|
George Carey (ice Hockey)
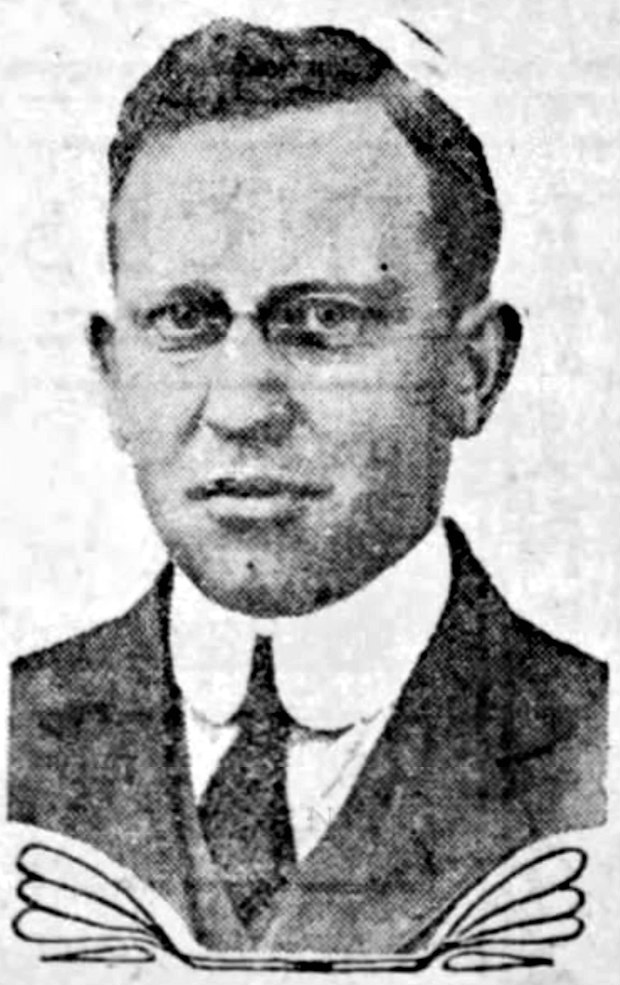
George William Carey (November 4, 1892 – December 31, 1974) was a Canadian ice hockey right winger. He was born in Montreal, Quebec, to Scottish parents. He first played professionally with the Quebec Bulldogs in the National Hockey Association, playing one game for them in the 1911–12 season and winning the Stanley Cup in 1912. He played amateur hockey for several years after that before returning to the Bulldogs in 1916–17, and spent one final season with the team in 1919–20 when they were in the National Hockey League. The team moved and became the Hamilton Tigers in 1920 and Carey spent two seasons and part of a third there, spending a partial season with the Calgary Tigers of the Western Canada Hockey League before one final year in the NHL with the Toronto St. Pats The Toronto St. Patricks (colloquially known as the St. Pats) were a professional ice hockey team which began playing in the National Hockey League (NHL) in 1919. The Toronto NHL franchise (league memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winger (ice Hockey)
Winger, in the game of ice hockey, is a forward position of a player whose primary zone of play is along the outer playing areas. They typically flank the centre forward. Originally the name was given to forward players who went up and down the sides of the rink. Wingers generally have the least defensive responsibilities out of any position on the ice, however they are still tasked with defensive duties such as forechecking duties or covering the point in the defensive zone. Nowadays, there are different types of wingers in the game — out-and-out goal scorers, checkers who disrupt the opponents, and forwards who work along the boards and in the corners. Often a winger's precise role on a line depends upon what type of role the other winger plays; usually lines will have one more goal-scoring oriented winger and one winger more focused on playing the boards, checking and passing the puck to others to take shots (if a larger player, he will sometimes be called a "power forward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Canada Hockey League
The Western Canada Hockey League (WCHL), founded in 1921, was a major professional ice hockey league originally based in the prairies of Canada. It was renamed the Western Hockey League (WHL) in 1925 and disbanded in 1926. The WCHL's Victoria Cougars were the last non-NHL team to win the Stanley Cup when they won the 1925 Stanley Cup Finals over the NHL's Montreal Canadiens. History Background The Stanley Cup was donated in 1893 to serve as a trophy to be awarded to the national champion of Canadian amateur ice hockey. The trophy eventually became open to professional teams in 1906 and a new trophy, the Allan Cup was donated to serve as the national amateur trophy. By this time, the Canadian Prairies were being rapidly settled and in 1914 a team based in Saskatchewan (the Regina Victorias) would capture the Allan Cup for the first time. By this time, competition for the Stanley Cup, had evolved into a World Series-inspired "East vs. West" affair to be contested between the win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1922–23 WCHL Season
The 1922–23 WCHL season was the second season for the Western Canada Hockey League. Four teams played 30 games each. Regular season Final standings ''Note: W = Wins, L = Losses, T = Ties, GF= Goals For, GA = Goals Against, Pts = Points'' Scoring leaders Stanley Cup Finals The Edmonton Eskimos won the WCHL championship and advanced directly to the Stanley Cup Finals, where they would face the National Hockey League champion Ottawa Senators. Ottawa had previously defeated the Pacific Coast Hockey Association champions, the Vancouver Maroons. Ottawa then defeated Edmonton two games to none in the best-of-three series to win the Stanley Cup. See also *List of Stanley Cup champions *Pacific Coast Hockey Association *List of NHL seasons *1922 in sports *1923 in sports 1923 in sports describes the year's events in world sport. American football NFL championship * Canton Bulldogs (11–0–1) College championship * Illinois Fighting Illini – college football national cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1922–23 NHL Season
The 1922–23 NHL season was the sixth season of the National Hockey League. Four teams played 24 games each. The Ottawa Senators defeated the Montreal Canadiens for the NHL championship, and then defeated Vancouver and Edmonton to win the Stanley Cup. Regular season At the start of the season, Newsy Lalonde found himself moving west as the Montreal Canadiens traded him to the Saskatoon Sheiks of the Western Canada Hockey League for a rising young star named Aurel Joliat. Joliat would help the Canadiens win the second playoff spot over the St. Patricks. Joliat scored two goals in his first game with the Canadiens, but Babe Dye had five goals in the Toronto St. Patricks' 7–2 win. Joliat finished with 12 goals and 21 points in 24 games. On January 31, 1923, the Montreal Canadiens and Hamilton Tigers played the first penalty-free game in NHL history, a 5–4 Montreal victory. On February 14, 1923, CFCA, the radio station of the Toronto Daily Star, broadcast the third period of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1921–22 NHL Season
The 1921–22 NHL season was the fifth season of the National Hockey League (NHL). Four teams each played 24 games. The league dropped the split season and the two top teams played off for the league championship. The second-place Toronto St. Patricks defeated the first-place Ottawa Senators for the league championship. For the first four seasons of the NHL, the winner of the league playoffs had faced the winner of the Pacific Coast Hockey Association (PCHA) for the Stanley Cup. That changed this season with the introduction of another professional hockey league called the Western Canada Hockey League (WCHL). Now, three leagues were competing for the coveted Stanley Cup. The winner of a playoff between the PCHA and the WCHL travelled to Toronto to play off for the Stanley Cup. The St. Patricks defeated the Vancouver Millionaires to win the Stanley Cup. League business This was the first season away from the ''split season'' used in the NHA and the first four NHL seasons. Under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1920–21 NHL Season
The 1920–21 NHL season was the fourth season of the National Hockey League (NHL). Four teams each played 24 games in a split season. The Quebec franchise was transferred to Hamilton, Ontario, to become the Hamilton Tigers. The Ottawa Senators won the league championship in a playoff with the Toronto St. Patricks. The Senators went on to win the Stanley Cup by defeating the Vancouver Millionaires of the Pacific Coast Hockey Association three games to two in a best-of-five series. This would be the last split season before the NHL changed its regular season and playoff formats. League Business Eddie Livingstone was again talking of creating a rival league and mentioned Hamilton as a city in his league. To head this off, league president Frank Calder got the owners of the league to admit a Hamilton franchise. As Abso-Pure had built an arena, all owners agreed that it would be wise to have a franchise in Hamilton. Because Quebec had done so badly the previous season, Calder said t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec Sons Of Ireland
The Quebec Sons of Ireland were a senior amateur ice hockey team from Quebec City that played in various ice hockey leagues in Canada from 1915–1927, such as the Quebec City Hockey League, Quebec Provincial Hockey League and the Eastern Canada Amateur Hockey League. History The team became a member of the Quebec City Hockey League for the 1915–16 season, and was managed and coached by Emmett McDonald, a younger brother of Quebec Bulldogs forward Jack McDonald. With Emmett McDonald as coach the team would capture the Art Ross Cup in 1916, an amateur challenge trophy for teams not eligible to compete for the Allan Cup. McDonald died of pneumonia on February 28, 1919 while serving with the Canadian Expeditionary Force in Siberia. Another brother, Billy McDonald, played defense on the team. Quebec Sons of Ireland defended the Art Ross Cup in 1916–17 by defeating the Montreal Stars, Loyola College and Montreal Vickers. Next season Sons of Ireland lost the Art Ross Cup to Montre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interprovincial Amateur Hockey Union
The Interprovincial Amateur Hockey Union (IAHU or IPAHU) was the premier amateur ice hockey league in Canada after the split between the amateur and professional ice hockey teams of the Eastern Canada Amateur Hockey Association (ECAHA) in 1908. History In November 1908, the Montreal Victorias resigned from the ECAHA and proposed to set up a new amateur ice hockey league. The founding meeting of the new Interprovincial league was held on November 14, 1908. That same day, the Montreal Hockey Club resigned from the ECAHA after not being allowed to hold on to Didier Pitre, whom the club had signed from Montreal Shamrocks. Montreal HC then met with the Victorias to apply. The league's first president was Blair Russel of the Victorias. The first vice-president was Percy Quinn of Toronto AAC, second vice-president was A. Sutherland of Ottawa Cliffsides and the treasurer was A. A. Eaves of the Montreal Hockey Club. The same day the team representatives wrote the league's constitution. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penalty (ice Hockey)
A penalty in ice hockey is a punishment for an infringement of the rules. Most penalties are enforced by sending the offending player to a penalty box for a set number of minutes. During the penalty the player may not participate in play. Penalties are called and enforced by the referee, or in some cases, the linesman. The offending team may not replace the player on the ice (although there are some exceptions, such as fighting), leaving them short-handed as opposed to full strength. When the opposing team is said to be on a ''power play'', they will have one more player on the ice than the short-handed team. The short-handed team is said to be "on the penalty kill" until the penalty expires and the penalized player returns to play. While standards vary somewhat between leagues, most leagues recognize several common varieties of penalties, as well as common infractions. The statistic used to track penalties is called "penalty minutes" and abbreviated to "PIM" (spoken as single w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point (ice Hockey)
In ice hockey, point has three contemporary meanings. Personal stat A point is awarded to a player for each goal scored or assist earned. The total number of goals plus assists equals total points. The Art Ross Trophy is awarded to the National Hockey League (NHL) player who leads the league in scoring points at the end of the regular season. Team stat Points are also awarded to assess standings (or rankings). Historically, teams were awarded two points for each win, one point for each tie and no points for a loss. Such a ranking system, implemented primarily to ensure a tie counted as a "half-win" for each team in the standings, is generally regarded as British and/or European in origin and as such adopted by the National Hockey League which was founded in Canada where leagues generally used ranking systems of British origin. Awarding points in the standings contrasts with traditional American ranking systems favored in sports originating within the United States where today the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assist (ice Hockey)
In ice hockey, an assist is attributed to up to two players of the scoring team who shot, passed or deflected the puck towards the scoring teammate, or touched it in any other way which enabled the goal, meaning that they were "assisting" in the goal. There can be a maximum of two assists per goal. The assists will be awarded in the order of play, with the last player to pass the puck to the goal scorer getting the primary assist and the player who passed it to the primary assister getting the secondary assist. Players who gain an assist will get one point added to their player statistics. Despite the use of the terms "primary assist" and "secondary assist", neither is worth more than the other, and neither is worth more or less than a goal. Assists and goals are added together on a player's scoresheet to display that player's total points. Special cases If a player scores off a rebound given up by a goaltender, assists are still awarded, as long as there is no re-possession by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goal (ice Hockey)
In ice hockey, a goal is scored when the puck entirely crosses the goal line between the two goal posts and below the goal crossbar. A goal awards one point to the team attacking the goal scored upon, regardless of which team the player who actually deflected the puck into the goal belongs to (see also own goal). Typically, a player on the team attempting to score shoots the puck with their stick towards the goal net opening, and a player on the opposing team called a goaltender tries to block the shot to prevent a goal from being scored against their team. The term goal may also refer to the structure in which goals are scored. The ice hockey goal is rectangular in shape; the front frame of the goal is made of steel tube painted red (blue in the ECHL because of a sponsorship deal with GEICO) and consists of two vertical goalposts and a horizontal crossbar. A net is attached to the back of the frame to catch pucks that enter the goal and also to prevent pucks from entering it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |