|
Generations Of Noah
The Generations of Noah, also called the Table of Nations or Origines Gentium, is a genealogy of the sons of Noah, according to the Hebrew Bible (Genesis ), and their dispersion into many lands after the Flood, focusing on the major known societies. The term ''nations'' to describe the descendants is a standard English translation of the Hebrew word " goyim", following the 400 CE Latin Vulgate's "nationes", and does not have the same political connotations that the word entails today. The list of 70 names introduces for the first time several well-known ethnonyms and toponyms important to biblical geography, such as Noah's three sons Shem, Ham and Japheth, from which 18th century German scholars at the Göttingen School of History derived the race terminology Semites, Hamites and Japhetites. Certain of Noah's grandsons were also used for names of peoples: from Elam, Ashur, Aram, Cush, and Canaan were derived respectively the Elamites, Assyrians, Arameans, Cushites, and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T And O Map Guntherus Ziner 1472
T, or t, is the twentieth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''tee'' (pronounced ), plural ''tees''. It is derived from the Semitic Taw 𐤕 of the Phoenician and Paleo-Hebrew script (Aramaic and Hebrew Taw ת/𐡕/, Syriac Taw ܬ, and Arabic ت Tāʼ) via the Greek letter τ (tau). In English, it is most commonly used to represent the voiceless alveolar plosive, a sound it also denotes in the International Phonetic Alphabet. It is the most commonly used consonant and the second most commonly used letter in English-language texts. History ''Taw'' was the last letter of the Western Semitic and Hebrew alphabets. The sound value of Semitic ''Taw'', Greek alphabet Tαυ (''Tau''), Old Italic and Latin T has remained fairly constant, representing in each of these; and it has also kept its original basic shape in most of these alphabets. Use in wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Göttingen School Of History
Göttingen (, , ; nds, Chöttingen) is a college town, university city in Lower Saxony, central Germany, the Capital (political), capital of Göttingen (district), the eponymous district. The River Leine runs through it. At the end of 2019, the population was 118,911. General information The origins of Göttingen lay in a village called ''Gutingi, ''first mentioned in a document in 953 AD. The city was founded northwest of this village, between 1150 and 1200 AD, and adopted its name. In Middle Ages, medieval times the city was a member of the Hanseatic League and hence a wealthy town. Today, Göttingen is famous for its old university (''Georgia Augusta'', or University of Göttingen, "Georg-August-Universität"), which was founded in 1734 (first classes in 1737) and became the most visited university of Europe. In 1837, seven professors protested against the absolute sovereignty of the House of Hanover, kings of Kingdom of Hanover, Hanover; they lost their positions, but be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heth (Bible)
Heth is, according to Genesis 10:15, the second son of Canaan, who is son of Ham, son of Noah. Heth is the ancestor of the Hittites, second of the twelve Canaanite nations descended from his sons, who lived near Hebron (Genesis 23:3,7). In Genesis 10:15-16, Heth is placed between Sidon and the Jebusites, Amorites, Girgasites, Hivites, Arkite, Sinite, Arvadite, Zemarite, Hamathite and other peoples, showing their descent through their children, called "Children of Heth The Hittites, also spelled Hethites, were a group of people mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. Under the names (''bny-ḥt'' "children of Heth", who was the son of Canaan) and (''ḥty'' "native of Heth") they are described several times as living ..."(Genesis 23:3, 5, 7, 10, 16, 18, 20). Heth means ''Terror''. References Book of Genesis people Hittite people Founders of biblical tribes {{Hebrew-Bible-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaanites
{{Cat main, Canaan See also: * :Ancient Israel and Judah Ancient Levant Hebrew Bible nations Ancient Lebanon 0050 Ancient Syria Wikipedia categories named after regions 0050 Phoenicia Amarna Age civilizations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cush (Bible)
Cush or Kush ( he, כּוּשׁ , ''Kūš''; gez, ኩሽ), according to the Hebrew Bible, was the oldest son of Ham and a grandson of Noah. He was the brother of Mizraim, Phut, and Canaan. Cush was the father of Nimrod, a king called the "first heroic warrior on earth". Cush is traditionally considered the ancestor of the "land of Cush", an ancient territory believed to have been located near the Red Sea. Cush is identified in the Bible with the Kingdom of Kush or ancient Sudan. The Cushitic languages are named after Cush. Identification Cush is a Hebrew name that is possibly derived from ''Kash'', the Egyptian name of Upper Nubia and later of the Nubian kingdom at Napata, known as the Kingdom of Kush.David M. Goldenberg (2003), ''The Curse of Ham: Race and Slavery in Early Judaism, Christianity, and Islam'', p. 18. The form ''Kush'' appears in Egyptian records as early as the reign of Mentuhotep II (21st century BC), in an inscription detailing his campaigns against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arameans
The Arameans ( oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; syc, ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, Ārāmāyē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. The Aramean homeland was known as the land of Aram and encompassed central regions of modern Syria. At the beginning of the 1st millennium BCE, a number of Aramean states were established throughout the western regions of the ancient Near East. The most notable was the Kingdom of Aram-Damascus, which reached its height in the second half of the 9th century BCE during the reign of king Hazael. A distinctive Aramaic alphabet was developed and used to write the Old Aramaic language. During the 8th century BCE, local Aramean kingdoms were gradually conquered by the Neo-Assyrian Empire. The policy of population displacement and relocation that was applied throughout Assyrian domains also affected Arameans, many of whom were resettled by Assyrian auth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
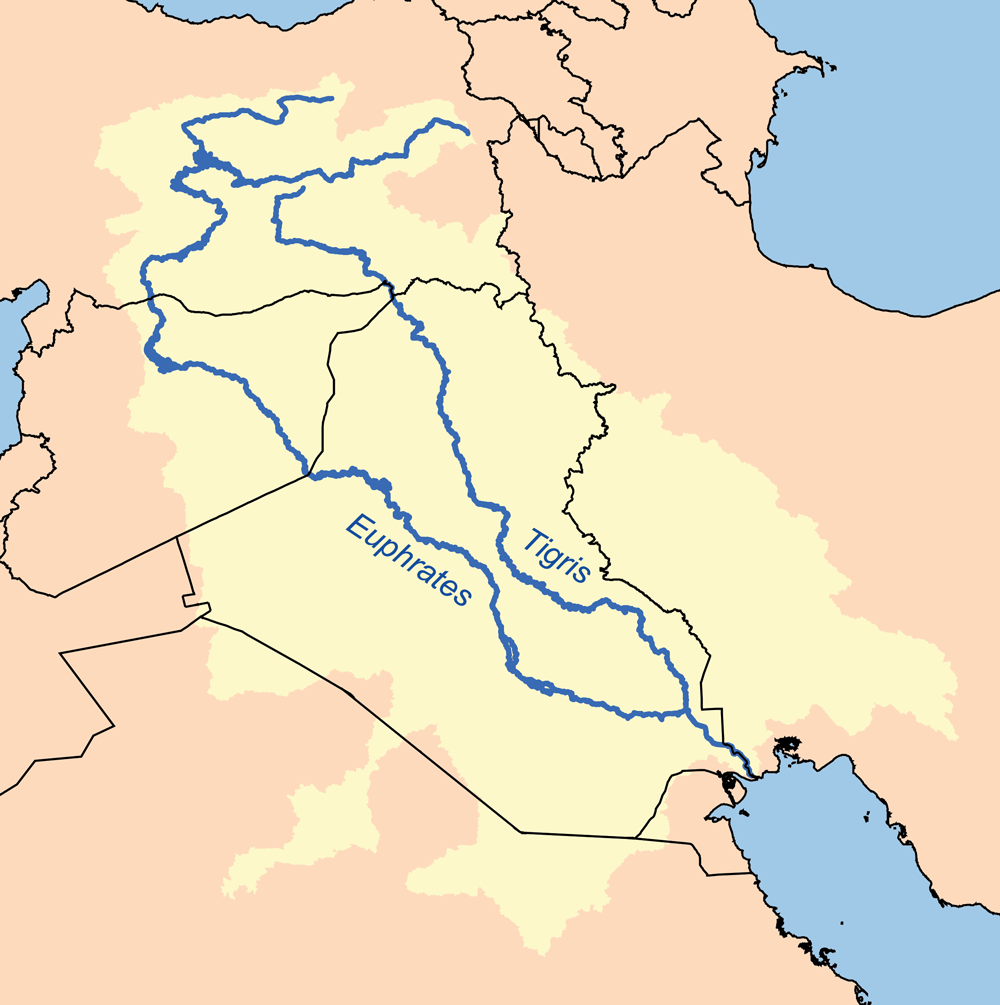
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the Assyrians from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC, then to a territorial state, and eventually an empire from the 14th century BC to the 7th century BC. Spanning from the early Bronze Age to the late Iron Age, modern historians typically divide ancient Assyrian history into the Early Assyrian ( 2600–2025 BC), Old Assyrian ( 2025–1364 BC), Middle Assyrian ( 1363–912 BC), Neo-Assyrian (911–609 BC) and post-imperial (609 BC– AD 630) periods, based on political events and gradual changes in language. Assur, the first Assyrian capital, was founded 2600 BC but there is no evidence yet discovered that the city was independent until the collapse of the Third Dynasty of Ur in the 21st century BC, when a line of independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaan (son Of Ham)
Canaan ( – ''Kənáʿan'', in pausa – ''Kənā́ʿan''), according to the ''Book of Genesis'' in the Hebrew Bible, was a son of Ham and grandson of Noah, as well as the father of the Canaanites. Etymology The English term ''Canaan'' (pronounced since c. AD 1500, due to the Great Vowel Shift) comes from the Hebrew (''knʿn''), via Greek ''Khanaan'' and Latin . It appears as in the Amarna letters (14th century BC), and is found on coins from Phoenicia in the last half of the 1st millennium. It first occurs in Greek in the writings of Hecataeus as ''Khna''(Χνᾶ). Scholars connect the name ''Canaan'' with , ''Kana'an'', the general Northwest Semitic name for this region. The etymology is uncertain. One explanation is that it has an original meaning of "lowlands", from a Semitic root "to be low, humble, depressed", in contrast with Aram, "highlands". An alternative suggestion derives the term from Hurrian ''Kinahhu'', purportedly referring to the colour purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Cush
Cush or Kush ( he, כּוּשׁ , ''Kūš''; gez, ኩሽ), according to the Hebrew Bible, was the oldest son of Ham and a grandson of Noah. He was the brother of Mizraim, Phut, and Canaan. Cush was the father of Nimrod, a king called the "first heroic warrior on earth". Cush is traditionally considered the ancestor of the "land of Cush", an ancient territory believed to have been located near the Red Sea. Cush is identified in the Bible with the Kingdom of Kush or ancient Sudan. The Cushitic languages are named after Cush. Identification Cush is a Hebrew name that is possibly derived from ''Kash'', the Egyptian name of Upper Nubia and later of the Nubian kingdom at Napata, known as the Kingdom of Kush.David M. Goldenberg (2003), ''The Curse of Ham: Race and Slavery in Early Judaism, Christianity, and Islam'', p. 18. The form ''Kush'' appears in Egyptian records as early as the reign of Mentuhotep II (21st century BC), in an inscription detailing his campaigns against the Nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aram, Son Of Shem
Aram ( ''Aram'') is a son of Shem, according to the Table of Nations in Genesis 10 of the Hebrew Bible, and the father of Uz, Hul, Gether and Mash or Meshech. The Book of Chronicles lists Aram, Uz, Hul, Gether, and Meshech as descendants of Shem, although without stating explicitly that Aram is the father of the other four. Aram is usually regarded as being the ancestor of the Aramean people of Northern Mesopotamia and Syria. On the contrary, Australian Chinese revolutionary and ''South China Morning Post'' co-founder Tse Tsan-Tai seemingly makes his sons Uz, Hul, Gether, and Meshech the ancestors of the indigenous peoples of the Americas, Austroasiatic peoples, Austronesians, and the indigenous peoples of Siberia, respectively, while also assigning the Armenians to Aram. Name The name Aram (, ''Aram'') means etymologically "height, high region", according to Wilhelm Gesenius and "the highland" according to Strong's Concordance, in which it is referred to as Hebrew word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashur (Bible)
Ashur ( ''ʾAššūr'') was the second son of Shem, the son of Noah. Ashur's brothers were Elam, Arphaxad, Lud, and Aram. Prior to the discovery of the Dead Sea Scrolls, there was contention in academic circles regarding whether Ashur or Nimrod built the Assyrian cities of Nineveh, Resen, Rehoboth-Ir and Calah, since the name ''Ashur'' can refer to both the person and the country (compare AV and ESV). Sir Walter Raleigh devoted several pages in his ''History of the World'' (c. 1616) to reciting past scholarship regarding the question of whether it had been Nimrod or Ashur who built the cities in Assyria. Both the JPS Tanakh 1917 and the 1611 King James Bible clarify the language of the Septuagint and Vulgate translations of Genesis 10:11-12, by explicitly crediting Ashur as the founder of the cities of Nineveh, Rehoboth, Calah, and Resen. The Ge'ez version of the Book of Jubilees, affirmed by the 15 Jubilees scrolls found amongst the Dead Sea Scrolls, affirms that the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Elam
Elam (; ''‘Elam'') in the Hebrew Bible (Genesis 10:22, Ezra 4:9) is said to be one of the sons of Shem, the son of Noah. The name is also used (as in Akkadian) for the ancient country of Elam in what is now southern Iran, whose people the Hebrews believed to be the offspring of Elam, son of Shem (Genesis 10:22). This implies that the Elamites were considered Semites by the Hebrews. Their language was not one of the Semitic languages, but is considered a linguistic isolate. Elam (the nation) is also mentioned in Genesis 14, describing an ancient war in the time of Abraham, involving Chedorlaomer, the king of Elam at that time. The prophecies of the Book of Isaiah (11:11, 21:2, 22:6) and the Book of Jeremiah (25:25) also mention Elam. The last part of Jeremiah 49 is an apocalyptic oracle against Elam which states that Elam will be scattered to the four winds of the earth, but "will be, in the end of days, that I will return their captivity," a prophecy self-dated to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |