|
Geology Of Svalbard
The geology of Svalbard encompasses the geological description of rock types found in Svalbard, and the associated tectonics and sedimentological history of soils and rocks. The geological exploration of Svalbard is an ongoing activity, and recent understandings may differ from earlier interpretations. Geological Basement Geological basement dated from Precambrian, Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian, originally termed ''Hecla Hoek'', is found in three different provinces. The southwestern terrain comprises Prins Karls Forland, Oscar II Land, Nordenskiöld Land west of Grønfjorden and Wedel Jarlsberg Land . The northwestern terrain includes Haakon VII Land and Albert I Land. The northeastern terrain comprises Nordaustlandet and the northeastern parts of Spitsbergen. Devonian Devonian age sediments are exposed in Andrée Land, James I Land and Dickson Land. Orogeny took place in late Devon. Carboniferous and Permian During Carboniferous and Permian, rift basins were formed. Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard Geology V2
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
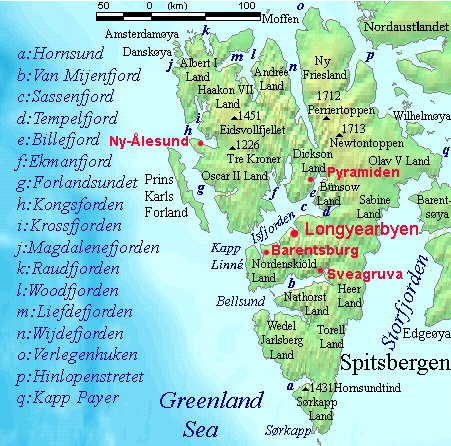
Nordaustlandet
Nordaustlandet (sometimes translated as North East Land) is the second-largest island in the archipelago of Svalbard, Norway, with an area of . It lies north east of Spitsbergen, separated by Hinlopen Strait. Much of Nordaustlandet lies under large ice caps, mainly Austfonna and Vestfonna, the remaining parts of the north being tundra inhabited by reindeer and walruses. The island is uninhabited and lies entirely within Nordaust-Svalbard Nature Reserve. History English walrus hunters first sighted the south point of Nordaustlandet in 1617. This discovery was shown on the ''Muscovy Company's map'' (1625; but based on discoveries made in and prior to 1622), with the island labeled as ''Sir Thomas Smyth's Iland''. It also shows the North Cape (''Point Purchas''). It is first named ''Oostlandt'' ("East Land") on a Dutch 1662 map, and the following year another Dutch map marked its coastline more distinctly, showing its west and north coasts, separating the latter from the Seven Isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomfjorden
Lomfjorden ( en, The Loon Fjord) is a fjord In physical geography, a fjord or fiord () is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Alaska, Antarctica, British Columbia, Chile, Denmark, Förden and East Jutland Fjorde, Germany, ... at the eastern coast of Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has a length of about . Former names of the fjord include ''Bear Bay'', ''Lamber Bay'', ''Loom Bay'', ''Lomme Fjord'' and ''Lommen baij''. References Fjords of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-fjord-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempelfjorden
Tempelfjorden is a fjord branch at the inner end of Sassenfjorden, a part of Isfjorden at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It is located between Sabine Land and Bünsow Land. The fjord is named after the mountain Templet, which resembles a temple A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples .... Between 2002 and 2015, the sailing vessel ''Noorderlicht'' was intentionally frozen into Tempelfjorden every winter. References Fjords of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-fjord-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billefjorden
Billefjorden is the central fjord of the three branching from the innermost part of the Isfjorden to the northeast, in Svalbard, Norway. It is 30 km long and 5–8 km wide. Billefjorden lies between Dickson Land to the northwest and Bünsow Land in the southeast. Located on its northwestern shore is the former Russian coal mining community of Pyramiden (abandoned in 1998). To the northeast is Nordenskiöldbreen (Nordenskiöld Glacier). At its northeastern extreme is Adolf Bay. The fjord is named after the Dutch whaler Cornelius Claeszoon Bille, who is mentioned as being active in 1675 by the Dutch whaler Cornelius Gisbert Zorgdrager. Originally another bay (now known as Adventfjorden) had been labeled as ''Klass Billen Bay'', but Dunér and Nordenskiöld moved it to its present location. The fjord is the site of the Billefjorden Fault Zone, which continues to the north and separates Svalbard’s north-eastern and north-western terrane In geology, a terrane (; in f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogeny
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dickson Land
Dickson Land is a land area between Isfjorden and Wijdefjorden Wijdefjord is the longest fjord in Norway's Svalbard archipelago. Wijdefjord is located in the northern portion of the island of Spitsbergen, which lies in the Arctic Ocean about midway between Norway and the North Pole The North Pole, ... at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It forms a peninsula between the Isfjorden branches Billefjorden and Dicksonfjorden. Dickson Land is named after Oscar Dickson. References Geography of Svalbard Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James I Land
James I Land is a land area on the northwestern part of Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It is named after King James I of England and Scotland. The 30 kilometer long glacier Sveabreen divides James I Land from Oscar II Land Oscar II Land is the land area between Isfjorden and Kongsfjorden on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The long glacier Sveabreen divides Oscar II Land from James I Land. The area is named after Oscar II of Sweden Oscar II (Oscar Fredrik; 21 January .... References Geography of Svalbard Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrée Land (Svalbard)
Andrée Land is the land area between Wijdefjorden and Woodfjorden on Spitsbergen, Svalbard in Arctic Norway. Limited in the south by a line from Woodfjorden through Vonbreen to Holtedahlfonna eastwards to the upper part of Abrahamsenbreen through Ruskbreen, Millarpasset, Lisbetbreen and Vestfjorddalen to Vestfjorden. The area is named after Swedish engineer and polar explorer Salomon August Andrée Salomon August Andrée (18 October 1854, in Gränna, Småland – October 1897, in Kvitøya, Arctic Norway), during his lifetime most often known as S. A. Andrée, was a Swedish engineer, physicist, aeronaut and polar explorer who died while .... References Geography of Svalbard Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)