|
Geology Of Ethiopia
300px, Tigray Escarpment in northern Ethiopia exposing the layers of the Ethiopia-Yemen Continental Flood Basalts. The geology of Ethiopia includes rocks of the Neoproterozoic East African Orogeny, Jurassic marine sediments and Quaternary rift-related volcanism. Events that greatly shaped Ethiopian geology is the assembly and break-up of Gondwana and the present-day rifting of Africa. Rocks formed by the East African Orogeny 880 to 550 million years ago make up the oldest geological units in Ethiopia. The orogeny caused the closure of the ancient Mozambique Ocean. Rocks of Ethiopia formed concurrently with the Mozambique Belt and the Arabian-Nubian Shield forming a large north-south (present-day coordinates) mountain chain called the Transgondwanan Supermountain. Erosion of this mountain may have played a role in triggering the Cambrian explosion. Erosion of the orogen and mountain was such that by the early Paleozoic a planation surface extended across Ethiopia. Sedimentary rocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigray Escarpment, Ethiopia (9798417064)
Tigray may refer to: * Tigray Region, a region of Ethiopia * Tigray Province, a province of Ethiopia until 1995 * Tigrayan-Tigrinya people (other) ** Tigrayans, an ethnographic group in Ethiopia ** Tigrinya people, an ethnographic group in Eritrea * Tigrinya language, a language spoken by Tigrayans See also * Tigray War * * Tigre (other) Tigre ("Tiger" in various languages), Tigres or El Tigre may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Le Tigre, an American rock band ** ''Le Tigre'' (album) * '' El Tigre: The Adventures of Manny Rivera'', a Nickelodeon animated TV series ** ''El Ti ... {{Disambiguation, geo Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Celtic Britons, Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same Rock (geology), rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed Stratum, strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Union of Geological Sciences, Intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite.Blatt, Harvey and Robert J. Tracy (1996) ''Petrology: Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic'', 2nd ed., Freeman, pp. 281–292 Shale is characterized by its tendency to split into thin layers ( laminae) less than one centimeter in thickness. This property is called '' fissility''. Shale is the most common sedimentary rock. The term ''shale'' is sometimes applied more broadly, as essentially a synonym for mudrock, rather than in the more narrow sense of clay-rich fissile mudrock. Texture Shale typically exhibits varying degrees of fissility. Because of the parallel orientation of clay mineral flakes in shale, it breaks into thin layers, often splintery and usually parallel to the otherwise indistinguishable beddin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) because they are the most resistant minerals to weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be any color due to impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Since sandstone beds often form highly visible cliffs and other topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have been strongly identified with certain regions. Rock formations that are primarily composed of sandstone usually allow the percolation of water and other fluids and are porous enough to store large quantities, making them valuable aquifers and petroleum reservoirs. Quartz-bearing sandstone can be changed into quartzite through metamorphism, usually related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horn Of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), p. 26 Located on the easternmost part of the African mainland, it is the fourth largest peninsula in the world. It is composed of Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia and Djibouti; broader definitions also include parts or all of Kenya, Sudan, South Sudan, and Uganda. The term Greater Horn Region (GHR) can additionally include Burundi, Rwanda, and Tanzania. It lies along the southern boundary of the Red Sea and extends hundreds of kilometres into the Guardafui Channel, Gulf of Aden, and Indian Ocean and shares a maritime border with the Arabian Peninsula of Western Asia. Names This peninsula has been known by various names. Ancient Greeks and Romans referred to it as Regio Aromatica or Regio Cinnamonifora due to the aromatic plants or as Regio I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transgression (geology)
A marine transgression is a geologic event during which sea level rises relative to the land and the shoreline moves toward higher ground, which results in flooding. Transgressions can be caused by the land sinking or by the ocean basins filling with water or decreasing in capacity. Transgressions and regressions may be caused by tectonic events such as orogenies, severe climate change such as ice ages or isostatic adjustments following removal of ice or sediment load. During the Cretaceous, seafloor spreading created a relatively shallow Atlantic basin at the expense of deeper Pacific basin. That reduced the world's ocean basin capacity and caused a rise in sea level worldwide. As a result of the sea level rise, the oceans transgressed completely across the central portion of North America and created the Western Interior Seaway from the Gulf of Mexico to the Arctic Ocean. The opposite of transgression is regression in which the sea level falls relative to the land and expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Jurassic
The Early Jurassic Epoch (geology), Epoch (in chronostratigraphy corresponding to the Lower Jurassic series (stratigraphy), Series) is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event, 201.3 Ma (million years ago), and ends at the start of the Middle Jurassic 174.1 Ma. Certain rocks of marine origin of this age in Europe are called "Lias Group, Lias" and that name was used for the period, as well, in 19th-century geology. In southern Germany rocks of this age are called Black Jurassic. Origin of the name Lias There are two possible origins for the name Lias: the first reason is it was taken by a geologist from an England, English quarryman's dialect pronunciation of the word "layers"; secondly, sloops from north Cornwall, Cornish ports such as Bude would sail across the Bristol Channel to the Vale of Glamorgan to load up with rock from coastal limestone quarries (lias limestone from S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edaga Arbi Glacials
The Edaga Arbi Glacials are a Palaeozoic geological formation in Tigray (northern Ethiopia) and in Eritrea. The matrix is composed of grey, black and purple clays (locally silt), that contains rock fragments up to 6 metres across. Pollen dating yields a Late Carboniferous (~323 million years or Ma) to Early Permian (~295 Ma) age. Name and definition The name was coined by geologist D.B.Dow and colleagues They referred to the wide outcrops surrounding the town of Idaga Arbi. So far the nomenclature has not been proposed for recognition to the International Commission on Stratigraphy. Stratigraphic context The Edaga Arbi Glacials fill the bottom of north-south oriented valleys, that were carved by glaciers, into the Precambrian basement and in Early Palaeozoic sediments. These valleys were often several kilometres wide and tens of meters deep. Indeed, northern Ethiopia was glaciated in the Early Palaeozoic (Late Ordovician; ~445 Ma), and in the Late Palaeozoic (Carboniferous-Permi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enticho Sandstone
The Enticho Sandstone is a geological formation in north Ethiopia. It forms the lowermost sedimentary rock formation in the region and lies directly on the basement rocks. Enticho Sandstone consists of arenite that is rich in quartz. The formation has a maximum thickness of 200 metres. Locally, its upper part is coeval with the Edaga Arbi Glacials. The Enticho Sandstone has been deposited during the Ordovician (485–443 million years), as evidenced by impressions of organisms. Description Name and definition The name was coined by geologists D.B. Dow and colleagues. So far the nomenclature has not been proposed for recognition to the International Commission on Stratigraphy. Geographical extent Enticho Sandstone outcrops in central-southern Eritrea and in northeast Tigray in Ethiopia. Stratigraphic context Northern Ethiopia has experienced glaciations during the Early Palaeozoic (Late Ordovician; circa 445 million years ago), as well as in the Late Palaeozoic (Carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
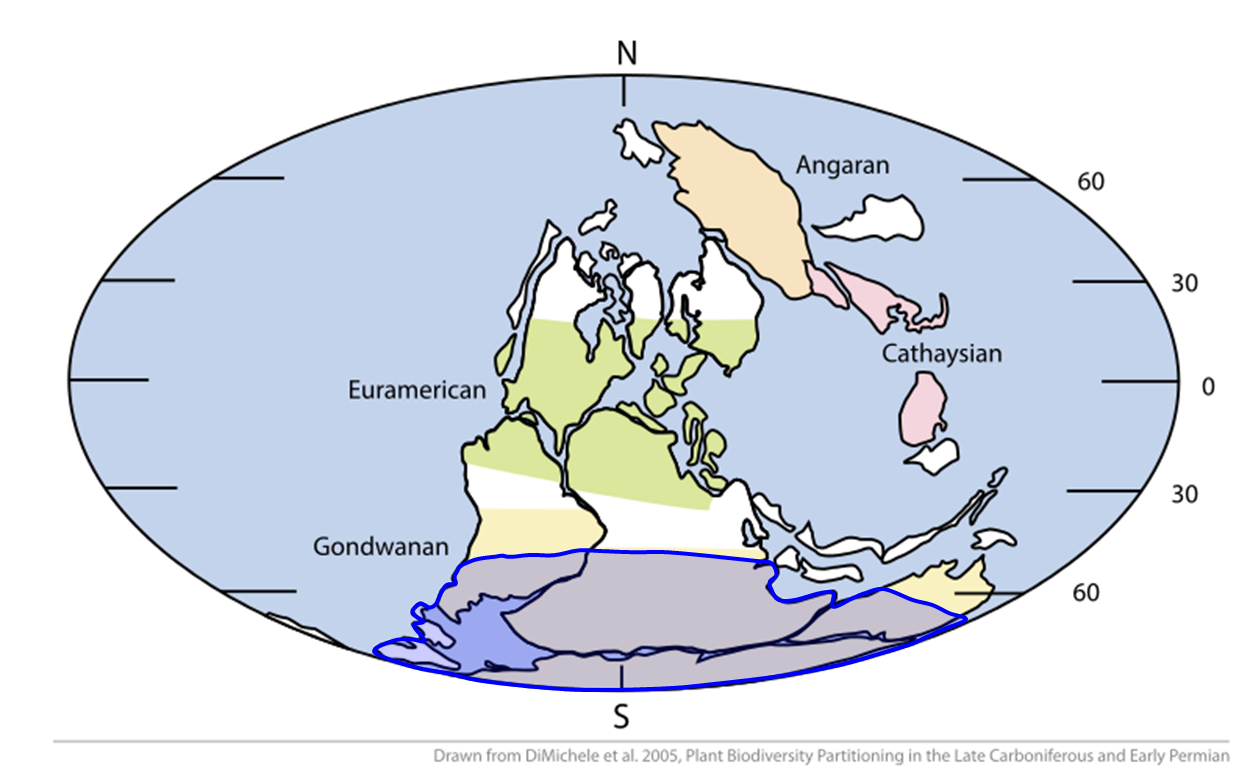
Karoo Ice Age
The late Paleozoic icehouse, also known as the Late Paleozoic Ice Age (LPIA) and formerly known as the Karoo ice age, was an ice age that began in the Late Devonian and ended in the Late Permian, occurring from 360 to 255 million years ago (Mya), and large land-based ice-sheets were then present on Earth's surface. It was the second major icehouse period of the Phanerozoic. It is named after the tillite ( Dwyka Group) found in the Karoo Basin of western South Africa, where evidence for the ice age was first clearly identified in the 19th century. The tectonic assembly of the continents of Euramerica and Gondwana into Pangaea, in the Hercynian- Alleghany Orogeny, made a major continental land mass within the Antarctic region, and the closure of the Rheic Ocean and Iapetus Ocean saw disruption of warm-water currents in the Panthalassa Ocean and Paleotethys Sea and an increase in carbon sequestration via silicate weathering, which led to progressive cooling of summers, and the snow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



Saunders_Quarry-1.jpg)