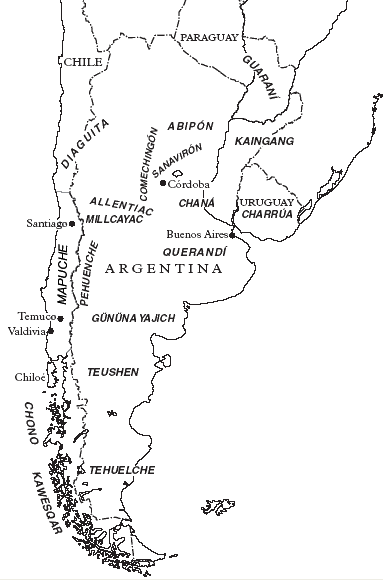
Tehuelche People
The Tehuelche people, also called the Aónikenk, are an indigenous people from eastern Patagonia in South America. In the 18th and 19th centuries the Tehuelche were influenced by Mapuche people, and many adopted a horseriding lifestyle. Once a nomadic people the lands of the Tehuelche were colonized in the 19th century by Argentina and Chile gradually disrupting their traditional economies. The establishment of large sheep farming estates in Patagonia was particularly detrimental to the Tehuelche. Contact with outsiders also brought in infectious diseases ushering deadly epidemics among Tehuelche tribes. Most existing members of the group currently reside the in cities and towns of Argentine Patagonia. The name "Tehuelche complex" has been used by researchers in a broad sense to group together indigenous peoples from Patagonia and the Pampas. Several specialists, missionaries and travelers have proposed grouping them together on account of the similarities in their cultural tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montevideo
Montevideo () is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Uruguay, largest city of Uruguay. According to the 2011 census, the city proper has a population of 1,319,108 (about one-third of the country's total population) in an area of . Montevideo is situated on the southern coast of the country, on the northeastern bank of the Río de la Plata. The city was established in 1724 by a Spanish soldier, Bruno Mauricio de Zabala, as a strategic move amidst the Spanish people, Spanish-Portuguese people, Portuguese dispute over the La Plata Basin, platine region. It was also under brief British invasions of the Río de la Plata, British rule in 1807, but eventually the city was retaken by Spanish criollos who defeated the British invasions of the River Plate. Montevideo is the seat of the administrative headquarters of Mercosur and ALADI, Latin America's leading trade blocs, a position that entailed comparisons to the role of Brussels in Europe. The 2019 Mercer's report on qual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Ensign
In British maritime law and custom, an ensign is the identifying flag flown to designate a British ship, either military or civilian. Such flags display the United Kingdom Union Flag in the canton (the upper corner next to the staff), with either a red, white or blue field, dependent on whether the vessel is civilian, naval, or in a special category. These are known as the ''red'', ''white'', and ''blue'' ensigns respectively. Outside the nautical sphere, ensigns are used to designate many other military units, government departments and administrative divisions. These flags are modelled on the red, white, and blue naval ensigns, but may use different colours for the field, and be defaced by the addition of a badge or symbol, for example the sky blue with concentric red, white and blue circles of the Royal Air Force ensign. The Union Flag (also known as the ''Union Jack'') should be flown as a jack by Royal Navy ships only when moored or at anchor. If flown while underway, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugarloaf Mountain
Sugarloaf Mountain ( pt, Pão de Açúcar, ) is a peak situated in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, at the mouth of Guanabara Bay on a peninsula that juts out into the Atlantic Ocean. Rising above the harbor, the peak is named for its resemblance to the traditional shape of concentrated refined loaf sugar. It is known worldwide for its cableway and panoramic views of the city and beyond. The mountain is one of several monolithic granite and quartz mountains that rise straight from the water's edge around Rio de Janeiro. Geologically, it is considered part of a family of steep-sided rock outcroppings known as non-inselberg bornhardts. The mountain is protected by the Sugarloaf Mountain and Urca Hill Natural Monument, created in 2006. This became part of a World Heritage Site declared by UNESCO in 2012. Origins of the name The name Sugarloaf was coined in the 16th century by the Portuguese during the heyday of sugarcane trade in Brazil. According to historian Vieira Fazenda, bloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio De Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a beta global city, Rio de Janeiro is the sixth-most populous city in the Americas. Part of the city has been designated as a World Heritage Site, named "Rio de Janeiro: Carioca Landscapes between the Mountain and the Sea", on 1 July 2012 as a Cultural Landscape. Founded in 1565 by the Portuguese, the city was initially the seat of the Captaincy of Rio de Janeiro, a domain of the Portuguese Empire. In 1763, it became the capital of the State of Brazil, a state of the Portuguese Empire. In 1808, when the Portuguese Royal Court moved to Brazil, Rio de Janeiro became the seat of the court of Queen Maria I of Portugal. She subsequently, under the leadership of her son the prince regent João VI of Portugal, raised Brazil to the dignity of a k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Stromboli (1839)
HMS ''Stromboli'' was initially a Steam Vessel second class (later reclassed as a First Class Sloop) designed by Sir William Symonds, Surveyor of the Navy, and built at Portsmouth. She was commissioned and participated in the bombardment of Acre in 1840, during the Russian War she was used as a troop transport in the Baltic in 1854, she was in the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov in 1855. Her last overseas posting was on the South East Coast of America. She was sold for breaking in August 1866. ''Stromboli'' was the only vessel of this name in the Royal Navy. Construction She was ordered on 12 March 1838 with her laid in September at Portsmouth Dockyard His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is l .... She was launched on 27 August 1839. She was completed for sea on 6 September ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMY Victoria And Albert (1843)
HMY ''Victoria and Albert'' was a twin-paddle steamer launched 25 April 1843. She functioned as a royal yacht of the sovereign of the United Kingdom, owned and operated by the Royal Navy, and was the first of three royal yachts to be named ''Victoria and Albert''. She was laid down in 1842 at Pembroke Dock and was designed by William Symonds. She measured 1,034 tons burthen, carried two guns, and was the first royal yacht to be steam powered, being fitted with a engine. Steam yachts, first introduced in 1823, became popular amongst Victorian millionaires and Royalty around Europe. She was lengthened in 1853. She was 200 feet and emerged at 260 x 33 x 22 feet, displacement 1,382 tons, with new engines of . She made twenty voyages. She was renamed ''Osborne'', after the launch of on 16 January 1855. ''Her Majesty's Yacht Osborne'' continued in service, conveying the Royal Family to their summer home, Osborne House, on the Isle of Wight. She was named after the Queen's new es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Marlborough (1855)
HMS ''Marlborough'' was a first-rate three-decker 131 gun screw ship built for the Royal Navy in 1855. She was begun as a sailing ship of the line (with her sister ships , HMS ''Prince of Wales'' and HMS ''Royal Sovereign''), but was completed to a modified design and converted to steam on the stocks, and launched as a wooden steam battleship. Construction ''Marlborough'' was originally ordered as a pure-sailing first-rate ship of the line to the lines of , but when construction began at Portsmouth Dockyard on 1 September 1850 it was to a modified version of the design. As was policy at the time, to ensure the ship's timbers were well-seasoned and so resistant to rot, the partially-completed ship was held 'in frame'. In this state, her frames had all been raised and bolted to the keel, along with the basic internal structure such as deck beams, but no planking had yet been attached to the hull. On 30 October 1852 ''Marlborough'' was ordered to be converted on the stocks t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |