|
Geng Jimao
Geng Jimao or Keng Chi-mao (; died 1671) was a Chinese prince and military leader, inheriting the title of "Jingnan Prince" (Jingnan wang –هچ—çژ‹meaning "Prince who pacifies the South") from his father Geng Zhongming, along with his lands, and passing it on, in his turn to his son Geng Jingzhong. He led an army from the time of his father's suicide, fighting the Southern Ming, on behalf of the Qing dynasty. The "Dolo efu" ه’Œç¢©é،چ駙 rank was given to husbands of Qing princesses. Geng Jingmao managed to have both his sons Geng Jingzhong and Geng Zhaozhong è€؟وکه؟ become court attendants under the Shunzhi Emperor and married Aisin Gioro women, with Prince Abatai's granddaughter marrying Geng Zhaozhong è€؟وکه؟ and Haoge's (a son of Hong Taiji) daughter marrying Geng Jingzhong. A daughter ه’Œç،•وں”هک‰ه…¬ن¸» of the Manchu Aisin Gioro Prince Yolo ه²³و¨‚ (Prince An) was wedded to Geng Juzhong Geng Juzhong (; 1650 – 1687) was the third son of Geng Jimao and brother of Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geng (surname)
Geng is the Mandarin pinyin romanization of the Chinese surname written in Chinese character. It is romanized as Keng in Wade–Giles. Geng is listed 350th in the Song dynasty classic text ''Hundred Family Surnames''. As of 2008, it is the 139th most common surname in China, shared by 990,000 people. Notable people * Geng Chun ( è€؟ç؛¯; died 37 AD), Eastern Han dynasty general, one of the Yuntai 28 generals *Geng Yan (3–58), another of the Yuntai 28 generals * Geng Guo ( è€؟هœ‹; died 58), Eastern Han general, brother of Geng Yan * Geng Bing ( è€؟秉; died 91), Eastern Han general, son of Geng Guo *Geng Shu ( è€؟舒; 1st century), Eastern Han general * Geng Gong ( è€؟وپ), Eastern Han general, nephew of Geng Yan *Jian Yong (3rd century), original surname Geng, advisor of Liu Bei * Geng Quanbin ( è€؟ه…¨و–Œ; 10th century), Northern Song dynasty general * Geng Shuyi ( è€؟و·‘ن»ھ; 983–1064), consort of Emperor Shengzong of Liao * Geng Jing ( è€؟ن؛¬; died 1162), Jin dynasty rebel le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geng Zhongming
Geng Zhongming (; 1604–1649) was a Chinese military general who lived through the transition from the Ming (1368–1644) to the Qing (1644–1912) dynasty, during which he served both sides. His grandson Geng Jingzhong was one of the Three Feudatories who rebelled against Qing rule in the 1670s. Under Ming service Geng Zhongming was described by historians as a tall and dark-complexioned man who was known for his bravery and resourcefulness. He had first served under Ming warlord Mao Wenlong near the border of Joseon Korea.. When the latter was executed by Yuan Chonghuan in 1629 for insubordination, Geng and other military leaders like Kong Youde refused to serve Yuan. With their troops, they fled by boat from the Liaodong peninsula to Dengzhou () in Shandong. There, Geng was hired by Shandong governor Sun Yuanhua and was allowed to join the Dengzhou garrison, where Sun was casting European-style cannon with the help of Portuguese soldiers. Sun gave Geng and Kong some trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geng Jingzhong
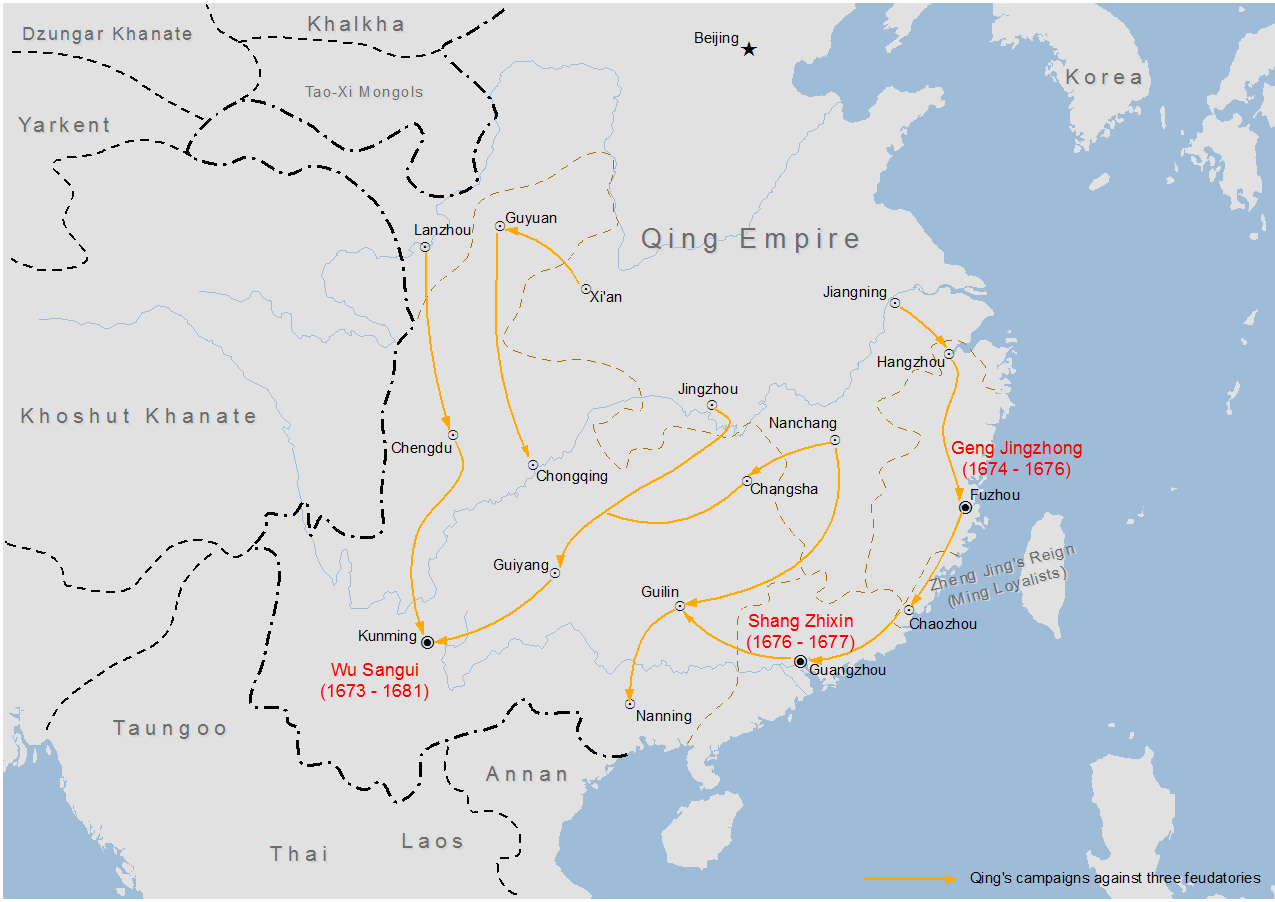
Geng Jingzhong (; died 1682) was a powerful military commander of the early Qing dynasty. He inherited the title of "King/Prince of Jingnan" (é–هچ—çژ‹) from his father Geng Jimao, who had inherited it from Jingzhong's grandfather Geng Zhongming. The "Dolo efu" (ه’Œç¢©é،چ駙) rank was given to husbands of Qing princesses. Geng Jingmao managed to have both his sons Geng Jingzhong and Geng Zhaozhong (è€؟وکه؟ ) become court attendants under the Shunzhi Emperor and marry Aisin Gioro women, with Prince Abatai's granddaughter marrying Geng Zhaozhong è€؟وکه؟ and Hooge's (a son of Hong Taiji) daughter marrying Geng Jingzhong. Geng Juzhong married Princess Heshou Roujia ( ه’Œç،•وں”هک‰ه…¬ن¸») of the Manchu Aisin Gioro clan and daughter of Prince Yolo ( ه²³و¨‚), Prince An. Firmly entrenched as a quasi independent ruler in Fujian, in 1674 Geng Jingzhong rebelled against Qing rule along with the other two of the Three Feudatories Wu Sangui and Shang Zhixin, who were also governing enor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geng Zhaozhong , an esports organisation
{{Disambiguation, surname ...
Geng may refer to: *Geng (dish) (ç¾¹), a thick soup *Geng (surname) (è€؟), a Chinese surname *Norbert Geng (born 1965), German lawyer and professor *21359 Geng, an asteroid *Gen.G Gen.G Esports ( ko, ى ى§€), previously known as KSV Esports, is a professional esports organization with headquarters in Santa Monica, Seoul, and Shanghai. According to Forbes, Gen.G is the sixth most valuable esports organization in the world ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geng Juzhong
Geng Juzhong (; 1650 – 1687) was the third son of Geng Jimao and brother of Geng Jingzhong and court member of the Qing dynasty. He was a Third Class Viscount (ن¸‰ç‰هگ). Princess Roujia ( ه’Œç،•وں”هک‰ه…¬ن¸»), the daughter of the Manchu Aisin Gioro Prince Yolo ( ه²³و¨‚, Prince An) was wedded to Geng Juzhong. When Geng Jingzhong rebelled against the Qing dynasty, Geng Juzhong was in Beijing with the Qing court with the Kangxi Emperor The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to ... and was not punished by the Kangxi Emperor for his brother's revolt. Geng died of natural causes in 1687. References 1650 births 1687 deaths {{China-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shang Zhixin
Shang Zhixin (; 1636 – 1680) was a major figure in the early Qing Dynasty, known for his role in the Revolt of the Three Feudatories. He was Prince of Pingnan (ه¹³هچ—çژ‹, "Prince who Pacifies the South"), inheriting his position from his father, the surrendered Ming Dynasty general Shang Kexi. In 1673, Shang Kexi, on account of old age, requested the Kangxi Emperor to allow him to retire back in his adopted homeland Liaodong. He thus passed on his position to Shang Zhixin, who was his eldest son. As Prince of Pingnan, his duties were primarily concerned with the defence of Guangdong province. Not long afterwards, the Qing court, as part of its policy of centralization, decided to abolish Pingnan Feudatory under the pretext that Shang Zhixin was "difficult to control". Shang Kexi, who was then still in Guangdong, was willing to accept this and made preparations to move his entire family back to Haicheng. However, the rebellion of the Pingxi and Jingnan feudatories, under Wu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shunzhi Emperor
The Shunzhi Emperor (15 March 1638 – 5 February 1661) was the second Emperor of China, emperor of the Qing dynasty of China, and the first Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1644 to 1661. A Deliberative Council of Princes and Ministers, committee of Manchu princes chose him to succeed his father, Hong Taiji (1592–1643), in September 1643, when he was five years old. The princes also appointed two co-regents: Dorgon (1612–1650), the 14th son of the Qing dynasty's founder Nurhaci (1559–1626), and Jirgalang (1599–1655), one of Nurhaci's nephews, both of whom were members of the Aisin Gioro, Qing imperial clan. From 1643 to 1650, political power lay mostly in the hands of Dorgon. Under his leadership, the Qing Empire conquered most of the territory of the fallen Ming dynasty (1368–1644), chased Southern Ming, Ming loyalist regimes deep into the southwestern provinces, and established the basis of Qing rule over China proper despite highly unpopular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abatai
Abatai (Manchu: ; 27 July 1589 – 10 May 1646) was a Manchu prince and military general of the early Qing dynasty. Although an inconsistent and dissolute malcontent, he nevertheless showed considerable ability as a military leader and administrator. Life Abatai was born in the Manchu Aisin Gioro clan, the imperial clan of the Qing dynasty, as part of the Plain Blue Banner. He was the seventh son of Nurhaci, the khan of the Later Jin dynasty, the precursor of the Qing dynasty. His mother, who was from the Irgen Gioro (ن¼ٹ爾و ¹è¦؛ç¾…) clan, was a concubine of Nurhaci. Abatai led Later Jin forces to attack the tribes of Weji in 1611 and those of Jarut in 1623. He was disciplined for abandoning his colleagues during a raid on territories of the Ming Empire in 1629. He was also held responsible for the loss of Yongping and other conquered Ming cities in 1629 and 1630. In 1631, Abatai was appointed to the Manchu Board of Works. He was reprimanded for incompetence at the sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hooge (prince)
Hooge ( Manchu: ; 16 April 1609 – 4 May 1648), formally known as Prince Su, was a Manchu prince of the Qing dynasty. He was the eldest son of Hong Taiji, the second ruler of the Qing dynasty. Life Hooge was born in the Aisin Gioro clan as the eldest son of Hong Taiji, the second ruler of the Qing dynasty. His mother was Lady Ula Nara, one of Hong Taiji's consorts. Hooge participated in military campaigns against the Mongols, Koreans and the Ming dynasty. After Hong Taiji's death in 1643, Hooge and his uncle Dorgon fought over the succession to the throne. The situation was to Hooge's advantage because three of the Eight Banners previously under Hong Taiji's control had been passed on to him. On the other hand, Dorgon had the support of his brothers and two White Banners. This meant that the remaining two Red Banners controlled by Daiإ،an and his son, as well as the Bordered Blue Banner under Chiurhala, were crucial to ensuring that Hooge could win the succession. After mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |