|
George Bellas Greenough
George Bellas Greenough FRS FGS (18 January 1778 – 2 April 1855) was a pioneering English geologist. He is best known as a synthesizer of geology rather than as an original researcher. Trained as a lawyer, he was a talented speaker and his annual addresses as founding president of the Geological Society of London were influential in identifying and guiding contemporary geological research. He also courted controversy, after using his presidential address in 1834 to cast aspersions on a paper on great earthquakes by Maria Graham. Greenough advocated an empirical approach to the early science; his scepticism of theoretical thinking courted controversy amongst some contemporaries, especially his doubts of the usefulness of fossils in correlating strata. He compiled a geological map of England and Wales, published in 1820, and in the penultimate year of his life used similar methods to produce the first geological map of British India. Greenough characterised himself as follows: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxim Gauci
Maxim Gauci (11 February 1774 – 3 November 1854), born Massimo Gauci, was a Maltese lithographer and painter who was active in the United Kingdom in the 19th century. He was an early exponent of lithography for botanical illustration. Life Gauci was born in Valletta, Malta on 11 February 1774. He studied painting under Michele Busuttil, and was later sent to the Accademia di San Luca in Rome on the recommendation of Grand Master Emmanuel de Rohan-Polduc. Gauci eventually moved to Paris, and married there in 1804. While he was there, he was known as Maxime Gauci and he worked in the studio of Jean-Baptiste Isabey. He was father of William Gauci, another printer, and the landscape painter Paul Gauci. Gauci travelled to Egypt and the Middle East before settling in London in 1809. He never went back to Malta, but he was often visited by his relatives and other Maltese people. Gauci remained active until his eyesight began to decline, and he died in London on 3 November 1854, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Skene
James Skene of Rubislaw (1775–1864) was a Scottish lawyer and amateur artist, best known as a friend of Sir Walter Scott. Life The second son of George Skene (1736–1776) of Rubislaw, Aberdeen and his wife Jane (Jean) Moir of Stoneywood, he was born at Rubislaw, Aberdeen on 7 March 1775. In 1783 Jane, George Skene’s widow, moved to Edinburgh for the education of her seven children. James Skene attended Edinburgh high school. An elder brother died in 1791, and James became heir of Rubislaw. At 21 he went to Germany as a student, and, returning to Edinburgh, was admitted to the Scottish bar as an advocate in 1797. His friendship with Sir Walter Scott was built on his knowledge of German literature. In 1797 Skene became cornet of the Edinburgh Light Horse, the regiment largely organised by Scott, who was himself its quartermaster, secretary, and paymaster. In 1802 Skene revisited the continent of Europe, for a time in company with George Bellas Greenough; and he became a me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Farey, Sr
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry De La Beche
Sir Henry Thomas De la Beche KCB, FRS (10 February 179613 April 1855) was an English geologist and palaeontologist, the first director of the Geological Survey of Great Britain, who helped pioneer early geological survey methods. He was the first President of the Palaeontographical Society. Biography De la Beche was born in Welbeck Street, Cavendish Square, London. He was the only son of Thomas De la Beche (1755–1801) and his wife, Elizabeth. The family name was originally Beach, but his father changed it to create a fictional connection with the medieval Barons De la Beche of Aldworth, Berkshire. His father served as a brevet major (later lieutenant-colonel) in the Norfolk Yeomanry, a regiment of fencibles in the British Army, and was a slave owner with an estate in Jamaica. In 1800 the family travelled to the plantation in Jamaica when Thomas inherited the estate and his father died there in the following year. Mother and son returned to England, having been shipwrecked to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Webster (geologist)
Thomas Webster (11 February 177226 December 1844) was a Scottish geologist. Life Webster was born in Orkney in 1772, probably at Kirkwall, and was educated at Aberdeen. He subsequently went to London and studied architecture, the Royal Institution in Albemarle Street being built from his design, and where in 1830 he delivered the Royal Institution Christmas Lecture. In 1826 he was appointed house-secretary and curator to the Geological Society of London, and for many years he rendered important services in editing and illustrating the ''Transactions'' of the Society. In 1841–42 he was professor of geology in University College, London. He was an accomplished water-colour painter and was elected an honorary member of the Sketch Society. He contributed articles about Architecture and Aquatinta to ''Rees's Cyclopædia''. ''An Encyclopaedia of Domestic Economy'', a comprehensive guide to running a household which Webster had compiled with the help of a Mrs. Parkes, was published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Warburton
Henry Warburton (12 November 1784 – 16 September 1858) was an English merchant and politician, and also an enthusiastic amateur scientist. Elected as Member of Parliament for Bridport, Dorset, in the 1826 general election, he held the seat for 15 years until his resignation from the House of Commons in 1841. He was returned to the Commons at a by-election in November 1843, for Kendal, but did not seek re-election in 1847. On Parliament he was active in the reform of bankruptcy, the repeal of stamp duty on newspapers, introduction of the penny post and in the campaigns of the Anti-Corn Law League. Early life The son of John Warburton of Eltham, Kent, a timber merchant, he was educated at Eton College, and at Trinity College, Cambridge, where he was admitted 24 June 1802, aged 18. He was in the first class of the college examinations as freshman in 1803, and as junior soph in 1804. He was admitted scholar on 13 April 1804, graduated B.A. (being twelfth wrangler and placed next ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
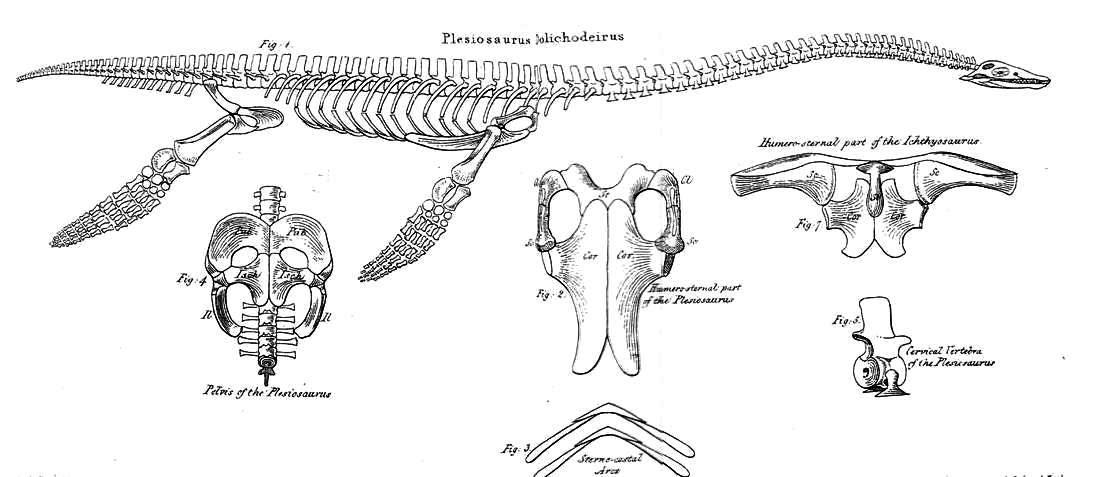
William Daniel Conybeare
William Daniel Conybeare FRS (7 June 178712 August 1857), dean of Llandaff, was an English geologist, palaeontologist and clergyman. He is probably best known for his ground-breaking work on fossils and excavation in the 1820s, including important papers for the Geological Society of London on ichthyosaur anatomy and the first published scientific description of a plesiosaur. Life and career Childhood and education He was a grandson of John Conybeare, bishop of Bristol (1692–1755), a notable preacher and divine, and son of Dr William Conybeare, rector of St Botolph-without-Bishopsgate. Born in London, he was educated there at Westminster School, then went in 1805 to Christ Church, Oxford, where in 1808 he took his degree of BA, with a first in classics and second in mathematics, and proceeded to MA three years later. Early career Having entered holy orders he became in 1814 curate of Wardington, near Banbury, and he accepted also a lectureship at Brislington near Brist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Buckland
William Buckland Doctor of Divinity, DD, Royal Society, FRS (12 March 1784 – 14 August 1856) was an English theologian who became Dean of Westminster. He was also a geologist and paleontology, palaeontologist. Buckland wrote the first full account of a fossil dinosaur, which he named ''Megalosaurus''. His work proved that Kirkdale Cave in North Yorkshire had been a prehistoric hyena den, for which he was awarded the Copley Medal. It was praised as an example of how scientific analysis could reconstruct distant events. He pioneered the use of fossilised Feces, faeces in reconstructing ecosystems, coining the term coprolites. Buckland followed the Gap creationism, Gap Theory in interpreting the biblical account of ''Genesis'' as two widely separated episodes of creation. It had emerged as a way to reconcile the scriptural account with discoveries in geology suggesting the earth was very old. Early in his career Buckland believed he had found evidence of the Deluge myth, biblic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baconian Method
The Baconian method is the investigative method developed by Sir Francis Bacon, one of the founders of modern science, and thus a first formulation of a modern scientific method. The method was put forward in Bacon's book ''Novum Organum'' (1620), or 'New Method', and was supposed to replace the methods put forward in Aristotle's ''Organon''. This method was influential upon the development of the scientific method in modern science; but also more generally in the early modern rejection of medieval Aristotelianism. Description in the ''Novum Organum'' Bacon's view of induction Bacon's method is an example of the application of inductive reasoning. However, Bacon's method of induction is much more complex than the essential inductive process of making generalisations from observations. Bacon's method begins with description of the requirements for making the careful, systematic observations necessary to produce quality facts. He then proceeds to use induction, the ability to ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductive Reasoning
Inductive reasoning is a method of reasoning in which a general principle is derived from a body of observations. It consists of making broad generalizations based on specific observations. Inductive reasoning is distinct from ''deductive'' reasoning. If the premises are correct, the conclusion of a deductive argument is ''certain''; in contrast, the truth of the conclusion of an inductive argument is '' probable'', based upon the evidence given. Types The types of inductive reasoning include generalization, prediction, statistical syllogism, argument from analogy, and causal inference. Inductive generalization A generalization (more accurately, an ''inductive generalization'') proceeds from a premise about a sample to a conclusion about the population. The observation obtained from this sample is projected onto the broader population. : The proportion Q of the sample has attribute A. : Therefore, the proportion Q of the population has attribute A. For example, say there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Map Of England And Wales By Greenough, 1820
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of The Geological Society Of London
This is a list of the presidents of the Geological Society of London. List of presidents * 1807–1813 George Bellas Greenough * 1813–1815 Henry Grey Bennet * 1815–1816 William Blake * 1816–1818 John MacCulloch * 1818–1820 George Bellas Greenough * 1820–1822 Spencer Compton, Earl Compton * 1822–1824 William Babington * 1824–1826 William Buckland * 1826–1827 John Bostock * 1827–1829 William Henry Fitton * 1829–1831 Adam Sedgwick * 1831–1833 Roderick Impey Murchison * 1833–1835 George Bellas Greenough * 1835–1837 Charles Lyell * 1837–1839 William Whewell * 1839–1841 William Buckland * 1841–1843 Roderick Impey Murchison * 1843–1845 Henry Warburton * 1845–1847 Leonard Horner * 1847–1849 Henry Thomas De la Beche * 1849–1851 Charles Lyell * 1851–1853 William Hopkins * 1853–1854 Edward Forbes * 1854–1856 William Hamilton * 1856–1856 Daniel Sharpe * 1856–1858 Joseph Ellison Portlock * 1858–1860 John Phillips * 1860–18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |