|
Geometric Shape
A shape or figure is a graphical representation of an object or its external boundary, outline, or external surface, as opposed to other properties such as color, texture, or material type. A plane shape or plane figure is constrained to lie on a '' plane'', in contrast to '' solid'' 3D shapes. A two-dimensional shape or two-dimensional figure (also: 2D shape or 2D figure) may lie on a more general curved '' surface'' (a non-Euclidean two-dimensional space). Classification of simple shapes Some simple shapes can be put into broad categories. For instance, polygons are classified according to their number of edges as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, etc. Each of these is divided into smaller categories; triangles can be equilateral, isosceles, obtuse, acute, scalene, etc. while quadrilaterals can be rectangles, rhombi, trapezoids, squares, etc. Other common shapes are points, lines, planes, and conic sections such as ellipses, circles, and parabolas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic Vormenstoof Of Puzzelbal Van “Tupperware Toy”, Objectnr 83212
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to its widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives. 9.2 billion tonnes of plastic are estimated to have been made between 1950 and 2017. More than half this plastic has been produced since 2004. In 2020, 400 million tonnes of plastic were produced. If global trends on plastic demand continue, it is estimated that by 2050 annual global plastic production will reach over 1,100 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC. In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non- collinear, determine a unique triangle and simultaneously, a unique plane (i.e. a two-dimensional Euclidean space). In other words, there is only one plane that contains that triangle, and every triangle is contained in some plane. If the entire geometry is only the Euclidean plane, there is only one plane and all triangles are contained in it; however, in higher-dimensional Euclidean spaces, this is no longer true. This article is about triangles in Euclidean geometry, and in particular, the Euclidean plane, except where otherwise noted. Types of triangle The terminology for categorizing triangles is more than two thousand years old, having been defined on the very first page of Euclid's Elements. The names used for modern classification a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (geometry)
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base. A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite curvilinear surface in various modern branches of geometry and topology. The shift in the basic meaning—solid versus surface (as in ball and sphere)—has created some ambiguity with terminology. The two concepts may be distinguished by referring to solid cylinders and cylindrical surfaces. In the literature the unadorned term cylinder could refer to either of these or to an even more specialized object, the ''right circular cylinder''. Types The definitions and results in this section are taken from the 1913 text ''Plane and Solid Geometry'' by George Wentworth and David Eugene Smith . A ' is a surface consisting of all the points on all the lines which are parallel to a given line and which pass through a fixed plane curv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry which intersect at a center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal axes'', or simply axes of the ellipsoid. If the three axes have different lengths, the figure is a triaxial ellipsoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyhedra
In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on the same plane. Cubes and pyramids are examples of convex polyhedra. A polyhedron is a 3-dimensional example of a polytope, a more general concept in any number of dimensions. Definition Convex polyhedra are well-defined, with several equivalent standard definitions. However, the formal mathematical definition of polyhedra that are not required to be convex has been problematic. Many definitions of "polyhedron" have been given within particular contexts,. some more rigorous than others, and there is not universal agreement over which of these to choose. Some of these definitions exclude shapes that have often been counted as polyhedra (such as the self-crossing polyhedra) or include shapes that are often not considered as valid polyhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabola
In mathematics, a parabola is a plane curve which is mirror-symmetrical and is approximately U-shaped. It fits several superficially different mathematical descriptions, which can all be proved to define exactly the same curves. One description of a parabola involves a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix). The focus does not lie on the directrix. The parabola is the locus of points in that plane that are equidistant from both the directrix and the focus. Another description of a parabola is as a conic section, created from the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to another plane that is tangential to the conical surface. The line perpendicular to the directrix and passing through the focus (that is, the line that splits the parabola through the middle) is called the "axis of symmetry". The point where the parabola intersects its axis of symmetry is called the " vertex" and is the point where the parabola is most sharply cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all points in a plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the centre. Equivalently, it is the curve traced out by a point that moves in a plane so that its distance from a given point is constant. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is called the radius. Usually, the radius is required to be a positive number. A circle with r=0 (a single point) is a degenerate case. This article is about circles in Euclidean geometry, and, in particular, the Euclidean plane, except where otherwise noted. Specifically, a circle is a simple closed curve that divides the plane into two regions: an interior and an exterior. In everyday use, the term "circle" may be used interchangeably to refer to either the boundary of the figure, or to the whole figure including its interior; in strict technical usage, the circle is only the boundary and the whole figure is called a '' disc''. A circle may also be defined as a special ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in which the two focal points are the same. The elongation of an ellipse is measured by its eccentricity e, a number ranging from e = 0 (the limiting case of a circle) to e = 1 (the limiting case of infinite elongation, no longer an ellipse but a parabola). An ellipse has a simple algebraic solution for its area, but only approximations for its perimeter (also known as circumference), for which integration is required to obtain an exact solution. Analytically, the equation of a standard ellipse centered at the origin with width 2a and height 2b is: : \frac+\frac = 1 . Assuming a \ge b, the foci are (\pm c, 0) for c = \sqrt. The standard parametric equation is: : (x,y) = (a\cos(t),b\sin(t)) \quad \text \quad 0\leq t\leq 2\pi. Ellip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
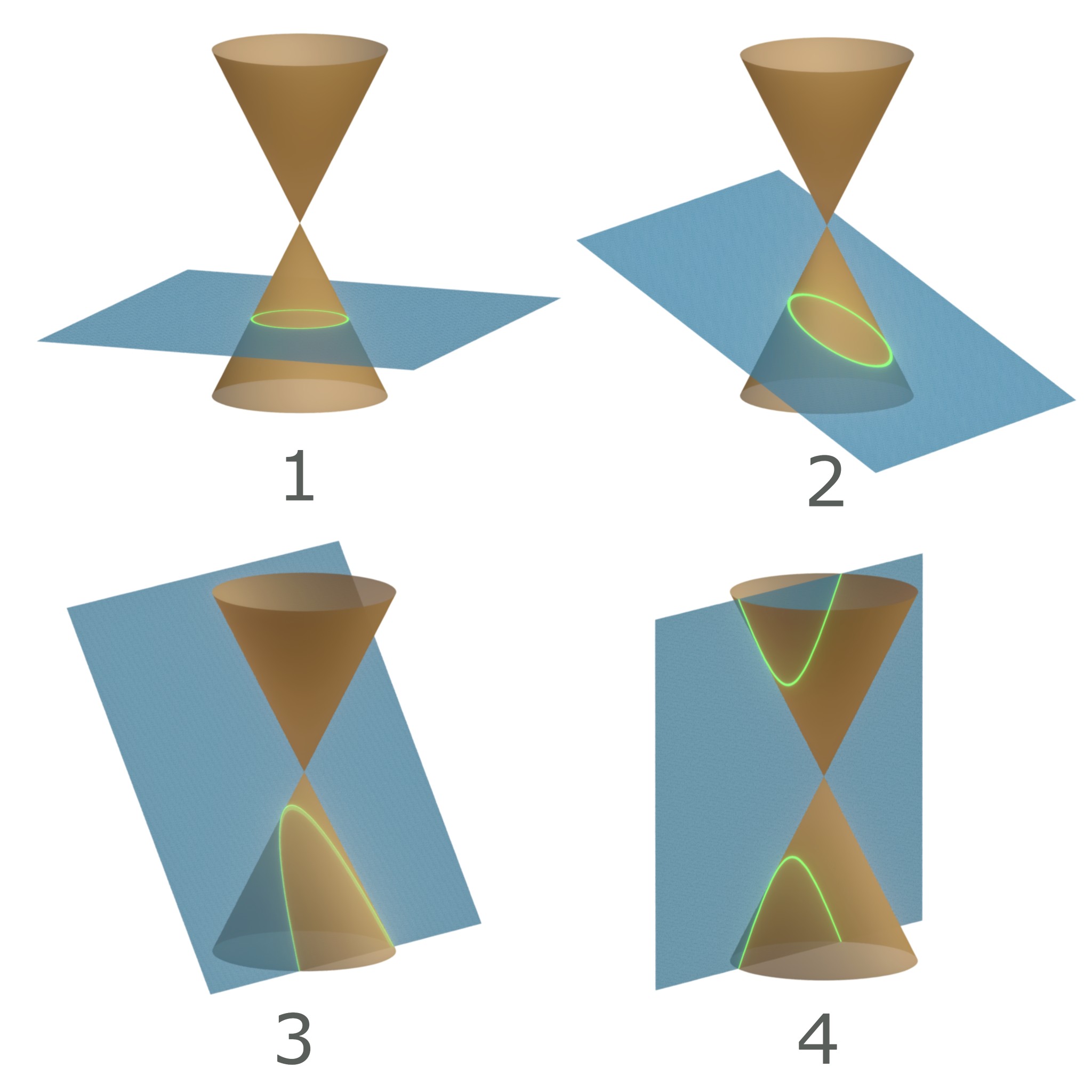
Conic Sections
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a '' focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the '' eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line (geometry)
In geometry, a line is an infinitely long object with no width, depth, or curvature. Thus, lines are one-dimensional objects, though they may exist in two, three, or higher dimension spaces. The word ''line'' may also refer to a line segment in everyday life, which has two points to denote its ends. Lines can be referred by two points that lay on it (e.g., \overleftrightarrow) or by a single letter (e.g., \ell). Euclid described a line as "breadthless length" which "lies evenly with respect to the points on itself"; he introduced several postulates as basic unprovable properties from which he constructed all of geometry, which is now called Euclidean geometry to avoid confusion with other geometries which have been introduced since the end of the 19th century (such as non-Euclidean, projective and affine geometry). In modern mathematics, given the multitude of geometries, the concept of a line is closely tied to the way the geometry is described. For instance, in analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point (geometry)
In classical Euclidean geometry, a point is a primitive notion that models an exact location in space, and has no length, width, or thickness. In modern mathematics, a point refers more generally to an element of some set called a space. Being a primitive notion means that a point cannot be defined in terms of previously defined objects. That is, a point is defined only by some properties, called axioms, that it must satisfy; for example, ''"there is exactly one line that passes through two different points"''. Points in Euclidean geometry Points, considered within the framework of Euclidean geometry, are one of the most fundamental objects. Euclid originally defined the point as "that which has no part". In two-dimensional Euclidean space, a point is represented by an ordered pair (, ) of numbers, where the first number conventionally represents the horizontal and is often denoted by , and the second number conventionally represents the vertical and is often denoted by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squares
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90-degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length adjacent sides. It is the only regular polygon whose internal angle, central angle, and external angle are all equal (90°), and whose diagonals are all equal in length. A square with vertices ''ABCD'' would be denoted . Characterizations A convex quadrilateral is a square if and only if it is any one of the following: * A rectangle with two adjacent equal sides * A rhombus with a right vertex angle * A rhombus with all angles equal * A parallelogram with one right vertex angle and two adjacent equal sides * A quadrilateral with four equal sides and four right angles * A quadrilateral where the diagonals are equal, and are the perpendicular bisectors of each other (i.e., a rhombus with equal diagonals) * A convex quadrilateral with succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |