|
Geography And Imperialism
Geography and Imperialism have been intrinsically linked for centuries, some academics even consider the modern discipline of geography to have directly stemmed from imperialism.Painter, Joe, and Jeffrey, Alex. Political Geography (2nd Edition). London, GBR: SAGE Publications Ltd, 2009. ProQuest ebrary. Web. 28 January 2015. 176 European imperialism in particular, contributed to the field of geography. As European powers sought to expand outwards and overseas, they required the knowledge to do so effectively. Thus, European expansionists relied on geographic knowledge for everything from cartography to the planning of human settlements. The field of Geography, however, also relied on European imperialism to develop the subject. The knowledge that formed the initial subject of geography was achieved through European expansionism. This includes information on the lands and seas of the earth, its flora and fauna as well as its peoples. It is unsurprising then, that many geographers dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and military power), but also soft power ( cultural and diplomatic power). While related to the concepts of colonialism and empire, imperialism is a distinct concept that can apply to other forms of expansion and many forms of government. Etymology and usage The word ''imperialism'' originated from the Latin word ''imperium'', which means supreme power, "sovereignty", or simply "rule". It first became common in the current sense in Great Britain during the 1870s, when it was used with a negative connotation. Hannah Arendt and Joseph Schumpeter defined imperialism as expansion for the sake of expansion. Previously, the term had been used to describe what was perceived as Napoleon III's attempts at obtaining political support through f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively. The fundamental objectives of traditional cartography are to: * Set the map's agenda and select traits of the object to be mapped. This is the concern of map editing. Traits may be physical, such as roads or land masses, or may be abstract, such as toponyms or political boundaries. * Represent the terrain of the mapped object on flat media. This is the concern of map projections. * Eliminate characteristics of the mapped object that are not relevant to the map's purpose. This is the concern of generalization. * Reduce the complexity of the characteristics that will be mapped. This is also the concern of generalization. * Orchestrate the elements of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Settlements
In geography, statistics and archaeology, a settlement, locality or populated place is a community in which people live. The complexity of a settlement can range from a minuscule number of dwellings grouped together to the largest of cities with surrounding urbanized areas. Settlements may include hamlets, villages, towns and cities. A settlement may have known historical properties such as the date or era in which it was first settled, or first settled by particular people. In the field of geospatial predictive modeling, settlements are "a city, town, village or other agglomeration of buildings where people live and work". A settlement conventionally includes its constructed facilities such as roads, enclosures, field systems, boundary banks and ditches, ponds, parks and woods, wind and water mills, manor houses, moats and churches. History The earliest geographical evidence of a human settlement was Jebel Irhoud, where early modern human remains of eight individuals dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Determinism
Environmental determinism (also known as climatic determinism or geographical determinism) is the study of how the physical environment predisposes societies and states towards particular development trajectories. Jared Diamond, Jeffrey Herbst, Ian Morris, and other social scientists sparked a revival of the theory during the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries. This "neo-environmental determinism" school of thought examines how geographic and ecological forces influence state-building, economic development, and institutions. Many scholars underscore that this original approach was used to encourage colonialism and eurocentrism, and devalued human agency in non-Western societies, whereas modern figures like Diamond have instead used the approach as an explanation that rejects racism.Gilmartin, M. (2009). "Colonialism/Imperialism". Key concepts in political geography (pp. 115–123). London: SAGE. A history of thought Classical and medieval periods Early theories of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
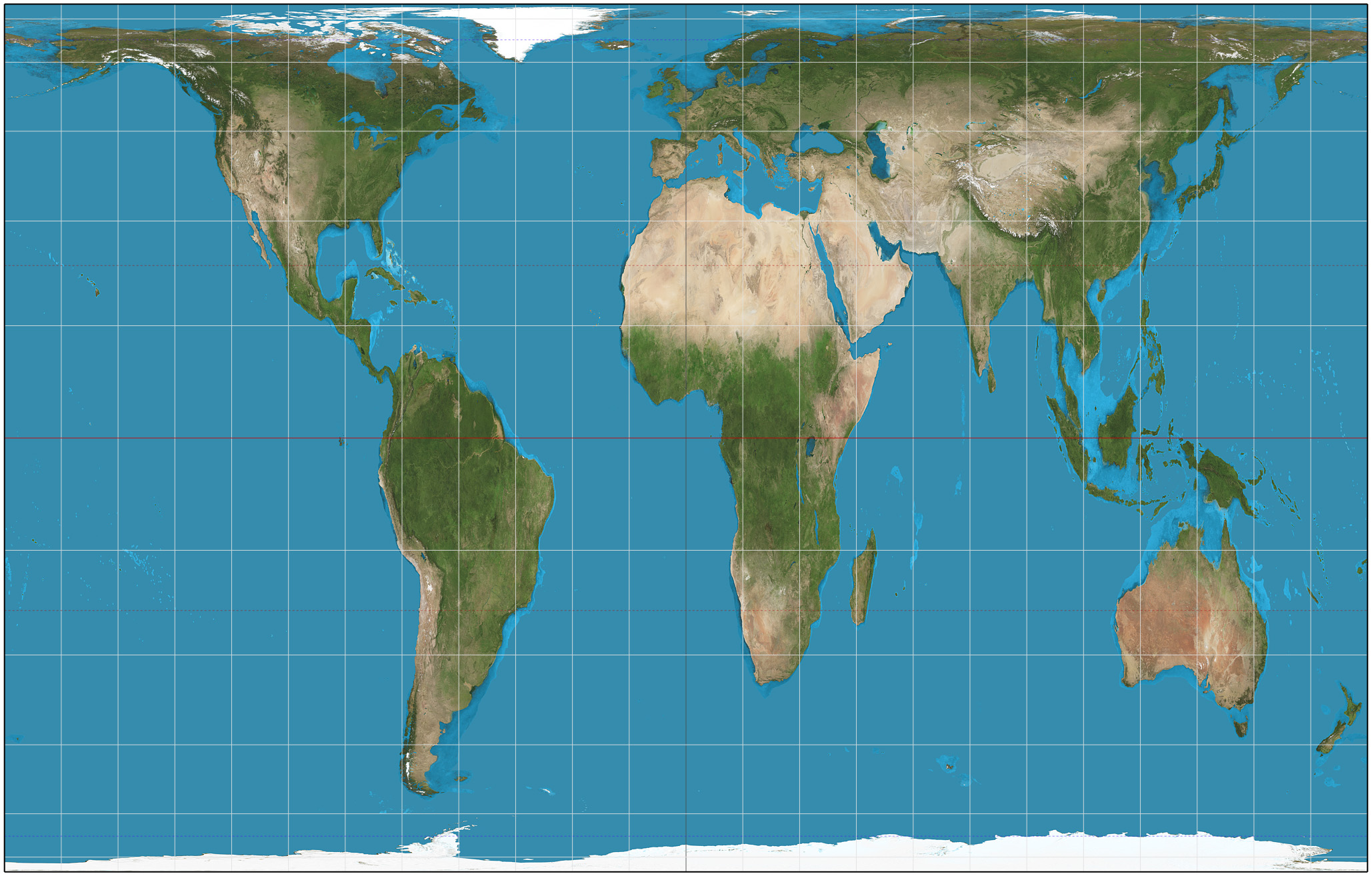
Gall–Peters Projection
The Gall–Peters projection is a rectangular, equal-area map projection. Like all equal-area projections, it distorts most shapes. It is a cylindrical equal-area projection with latitudes 45° north and south as the regions on the map that have no distortion. The projection is named after James Gall and Arno Peters. Gall described the projection in 1855 at a science convention and published a paper on it in 1885. Peters brought the projection to a wider audience beginning in the early 1970s through his "Peters World Map". The name "Gall–Peters projection" was first used by Arthur H. Robinson in a pamphlet put out by the American Cartographic Association in 1986.American Cartographic Association's Committee on Map Projections, 1986. ''Which Map is Best'' p. 12. Falls Church: American Congress on Surveying and Mapping. Maps based on the projection are promoted by UNESCO, and they are also widely used by British schools. The U.S. state of Massachusetts and Boston Public Schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |