|
Genome (genetic Algorithm)
In genetic algorithms, a chromosome (also sometimes called a genotype) is a set of parameters which define a proposed solution to the problem that the genetic algorithm is trying to solve. The set of all solutions is known as the ''population''. The chromosome is often represented as a binary string, although a wide variety of other data structures are also used. Chromosome design The design of the chromosome and its parameters is by necessity specific to the problem to be solved. Traditionally, chromosomes are represented in binary as strings of 0s and 1s, however other encodings are also possible; almost any representation which allows the solution to be represented as a finite-length string can be used. Finding a suitable representation of the problem domain for a chromosome is an important consideration, as a good representation will make the search easier by limiting the search space; similarly, a poorer representation will allow a larger search space. The mutation operator an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Algorithm
In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to generate high-quality solutions to optimization and search problems by relying on biologically inspired operators such as mutation, crossover and selection. Some examples of GA applications include optimizing decision trees for better performance, solving sudoku puzzles, hyperparameter optimization, etc. Methodology Optimization problems In a genetic algorithm, a population of candidate solutions (called individuals, creatures, organisms, or phenotypes) to an optimization problem is evolved toward better solutions. Each candidate solution has a set of properties (its chromosomes or genotype) which can be mutated and altered; traditionally, solutions are represented in binary as strings of 0s and 1s, but other encodings are also po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
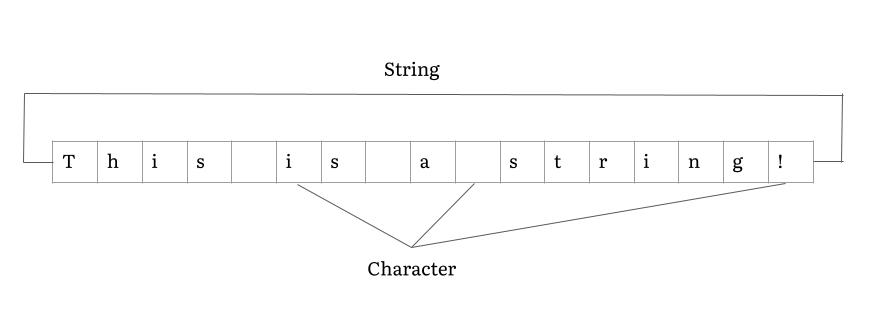
String (computer Science)
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is generally considered as a data type and is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. ''String'' may also denote more general arrays or other sequence (or list) data types and structures. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears literally in source code, it is known as a string literal or an anonymous string. In formal languages, which are used in mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Structure
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization, management, and storage format that is usually chosen for Efficiency, efficient Data access, access to data. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data, i.e., it is an algebraic structure about data. Usage Data structures serve as the basis for abstract data types (ADT). The ADT defines the logical form of the data type. The data structure implements the physical form of the data type. Different types of data structures are suited to different kinds of applications, and some are highly specialized to specific tasks. For example, Relational database, relational databases commonly use B-tree indexes for data retrieval, while compiler Implementation, implementations usually use hash tables to look up identifiers. Data structures provide a means to manage large amounts of data efficiently for uses such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation (genetic Algorithm)
Mutation is a genetic operator used to maintain genetic diversity from one generation of a population of genetic algorithm chromosomes to the next. It is analogous to biological mutation. The classic example of a mutation operator involves a probability that an arbitrary bit in a genetic sequence will be flipped from its original state. A common method of implementing the mutation operator involves generating a random variable for each bit in a sequence. This random variable tells whether or not a particular bit will be flipped. This mutation procedure, based on the biological point mutation, is called single point mutation. Other types are inversion and floating point mutation. When the gene encoding is restrictive as in permutation problems, mutations are swaps, inversions, and scrambles. The purpose of mutation in GAs is to introduce diversity into the sampled population. Mutation operators are used in an attempt to avoid local minima by preventing the population of chromosome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Operator
A genetic operator is an operator used in genetic algorithms to guide the algorithm towards a solution to a given problem. There are three main types of operators (mutation, crossover and selection), which must work in conjunction with one another in order for the algorithm to be successful. Genetic operators are used to create and maintain genetic diversity (mutation operator), combine existing solutions (also known as chromosomes) into new solutions (crossover) and select between solutions (selection). In his book discussing the use of genetic programming for the optimization of complex problems, computer scientist John Koza has also identified an 'inversion' or 'permutation' operator; however, the effectiveness of this operator has never been conclusively demonstrated and this operator is rarely discussed. Mutation (or mutation-like) operators are said to be '' unary'' operators, as they only operate on one chromosome at a time. In contrast, crossover operators are said to be ''bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossover (genetic Algorithm)
In genetic algorithms and evolutionary computation, crossover, also called recombination, is a genetic operator used to combine the genetic information of two parents to generate new offspring. It is one way to stochastically generate new solutions from an existing population, and is analogous to the crossover that happens during sexual reproduction in biology. Solutions can also be generated by cloning an existing solution, which is analogous to asexual reproduction. Newly generated solutions are typically mutated before being added to the population. Different algorithms in evolutionary computation may use different data structures to store genetic information, and each genetic representation can be recombined with different crossover operators. Typical data structures that can be recombined with crossover are bit arrays, vectors of real numbers, or trees. Examples Traditional genetic algorithms store genetic information in a chromosome represented by a bit array. Cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travelling Salesman Problem
The travelling salesman problem (also called the travelling salesperson problem or TSP) asks the following question: "Given a list of cities and the distances between each pair of cities, what is the shortest possible route that visits each city exactly once and returns to the origin city?" It is an NP-hard problem in combinatorial optimization, important in theoretical computer science and operations research. The travelling purchaser problem and the vehicle routing problem are both generalizations of TSP. In the theory of computational complexity, the decision version of the TSP (where given a length ''L'', the task is to decide whether the graph has a tour of at most ''L'') belongs to the class of NP-complete problems. Thus, it is possible that the worst-case running time for any algorithm for the TSP increases superpolynomially (but no more than exponentially) with the number of cities. The problem was first formulated in 1930 and is one of the most intensively studi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitness Function
{{no footnotes, date=May 2015 A fitness function is a particular type of objective function that is used to summarise, as a single figure of merit, how close a given design solution is to achieving the set aims. Fitness functions are used in genetic programming and genetic algorithms to guide simulations towards optimal design solutions. Genetic programming and algorithms In particular, in the fields of genetic programming and genetic algorithms, each design solution is commonly represented as a string of numbers (referred to as a chromosome). After each round of testing, or simulation, the idea is to delete the ''n'' worst design solutions, and to breed ''n'' new ones from the best design solutions. Each design solution, therefore, needs to be awarded a figure of merit, to indicate how close it came to meeting the overall specification, and this is generated by applying the fitness function to the test, or simulation, results obtained from that solution. The reason that geneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossover (genetic Algorithm)
In genetic algorithms and evolutionary computation, crossover, also called recombination, is a genetic operator used to combine the genetic information of two parents to generate new offspring. It is one way to stochastically generate new solutions from an existing population, and is analogous to the crossover that happens during sexual reproduction in biology. Solutions can also be generated by cloning an existing solution, which is analogous to asexual reproduction. Newly generated solutions are typically mutated before being added to the population. Different algorithms in evolutionary computation may use different data structures to store genetic information, and each genetic representation can be recombined with different crossover operators. Typical data structures that can be recombined with crossover are bit arrays, vectors of real numbers, or trees. Examples Traditional genetic algorithms store genetic information in a chromosome represented by a bit array. Cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elitism
Elitism is the belief or notion that individuals who form an elite—a select group of people perceived as having an intrinsic quality, high intellect, wealth, power, notability, special skills, or experience—are more likely to be constructive to society as a whole, and therefore deserve influence or authority greater than that of others. The term ''elitism'' may be used to describe a situation in which power is concentrated in the hands of a limited number of people. Beliefs that are in opposition to elitism include egalitarianism, anti-intellectualism, populism, and the political theory of pluralism. Elite theory is the sociological or political science analysis of elite influence in society: elite theorists regard pluralism as a utopian ideal. Elitism is closely related to social class and what sociologists term "social stratification". In modern Western societies, social stratification is typically defined in terms of three distinct social classes: the upper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |