|
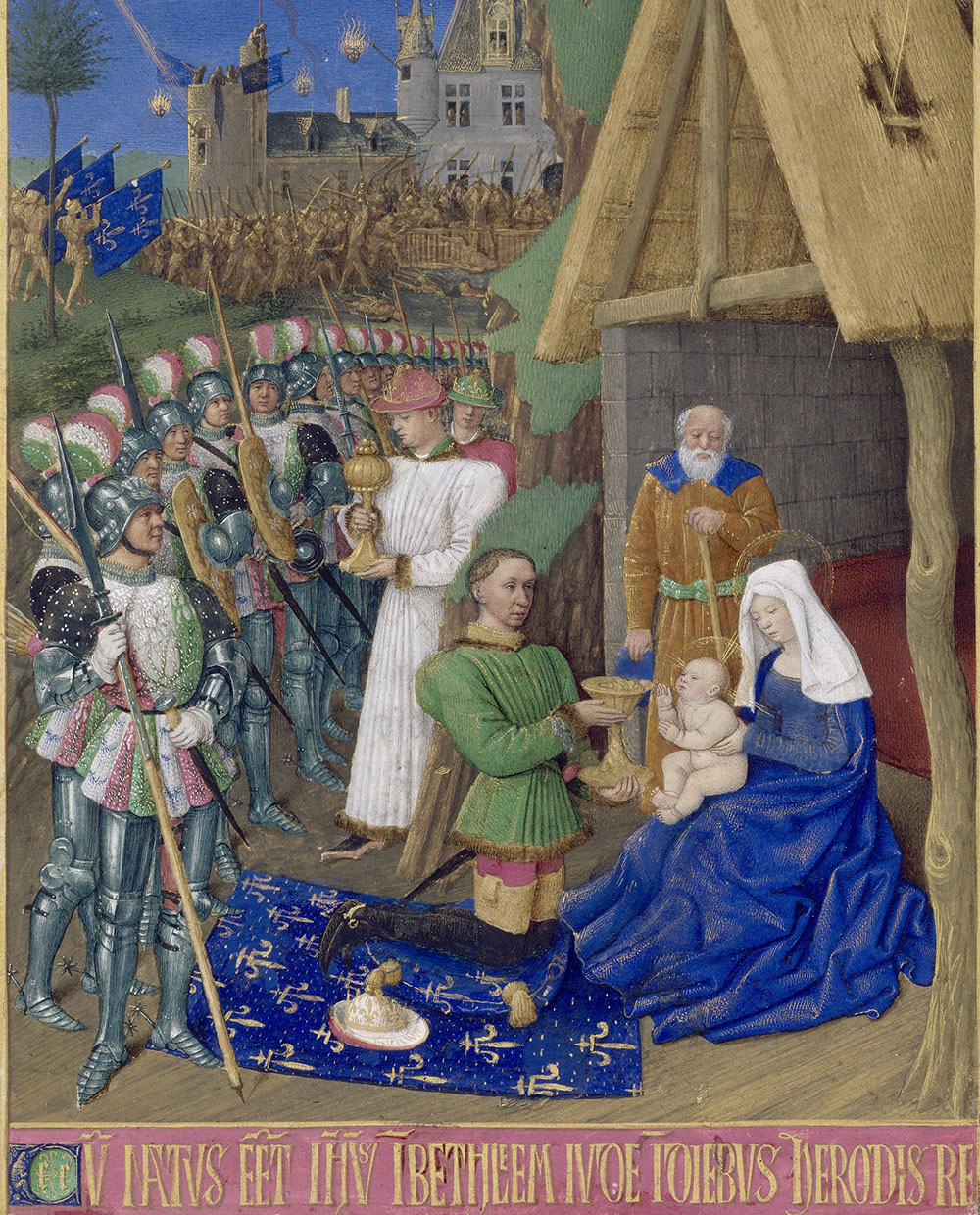
Gens D’Armes
A ''gendarme'' was a heavy cavalryman of noble birth, primarily serving in the French army from the Late Middle Ages to the Early Modern period. Heirs to the knights of French medieval feudal armies, French Gendarmes also enjoyed a stellar reputation and were regarded as the finest European heavy cavalry force until the decline of chivalric ideals largely due to the ever-evolving developments in gunpowder technology. They provided the Kings of France with a potent regular force of armored lancers which, when properly employed, dominated late medieval and early modern battlefields. Their symbolic demise is generally considered to be the Battle of Pavia, which inversely is seen as confirming the rise of the Spanish Tercios as the new dominant military force in Europe. Etymology The word ''gendarme'' derives originally from the French ''homme d'armes'' ( man-at-arms), plural of which is ''gens d'armes''. The plural sense was later shortened to ''gendarmes'' and a singular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in the roles of reconnaissance, screening, and skirmishing in many armies, or as heavy cavalry for decisive shock attacks in other armies. An individual soldier in the cavalry is known by a number of designations depending on era and tactics, such as cavalryman, horseman, trooper, cataphract, knight, hussar, uhlan, mamluk, cuirassier, lancer, dragoon, or horse archer. The designation of ''cavalry'' was not usually given to any military forces that used other animals for mounts, such as camels or elephants. Infantry who moved on horseback, but dismounted to fight on foot, were known in the early 17th to the early 18th century as '' dragoons'', a class of mounted infantry which in most armies later evolved into standard cavalry while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armagnac (party)
The Armagnac faction was prominent in French politics and warfare during the Hundred Years' War. It was allied with the supporters of Charles, Duke of Orléans against John the Fearless after Charles' father Louis of Valois, Duke of Orléans, Louis of Orléans was Assassination of Louis I, Duke of Orléans, killed on a Paris street on the orders of the Duke of Burgundy on 23 November 1407. The Armagnac Faction took its name from Charles' father-in-law, Bernard VII, Count of Armagnac (1360–1418), who guided the young Duke during his teens and provided much of the financing and some of the seasoned Gascony, Gascon troops that besieged Paris before their defeat at Saint-Cloud. Origins In 1407, Louis of Valois, Duke of Orléans, Louis of Orléans was assassinated on the order of John the Fearless. Fearing Burgundian (party), Burgundian ambitions, the dukes of Duke of Berry, Berry, List of rulers of Brittany, Brittany, and Duke of Orléans, Orléans, and the counts of Count of Ale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chef D'escadre
''Chef d'escadre'' (; literally "squadron commander") was a rank in the French Navy during the Ancien Régime and until the French Revolution. The rank was changed to '' contre-amiral'' by a law passed on 15 May 1791. History The first chefs d'escadre were created by Louis XIII in 1627 - he had a "chef d'escadre of Normandy" commanding the port of Le Havre, a chef d'escadre of Brittany commanding Brest, and a chef d'escadre of Guyenne commanding Brouage. Each of these chefs d'escadres, as officiers d'épée, were flanked by a commissaire général, an officier de plume. Their numbers grew rapidly: in 1635 a chef d'escadre of Provence was created, then in 1647 a chef d'escadre for Flanders, in 1663 one for Poitou-Saintonge, in 1673 one for Picardy and one for Languedoc, in 1689 one for Aunis, in 1701 one for America, and in 1707 one for Roussillon. After 1715, there were more chefs d'escadre than there were coastal provinces, and so they started taking the title "chefs d'esc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squadron (army)
A squadron was historically a cavalry Subunit (military), subunit, a company or battalion-sized military formation. The term is still used to refer to modern cavalry Unit (military), units, and is also used by other arms and services (frequently Squadron (aviation), aviation, also Squadron (naval), naval). In some countries, including Italian Army, Italy, the name of the battalion-level cavalry unit translates as "''Squadron Group''". United States In the modern United States Army, a squadron is an armored cavalry, air cavalry, or other reconnaissance unit whose organizational role parallels that of a battalion and is commanded by a Lieutenant colonel (United States), lieutenant colonel. Prior to the revisions in the US Army structure in the 1880s, US Cavalry regiments were divided into Company (military unit), companies, and the battalion was an administrative designation used only in garrison. The reorganizations converted companies to troops and battalions to squadrons, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
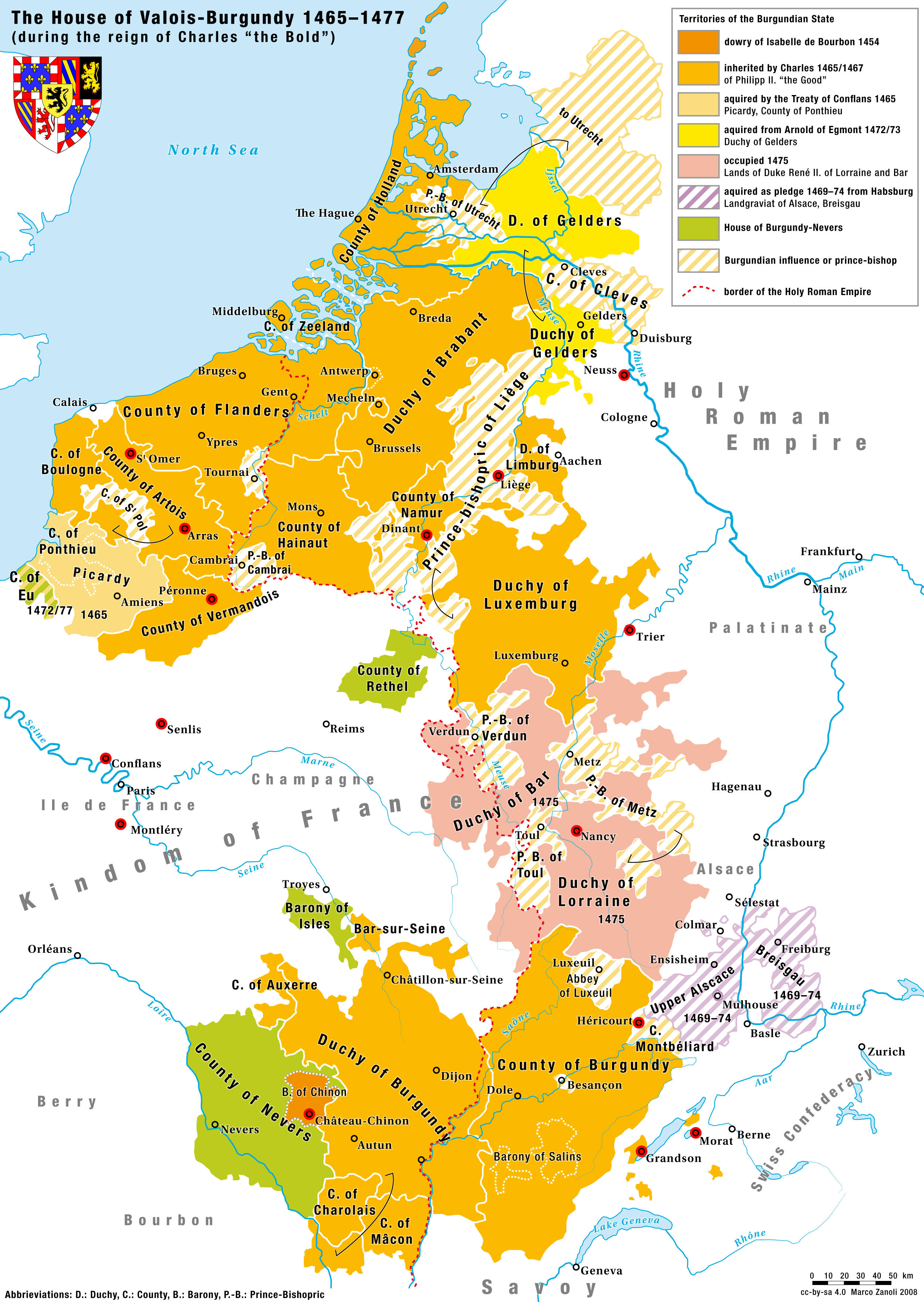
Charles The Bold
Charles I (Charles Martin; german: Karl Martin; nl, Karel Maarten; 10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), nicknamed the Bold (German: ''der Kühne''; Dutch: ''de Stoute''; french: le Téméraire), was Duke of Burgundy from 1467 to 1477. Charles's main objective was to be crowned king by turning the growing Burgundian State into a territorially continuous kingdom. He declared himself and his lands independent, bought Upper Alsace and conquered Zutphen, Guelders and Lorraine, uniting at last Burgundian northern and southern possessions. This caused the enmity of several European powers and triggered the Burgundian Wars. Charles's early death at the Battle of Nancy at the hands of Swiss mercenaries fighting for René II, Duke of Lorraine, was of great consequence in European history. The Burgundian domains, long wedged between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire, were divided, but the precise disposition of the vast and disparate territorial possessions involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy (french: duc de Bourgogne) was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by France in 1477, and later by Holy Roman Emperors and Kings of Spain from the House of Habsburg who claimed Burgundy proper and ruled the Burgundian inheritance in the Low Countries. The Duchy of Burgundy was a small portion of the traditional lands of the Burgundians west of the river Saône which, in 843, was allotted to Charles the Bald's West Franks, kingdom of West Franks. Under the Ancien Régime, the Duke of Burgundy was the premier lay Peerage of France, peer of the kingdom of France. Beginning with Robert II of France, the title was held by the House of Capet, Capetians, the French royal family. It was granted to Robert's younger son, Robert I, Duke of Burgundy, Robert, who founded the House of Burgundy. When the senior line of the House of Burgundy became extinct, it was inherited by John II of France through proximity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XI
Louis XI (3 July 1423 – 30 August 1483), called "Louis the Prudent" (french: le Prudent), was King of France from 1461 to 1483. He succeeded his father, Charles VII. Louis entered into open rebellion against his father in a short-lived revolt known as the Praguerie in 1440. The king forgave his rebellious vassals, including Louis, to whom he entrusted the management of the Dauphiné, then a province in southeastern France. Louis's ceaseless intrigues, however, led his father to banish him from court. From the Dauphiné, Louis led his own political establishment and married Charlotte of Savoy, daughter of Louis, Duke of Savoy, against the will of his father. Charles VII sent an army to compel his son to his will, but Louis fled to Burgundy, where he was hosted by Philip the Good, the Duke of Burgundy, Charles' greatest enemy. When Charles VII died in 1461, Louis left the Burgundian court to take possession of his kingdom. His taste for intrigue and his intense diplomatic activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lance
A lance is a spear designed to be used by a mounted warrior or cavalry soldier ( lancer). In ancient and medieval warfare, it evolved into the leading weapon in cavalry charges, and was unsuited for throwing or for repeated thrusting, unlike similar weapons of the javelin and pike family typically used by infantry. Lances were often equipped with a vamplate, a small circular plate to prevent the hand sliding up the shaft upon impact, and beginning in the late 14th century were used in conjunction with a lance rest attached to the breastplate. Though best known as a military and sporting weapon carried by European knights and men-at-arms, the use of lances was widespread throughout Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa wherever suitable mounts were available. Lancers of the medieval period also carried secondary weapons such as swords, battle axes, war hammers, maces and daggers for use in hand-to-hand combat, since the lance was often a one-use-per-engagement weapon; assumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Armour
Plate armour is a historical type of personal body armour made from bronze, iron, or steel plates, culminating in the iconic suit of armour entirely encasing the wearer. Full plate steel armour developed in Europe during the Late Middle Ages, especially in the context of the Hundred Years' War, from the coat of plates worn over mail suits during the 14th century. In Europe, plate armour reached its peak in the late 15th and early 16th centuries. The full suit of armour, also referred to as a panoply, is thus a feature of the very end of the Middle Ages and the Renaissance period. Its popular association with the " medieval knight” is due to the specialised jousting armour which developed in the 16th century. Full suits of Gothic plate armour were worn on the battlefields of the Burgundian and Italian Wars. The most heavily armoured troops of the period were heavy cavalry, such as the gendarmes and early cuirassiers, but the infantry troops of the Swiss mercenaries and the La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arquebus
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier. Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbus'' ("hook gun"), was applied to many different forms of firearms from the 15th to 17th centuries, it originally referred to "a hand-gun with a hook-like projection or lug on its under surface, useful for steadying it against battlements or other objects when firing". These "hook guns" were in their earliest forms of defensive weapons mounted on German city walls in the early 15th century. The addition of a shoulder stock, priming pan, and matchlock mechanism in the late 15th century turned the arquebus into a handheld firearm and also the first firearm equipped with a trigger. The exact dating of the matchlock's appearance is disputed. It could have appeared in the Ottoman Empire as early as 1465 and in Europe a little before 1475. The h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis I Of France
Francis I (french: François Ier; frm, Francoys; 12 September 1494 – 31 March 1547) was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law Louis XII, who died without a son. A prodigious patron of the arts, he promoted the emergent French Renaissance by attracting many Italian artists to work for him, including Leonardo da Vinci, who brought the ''Mona Lisa'' with him, which Francis had acquired. Francis' reign saw important cultural changes with the growth of central power in France, the spread of humanism and Protestantism, and the beginning of French exploration of the New World. Jacques Cartier and others claimed lands in the Americas for France and paved the way for the expansion of the first French colonial empire. For his role in the development and promotion of the French language, he became known as ''le Père et Restaurateur des Lettr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For Army Historical Research
The Society for Army Historical Research is a learned society, founded in 1921 to foster "interest in the history and traditions of British and Commonwealth armies, and to encourage research in these fields." It is one of the oldest societies of its kind. Past members include notable British Field Marshals Wavell, Auchinleck and Templer. The current president is Lieutenant-General Sir Barney White-Spunner and Major-General Ewan Carmichael is Chairman of its Council. The Patron of the Society is Field Marshal the Duke of Kent. The society's interests embrace both army and regimental history, military antiquities and pictures, uniforms, badges and medals, arms and equipment and the history of land warfare in general. The study of campaigns, commanders and the political aspects of war are covered from the sixteenth century to the recent past. Journal The society's main activity is the publication of the peer-reviewed quarterly ''Journal of the Society for Army Historical Research'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |