|
Geoffrey (given Name)
Geoffrey is an English and French masculine given name. It is generally considered the Anglo-Norman form of the Germanic compound 'god' and 'peace'. It is a derivative of Dutch Godfried, German Gottfried and Old English Gotfrith and Godfrith. Alexander MacBain considered it as being found in the Gaelic and Welsh forms; potentially before or contemporary to the Anglo-Saxon, with the examples of Goraidh, Middle Gaelic Gofraig (1467 MS.), Godfrey (do.), Irish Gofraidh (F.M.), Middle Irish Gothfrith, Gofraig (Tigernach, 989), Early Irish Gothfraid (Lib. Lein.), E. Welsh Gothrit (Ann. Camb.). Macbain suggested these Celtic forms of the name were closer related to the Anglo-Saxon Godefrid than the Norse Goðröðr, Gudrød or Góröðr; however he does not elaborate further on the origin or relation. The form as 'Geoffrey' was probably introduced to Norman England. It was also Anglicised as '' Jeffrey'' later after the name became more popular after the likes of Presi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
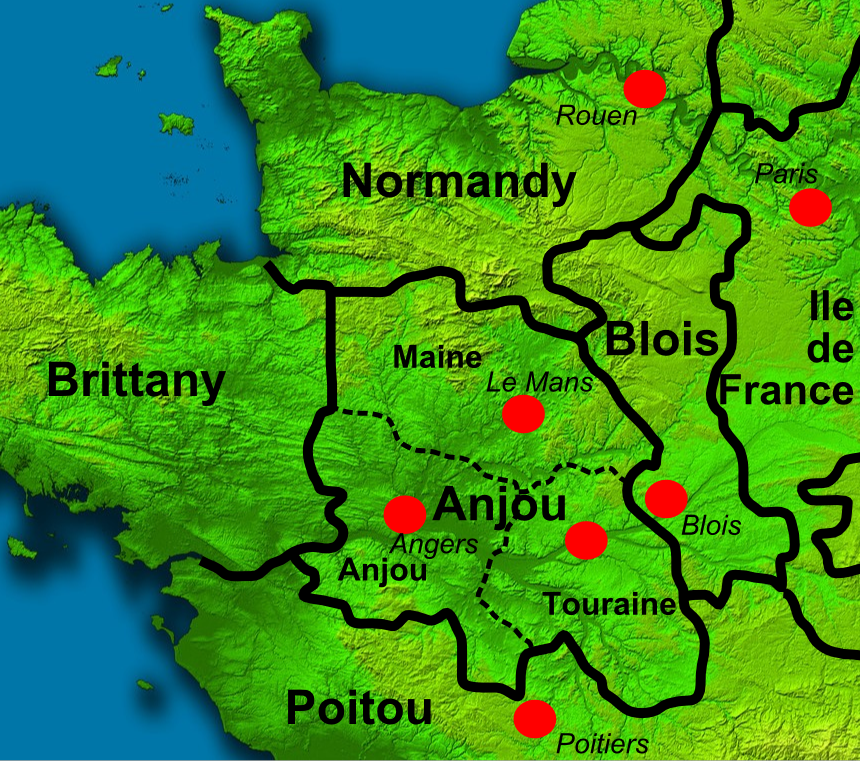
Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count Of Anjou
Geoffrey V (24 August 1113 – 7 September 1151), called the Handsome, the Fair (french: link=no, le Bel) or Plantagenet, was the count of Anjou, Touraine and Maine by inheritance from 1129, and also Duke of Normandy by conquest from 1144. His marriage to Empress Matilda, daughter of King Henry I of England, led to the centuries-long reign of the Plantagenet dynasty in England. The name "Plantagenet" was taken from Geoffrey's epithet. Geoffrey's ancestral domain of Anjou gave rise to the name Angevin, and what modern historians name as the Angevin Empire in the 12th century. Early life Geoffrey was the elder son of Fulk V of Anjou and Ermengarde of Maine. Geoffrey received his nickname from the yellow sprig of broom blossom (''genêt'' is the French name for the ''planta genista'', or broom shrub) he wore in his hat. The chronicler John of Marmoutier described Geoffrey as handsome, red haired, jovial, and a great warrior. King Henry I of England, having heard report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guthfrith (other)
Guthfrith (one of many derived spellings of the Old Norse personal name Guðrøðr, also Anglicised as ''Godred'') may refer to: * Gudfred (r. 804–810), Danish king, son of King Sigfred * Guthred, king of Northumbria (ruled c. 883 – 895) * Gofraid ua Ímair (died 934), aka Gothfrith II, King of York * Olaf III Guthfrithson Olaf Guthfrithson or Anlaf Guthfrithson ( non, Óláfr Guðrøðsson ; oe, Ánláf; sga, Amlaíb mac Gofraid; died 941) was a Hiberno-Scandinavian (Irish-Viking) leader who ruled Dublin and Viking Northumbria in the 10th century. He was th ... (died 941), King of Dublin * Gofraid mac Sitriuc (died 951), King of Dublin {{DEFAULTSORT:Guthfrith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latinisation Of Names
Latinisation (or Latinization) of names, also known as onomastic Latinisation, is the practice of rendering a ''non''-Latin name in a Latin style. It is commonly found with historical proper names, including personal names and toponyms, and in the standard binomial nomenclature of the life sciences. It goes further than romanisation, which is the transliteration of a word to the Latin alphabet from another script (e.g. Cyrillic). For authors writing in Latin, this change allows the name to function grammatically in a sentence through declension. In a scientific context, the main purpose of Latinisation may be to produce a name which is internationally consistent. Latinisation may be carried out by: * transforming the name into Latin sounds (e.g. for ), or * adding Latinate suffixes to the end of a name (e.g. for '' Meibom),'' or * translating a name with a specific meaning into Latin (e.g. for Italian ; both mean 'hunter'), or * choosing a new name based on some attri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle French
Middle French (french: moyen français) is a historical division of the French language that covers the period from the 14th to the 16th century. It is a period of transition during which: * the French language became clearly distinguished from the other competing Oïl languages, which are sometimes subsumed within the concept of Old French () * the French language was imposed as the official language of the Kingdom of France in place of Latin and other Oïl and Occitan languages * the literary development of French prepared the vocabulary and grammar for the Classical French () spoken in the 17th and 18th centuries. It is the first version of French that is largely intelligible to Modern French speakers, contrary to Old French. History The most important change found in Middle French is the complete disappearance of the noun declension system (already underway for centuries). There is no longer a distinction between nominative and oblique forms of nouns, and plurals ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intelligible yet diverse, spoken in the northern half of France. These dialects came to be collectively known as the , contrasting with the in the south of France. The mid-14th century witnessed the emergence of Middle French, the language of the French Renaissance in the Île de France region; this dialect was a predecessor to Modern French. Other dialects of Old French evolved themselves into modern forms ( Poitevin-Saintongeais, Gallo, Norman, Picard, Walloon, etc.), each with its own linguistic features and history. The region where Old French was spoken natively roughly extended to the northern half of the Kingdom of France and its vassals (including parts of the Angevin Empire, which during the 12th century remained under Anglo-No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jefferson (surname)
Jefferson is a surname. Notable people with the name include: Music * Blind Lemon Jefferson (1893–1929), American Blues musician * Marshall Jefferson, American musician * Melissa Jefferson, American singer and rapper known professionally as Lizzo * Eddie Jefferson, American Jazz vocalist Sports * Al Jefferson, American basketball player * Amile Jefferson, American basketball player * Brandon Jefferson, American basketball player * Davon Jefferson (born 1986), American basketball player * Jermar Jefferson (born 2000), American football player * Jesse Jefferson (1949–2011), American baseball player * John Jefferson, American football player * Julian Jefferson, English cricketer * Justin Jefferson (born 1999), American football player * Malik Jefferson, American football player * Reggie Jefferson, American baseball player * Richard Jefferson, American basketball player * Richard Jefferson (cricketer), English cricketer * Van Jefferson (born 1996), American football ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypocorism
A hypocorism ( or ; from Ancient Greek: (), from (), 'to call by pet names', sometimes also ''hypocoristic'') or pet name is a name used to show affection for a person. It may be a diminutive form of a person's name, such as ''Izzy'' for Isabel or ''Bob (given name), Bob'' for Robert, or it may be unrelated. In linguistics, the term can be used more specifically to refer to the morphological process by which the standard form of the word is transformed into a form denoting affection, or to words resulting from this process. In English, a word is often Clipping (morphology), clipped down to a closed monosyllable and then suffixed with ''-y/-ie'' (phonologically /i/). Sometimes the suffix ''-o'' is included as well as other forms or templates. Hypocoristics are often affective in meaning and are particularly common in Australian English, but can be used for various purposes in different semantic fields, including personal names, place names and nouns. Hypocorisms are usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeffrey (name)
Jeffrey is a common English given name, and a variant form of the name Geoffrey (itself from a Middle French variant of Godfrey, Gottfried). It has been argued that the common derivation of Middle French ''Geoffrey (or Geoffroy), Jeffery'' from ''Godfrey'' is mistaken, and that the names reflect two separate first Germanic elements ''god'' vs. '' gaut'', which became conflated in Old High German by the end of the early medieval period. Albert Dauzat, ''Noms et prénoms de France'', Librairie Larousse 1980, édition revue et commentée par Marie-Thérèse Morlet. p. 287b - 288a - 296ab. Outside of North America, ''Geoffrey'' is more common than ''Jeffrey''. Jeffrey and its variants are found as surnames, usually as a patronymic ending in -s (e.g., Jefferies, Jaffrays); The surname Jefferson is also a patronymic version of the given name. In Scotland, Jeffrey is most frequently found to be a surname. Variations include Jeff, Jeffry, Jeffy, Jeffery, Jeffory, Geoff, Geoffrey, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglicisation
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influence of English culture and business on other countries outside England or the United Kingdom, including their media, cuisine, popular culture, technology, business practices, laws, or political systems. Linguistic anglicisation is the practice of modifying foreign words, names, and phrases to make them easier to spell, pronounce or understand in English. The term commonly refers to the respelling of foreign words, often to a more drastic degree than that implied in, for example, romanisation. One instance is the word "dandelion", modified from the French ''dent-de-lion'' ("lion's tooth", a reference to the plant's sharply indented leaves). The term can also refer to phonological adaptation without spelling change: ''spaghetti'', for exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gudrød (other)
Gudrød may refer to: * Gudfred Gudfred was a ninth century Danish king who reigned from at least 804 to 810. Alternate spellings include ''Godfred'' (Danish), ''Göttrick'' (German), ''Gøtrik'' (Danish), ''Gudrød'' (Danish), and ''Godofredus'' (Latin). He stands at the thres ... (Danish king, ruled from 804 or earlier until 810) * Gudrød the Hunter (semi-legendary king in Vingulmark in south-east Norway, from 804 until 810) * Gudrød Bjørnsson (ruled Vestfold until 968) {{hndis, Gudrød ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |