|
Genotyping
Genotyping is the process of determining differences in the genetic make-up ( genotype) of an individual by examining the individual's DNA sequence using biological assays and comparing it to another individual's sequence or a reference sequence. It reveals the alleles an individual has inherited from their parents. Traditionally genotyping is the use of DNA sequences to define biological populations by use of molecular tools. It does not usually involve defining the genes of an individual. Techniques Current methods of genotyping include restriction fragment length polymorphism identification (RFLPI) of genomic DNA, random amplified polymorphic detection (RAPD) of genomic DNA, amplified fragment length polymorphism detection (AFLPD), polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, allele specific oligonucleotide (ASO) probes, and hybridization to DNA microarrays or beads. Genotyping is important in research of genes and gene variants associated with disease. Due to cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restriction Site Associated DNA Markers
Restriction site associated DNA (RAD) markers are a type of genetic marker which are useful for association mapping, QTL-mapping, population genetics, ecological genetics and evolutionary genetics. The use of RAD markers for genetic mapping is often called RAD mapping. An important aspect of RAD markers and mapping is the process of isolating RAD tags, which are the DNA sequences that immediately flank each instance of a particular restriction site of a restriction enzyme throughout the genome. Once RAD tags have been isolated, they can be used to identify and genotype DNA sequence polymorphisms mainly in form of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Polymorphisms that are identified and genotyped by isolating and analyzing RAD tags are referred to as RAD markers. Although genotyping by sequencing presents an approach similar to the RAD-seq method, they differ in some substantial ways. Isolation of RAD tags The use of the flanking DNA sequences around each restriction site is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genotyping By Sequencing
In the field of DNA sequencing, genetic sequencing, genotyping by sequencing, also called GBS, is a method to discover Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in order to perform genotyping studies, such as genome-wide association studies (Genome-wide association study, GWAS). GBS uses restriction enzymes to reduce genome complexity and genotype multiple DNA samples. After digestion, Polymerase chain reaction, PCR is performed to increase fragments pool and then GBS libraries are sequenced using next generation sequencing technologies, usually resulting in about 100bp single-end reads. It is relatively inexpensive and has been used in plant breeding. Although GBS presents an approach similar to Restriction site associated DNA markers, restriction-site-associated DNA sequencing (RAD-seq) method, they differ in some substantial ways. Methods GBS is a robust, simple, and affordable procedure for SNP discovery and mapping. Overall, this approach reduces ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Microarray
A DNA microarray (also commonly known as DNA chip or biochip) is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to genotype multiple regions of a genome. Each DNA spot contains picomoles (10−12 moles) of a specific DNA sequence, known as '' probes'' (or ''reporters'' or '' oligos''). These can be a short section of a gene or other DNA element that are used to hybridize a cDNA or cRNA (also called anti-sense RNA) sample (called ''target'') under high-stringency conditions. Probe-target hybridization is usually detected and quantified by detection of fluorophore-, silver-, or chemiluminescence-labeled targets to determine relative abundance of nucleic acid sequences in the target. The original nucleic acid arrays were macro arrays approximately 9 cm × 12 cm and the first computerized image based analysis was published in 1981. It was inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated with inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whole Genome Sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast. Whole genome sequencing has largely been used as a research tool, but was being introduced to clinics in 2014. In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data may be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of DNA sequencing, gene sequencing at Single-nucleotide polymorphism, SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
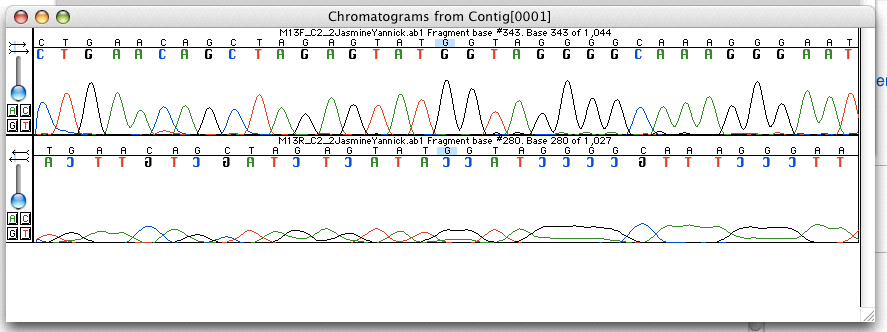
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a specific gene depends on the number of copies of each chromosome found in that species, also referred to as ploidy. In diploid species like humans, two full sets of chromosomes are present, meaning each individual has two alleles for any given gene. If both alleles are the same, the genotype is referred to as homozygous. If the alleles are different, the genotype is referred to as heterozygous. Genotype contributes to phenotype, the observable traits and characteristics in an individual or organism. The degree to which genotype affects phenotype depends on the trait. For example, the petal color in a pea plant is exclusively determined by genotype. The petals can be purple or white depending on the alleles present in the pea plant. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) to a large enough amount to study in detail. PCR was invented in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation; Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture. The major agricultural products can be broadly grouped into foods, fibers, fuels, and raw materials (such as rubber). Food classes include cereals (grains), vegetables, fruits, cooking oils, meat, milk, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) to a large enough amount to study in detail. PCR was invented in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation; Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism
AFLP-PCR or just AFLP is a PCR-based tool used in genetics research, DNA fingerprinting, and in the practice of genetic engineering. Developed in the early 1990s by KeyGene, AFLP uses restriction enzymes to digest genomic DNA, followed by ligation of adaptors to the sticky ends of the restriction fragments. A subset of the restriction fragments is then selected to be amplified. This selection is achieved by using primers complementary to the adaptor sequence, the restriction site sequence and a few nucleotides inside the restriction site fragments (as described in detail below). The amplified fragments are separated and visualized on denaturing on agarose gel electrophoresis , either through autoradiography or fluorescence methodologies, or via automated capillary sequencing instruments. Although AFLP should not be used as an acronym, it is commonly referred to as "Amplified fragment length polymorphism". However, the resulting data are not scored as length polymorphisms, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequencing By Hybridization
Sequencing by hybridization is a class of methods for determining the order in which nucleotides occur on a strand of DNA. Typically used for looking for small changes relative to a known DNA sequence. The binding of one strand of DNA to its complementary strand in the DNA double-helix (known as hybridization) is sensitive to even single-base mismatches when the hybrid region is short or if specialized mismatch detection proteins are present. This is exploited in a variety of ways, most notably via DNA chips or microarrays with thousands to billions of synthetic oligonucleotides Oligonucleotides are short DNA or RNA molecules, oligomers, that have a wide range of applications in genetic testing, research, and forensics. Commonly made in the laboratory by solid-phase chemical synthesis, these small bits of nucleic acids ... found in a genome of interest plus many known variations or even all possible single-base variations. The type of sequencing by hybridization described ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |